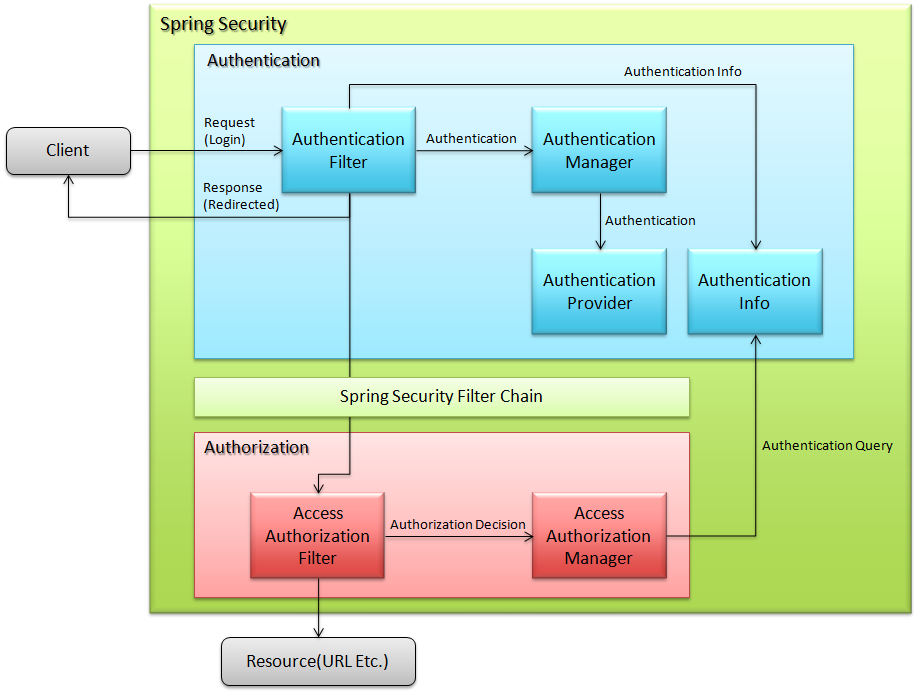
6.1. Spring Security Overview¶
Caution
This version is already obsolete. Please check the latest guideline.
Table of Contents
6.1.1. Overview¶
6.1.1.1. Authentication¶
6.1.1.2. Password hashing¶
6.1.1.3. Authorization¶
6.1.2. How to use¶
6.1.2.1. pom.xml settings¶
<dependency>
<groupId>org.terasoluna.gfw</groupId>
<artifactId>terasoluna-gfw-security-core</artifactId> <!-- (1) -->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.terasoluna.gfw</groupId>
<artifactId>terasoluna-gfw-security-web</artifactId> <!-- (2) -->
</dependency>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
terasoluna-gfw-security-core is not web dependent. As a result, when using from a domain layer project,
only terasoluna-gfw-security-core should be added to dependency.
|
(2)
|
terasoluna-gfw-web provides web related functionalities. It is dependent on terasoluna-gfw-security-core as well. Hence,
for Web projects, only terasoluna-gfw-security-web should be added to dependency.
|
6.1.2.2. Web.xml settings¶
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value> <!-- (1) -->
classpath*:META-INF/spring/applicationContext.xml
classpath*:META-INF/spring/spring-security.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
<filter>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <!-- (2) -->
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> <!-- (3) -->
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> <!-- (4) -->
</filter-mapping>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
In addition to applicationContext.xml, add the Spring Security configuration file to
the class path in contextConfigLocation. In this guideline, it is “spring-security.xml” file.
|
(2)
|
filter-name should be defined as the Bean name to be used internally in Spring Security, namely, “springSecurityFilterChain”.
|
(3)
|
Spring Security filter settings to enable various functionalities. |
(4)
|
Enable the settings for all requests. |
6.1.2.3. spring-security.xml settings¶
spring-mvc.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <sec:http use-expressions="true"> <!-- (1) --> <!-- omitted --> </sec:http> </beans>
Sr. No. Description (1)Spring EL expressions of access attribute can be enabled by setting use-expressions=”true”.Note
For the Spring EL expressions enabled by use-expressions=”true”, please refer to the following.
6.1.3. Appendix¶
6.1.3.1. Settings to assign a secure HTTP header¶
As shown below, security related headers can be set automatically in HTTP response by setting <sec:headers> element in <sec:http> of spring-security.xml.
By assigning these HTTP response headers, Web browser can detect an attack and deal with it.
This setting is not mandatory; however, it is recommended for strengthening security.
<sec:http use-expressions="true">
<!-- omitted -->
<sec:headers />
<!-- omitted -->
</sec:http>
In this setting, HTTP response headers related to following fields are set.
- Cache-Control
- X-Content-Type-Options
- Strict-Transport-Security
- X-Frame-Options
- X-XSS-Protection
| HTTP header name | Issues due to inappropriate settings (also includes cases where settings are not performed). | Behavior in case of appropriate settings |
|---|---|---|
Cache-Control |
In some cases, the contents that can be viewed by a logged-in user are cached and can also be viewed by another user, after the first user logs out.
|
Instruct such that the contents are not cached and ensure that the browser always fetches server information.
|
X-Content-Type-Options |
In some cases, browser determines operation contents just by checking the content details without using Content-Type. This may result in execution of unexpected scripts.
|
Ensure that the browser does not determine the operation contents just by checking the content details without using Content-Type. Restrict script execution if the MIME type does not match.
|
Strict-Transport-Security |
In spite of expecting access to a secure page by HTTPS, there is a possibility of HTTP-origin attack when the page is accessed using HTTP (Example: Man-In-The-Middle-Attack (MITM) intercepts a user’s HTTP request and redirects it to a malicious site.)
|
Once a legitimate web site is accessed using HTTPS, the browser automatically uses only HTTPS, thereby preventing the Man In The Middle Attack such as being redirected to a malicious site.
|
X-Frame-Options |
If screen of malicious Web site A is made unavailable for viewing and instead a legitimate site B is embedded using
<iframe> tag, the user who thinks that he has accessed site B, is made to access site A, by the attacker.In this condition, if ‘Send’ button of site A and link position of site B overlap, the attacker can make the user send a malicious request through site A, while the user thinks that the link of legitimate site B was clicked. (Clickjacking)
|
Ensure that the self-created Website (= site B) cannot be read in another Web site (= site A) using
<iframe> tag. |
X-XSS-Protection |
Determination of harmful script by XSS filter implemented in browser, is invalidated.
|
On realizing that the script is harmful, the XSS filter implemented in browser asks the user whether to execute it, or it is invalidated (behavior differs depending on browser).
|
The settings mentioned above can be performed individually as shown below in steps (1) to (5). Select them as and when required.
<sec:http use-expressions="true">
<!-- omitted -->
<sec:headers>
<sec:cache-control /> <!-- (1) -->
<sec:content-type-options /> <!-- (2) -->
<sec:hsts /> <!-- (3) -->
<sec:frame-options /> <!-- (4) -->
<sec:xss-protection /> <!-- (5) -->
</sec:headers>
<!-- omitted -->
</sec:http>
| Sr. No. | Description | HTTP response header that is output by default. | Attribute flag |
|---|---|---|---|
(1)
|
Instruct the client not to cache data.
|
Cache-Control:no-cache, no-store, max-age=0, must-revalidatePragma: no-cacheExpires: 0 |
No
|
(2)
|
Instruct the client not to decide the processing method automatically by ignoring the content type and using just the content details.
|
X-Content-Type-Options:nosniff |
No
|
(3)
|
Instruct to continue the HTTPS connection in the site accessed with HTTPS. (Ignored in case of HTTP site and not assigned as header field.)
|
Strict-Transport-Security:max-age=31536000 ; includeSubDomains |
Yes
|
(4)
|
Instruct whether the contents to be displayed in iframe.
|
X-Frame-Options:DENY |
Yes
|
(5)
|
Instruct to enable XSS filter functionality for the browser where the filter that can detect XSS attack is implemented.
|
X-XSS-Protection:1; mode=block |
Yes
|
Attributes can be set when individual settings are performed. Some of the attributes that can be set are as follows:
| Sr. No. | Option | Description | Example | HTTP response header that is output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
(3)
|
max-age-seconds |
Number of seconds stored in memory to access the relevant site using HTTPS only (365 days by default)
|
<sec:hsts max-age-seconds="1000" /> |
Strict-Transport-Security:max-age=1000 ; includeSubDomains |
(3)
|
include-subdomains |
Application instructions for sub-domain. Default value is
true. It is no longer output when set to false. |
<sec:hsts include-subdomains="false" /> |
Strict-Transport-Security:max-age=31536000 |
(4)
|
policy |
Instruct regarding the permission method to display contents in iframe. Default value is
DENY (display in frame is completely prohibited). It can also be changed to SAMEORIGIN(allows to read frame only for the page on same site). |
<sec:frame-options policy="SAMEORIGIN" /> |
X-Frame-Options:SAMEORIGIN |
(5)
|
enabled,block |
XSS filter can be disabled by setting it to
false; however, it is recommended to enable this filter. |
<sec:xss-protection enabled="false" block="false" /> |
X-XSS-Protection:0 |
Note
The processing for these headers is not supported in some browsers. Refer to the official site of the browser or the following pages.
- https://www.owasp.org/index.php/HTTP_Strict_Transport_Security (Strict-Transport-Security)
- https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Clickjacking_Defense_Cheat_Sheet (X-Frame-Options)
- https://www.owasp.org/index.php/List_of_useful_HTTP_headers (X-Content-Type-Options, X-XSS-Protection)
For details, refer to Official reference.