6.3. Authentication¶
Caution
This version is already obsolete. Please check the latest guideline.
Table of contents
- Overview
- How to use
- How to extend
- Appendix
6.3.1. Overview¶
In Spring Security, user authentication can be implemented by just performing configuration file settings. DB authentication, LDAP authentication, CAS authentication, JAAS authentication, X509 authentication and Basic authentication are the authentication methods provided by Spring Security. However, only DB authentication is described in this guideline.
Tip
For details of authentication types other than DB authentication, refer to the official document of each authentication method.
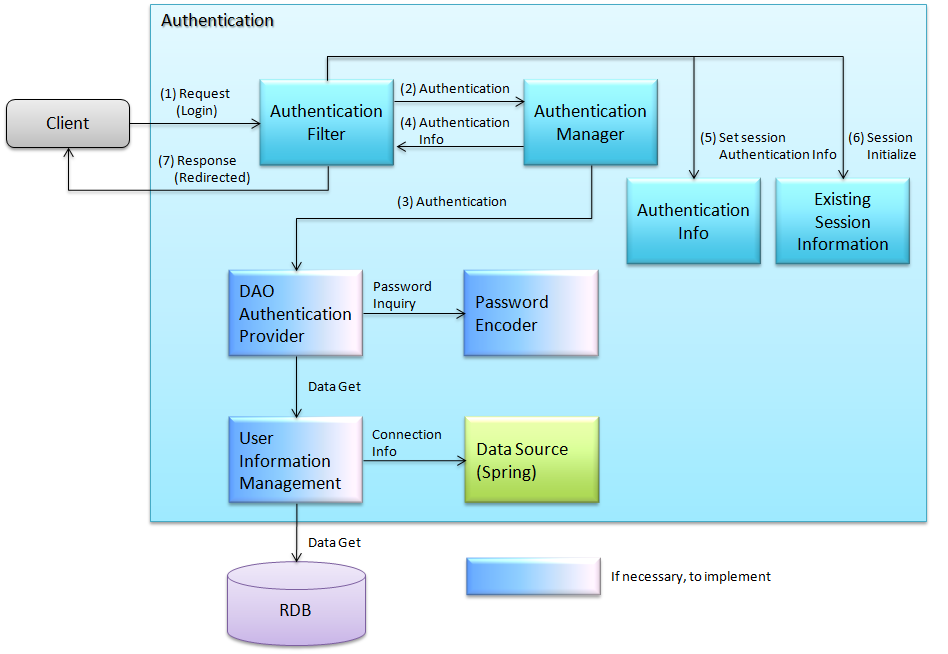
6.3.1.1. Login¶
Flow of Spring Security login process is as follows:
- Authentication filter is activated on receiving the request specifying authentication.
- Authentication filter extracts username and password from the request and generates authentication information. The generated authentication information is used as a parameter to execute authentication process of authentication manager.
- Authentication manager executes authentication process of the specified authentication provider. Authentication provider acquires user information from datasource (DB or LDAP) and performs user authentication such as password verification. When authentication is successful, authentication information that holds the authenticated information is created and returned to the authentication manager. When authentication fails, the authentication manager raises authentication failure exception.
- Authentication manager returns the received authentication information to authentication filter.
- Authentication filter stores the received authentication information (authenticated) in session.
- When authentication is successful, it initializes the session information before authentication and creates new session information.
- It redirects to the specified path of successful/failed authentication and returns session ID to client.
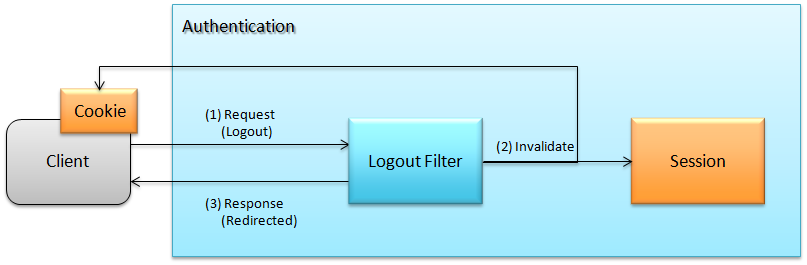
6.3.1.2. Logout¶
Flow of Spring Security logout process is as follows:
- Logout filter gets activated on receiving request for logout.
- It discards the session information. It sets a response such that client cookie (Cookie in figure) is discarded.
- It redirects to the specified logout path.
Note
The session information that remains after logout can be used by a third party. Hence, in order to prevent such spoofing, session information is discarded at the time of logout using
org.springframework.security.web.session.ConcurrentSessionFilter.
6.3.2. How to use¶
6.3.2.1. Setting <sec:http> element¶
auto-config attribute of <http> element in spring-security.xml to true.<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true"> <!-- (1) -->
<!-- omitted -->
</sec:http>
</beans>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
By setting
auto-config="true",it is enabled even if
<form-login>, <http-basic> and <logout> elements are not set. |
Note
<form-login>, <http-basic> and <logout> elements are explained here.
Element name Description <form-login>org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilteris enabled.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter is the Filter that performs authentication by extracting username and password from the request at the time of POST method.For details, refer to Setting <sec:form-login> element.<http-basic>org.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationFilteris enabled.BasicAuthenticationFilter is the filter that executes Basic authentication process according to RFC1945.For details on how to use, refer to BasicAuthenticationFilter JavaDoc.<logout>org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.LogoutFilter,org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.SecurityContextLogoutHandleris enabled.LogoutFilter is the Filter called at the time of Logout.org.springframework.security.web.authentication.rememberme.TokenBasedRememberMeServices(deleting Cookie) and,SecurityContextLogoutHandler(disabling session) is called.For details, refer to Setting <sec:logout> element.
6.3.2.2. Setting <sec:form-login> element¶
<sec:form-login> element is described in this section.spring-security.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true">
<sec:form-login login-page="/login"
default-target-url="/"
login-processing-url="/authentication"
always-use-default-target="false"
authentication-failure-url="/login?error=true"
authentication-failure-handler-ref="authenticationFailureHandler"
authentication-success-handler-ref="authenticationSuccessHandler" /> <!-- Perform steps (1) - (7) in the specified attribute order-->
</sec:http>
</beans>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify the login form screen path in
login-page attribute.When not specified, “/spring_security_login” will be default path and Login screen provided by Spring Security is used.
When an “Unauthenticated user” accesses a page that can only be accessed by an “Authenticated user”, the unauthenticated user is redirected to this path.
This guideline recommends changing to a system specific value rather than using the default value “/spring_security_login”, mentioned above.In this example, “/login” is specified.
|
(2)
|
In
default-target-url attribute, specify the destination path when authentication is successful.When not specified, “/” will be the default path.
When
authentication-success-handler-ref attribute is specified, this setting is not used. |
(3)
|
Specify the path for performing authentication process in
login-processing-url attribute.When not specified, “j_spring_security_check” will be the default path.
This guideline recommends changing to a system specific value rather than using the default value “j_spring_security_check”, mentioned above. In this example, “/authentication” is specified.
|
(4)
|
In
always-use-default-target attribute, specify whether it should always transit to the path specified in default-target-url after a successful login.When it is set as
true, it always transits to the path specified in default-target-url.When it is set as
false (default), it transits either to the “path for displaying secure page which somebody has tried accessing before the login” or “path specified in default-target-url”.When
authentication-success-handler-ref attribute is specified, this setting is not used. |
(5)
|
In
authentication-failure-url, specify the destination when authentication fails.When not specified, the path specified in
login-page attribute is applicable.When
authentication-failure-handler-ref attribute is specified, this setting is not used. |
(6)
|
Specify the handler class to be called in case of a failed authentication, in
authentication-failure-handler-ref attribute.For details, refer to Setting the handler class in case of authentication error.
|
(7)
|
Specify the handler class to be called in case of a successful authentication, in
authentication-success-handler-ref attribute. |
For attributes other than those mentioned above, refer to Spring Security manual.
Warning
Why it is not recommended to use Spring Security default values “/spring_security_login, /j_spring_security_check”.
If default value is used, the fact that the application is using Spring Security is revealed. As a result, if any Spring Security related vulnerability is detected, there is a higher risk of receiving an attack due to the vulnerability. In order to prevent these risks, it is recommended to avoid using default value.
6.3.2.2.1. Creating login form¶
src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/views/login.jsp
<form:form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/authentication" method="post"><!-- (1) --> <!-- omitted --> <input type="text" id="username" name="j_username"><!-- (2) --> <input type="password" id="password" name="j_password"><!-- (5) --> <input type="submit" value="Login"> </form:form>
Sr. No. Description (1)Specify the destination for performing authentication process, in the action attribute of form./authentication specified in the login-processing-url, should be specified as the destination path.Authentication process is executed by accessing ${pageContext.request.contextPath}/authentication.“POST” should be specified as the HTTP method.(4)Element handled as “User ID” in authentication process.Spring Security default value namely, “j_username”, should be specified in the name attribute.(5)Element handled as “Password” in authentication process.Spring Security default value namely, “j_password”, should be specified in the name attribute.Following code is added to display the authentication error message.
<c:if test="${param.error}"><!-- (1) --> <t:messagesPanel messagesAttributeName="SPRING_SECURITY_LAST_EXCEPTION"/><!-- (2) --> </c:if>
Sr. No. Description (1)Determine the error message set in request parameter.Please note that the determination process needs to be changed according tothe value set in the authentication-failure-url attribute of form-login element or the value set in “defaultFailureUrl” of authentication error handler.This example is shown with the setting as authentication-failure-url=”/login?error=true”.(2)Output the exception message that is to be output at the time of authentication error.It is recommended to output this message by specifyingorg.terasoluna.gfw.web.message.MessagesPanelTagprovided by common library.For details of “<t:messagesPanel>” tag, refer to Message Management.
Note
Settings required while accessing exception object of authentication error from JSP
Exception object of authentication error is stored in session scope with the attribute name
"SPRING_SECURITY_LAST_EXCEPTION".sessionattribute of JSPpagedirective should be set totruefor accessing the object stored in session scope from JSP.
src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/views/common/include.jsp<%@ page session="true"%>Default settings of blank project are such that session scope cannot be accessed from JSP. This is to ensure that the session is not used easily.
spring-mvc.xml
Define the Controller that displays login form.
<mvc:view-controller path="/login" view-name="login" /><!-- (1) -->
Sr. No. Description (1)If “/login” is accessed, define the controller that returns only “login” as the view name. src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/views/login.jsp is output byInternalResourceViewResolver.This simple controller need not be implemented in Java.Tip
Above settings are identical with next controller.
@Controller @RequestMapping("/login") public class LoginController { @RequestMapping public String index() { return "login"; } }
If the Controller with a single method that returns only the view name is necessary, it is better to use
<mvc:view-controller>.
6.3.2.2.2. Changing attribute name of login form¶
“j_username” and “j_password” are the Spring Security default values. They can be changed to any value by using <form-login> element settings.
spring-security.xml
Attributes of
usernameandpassword<sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true"> <sec:form-login username-parameter="username" password-parameter="password" /> <!-- Perform steps (1) and (2) in the specified attribute order --> <!-- omitted --> </sec:http>
Sr. No. Description (1)Inusername-parameterattribute,nameattribute of input fieldusernameis changed to “username”.(2)Inpassword-parameterattribute,nameattribute of input fieldpasswordis changed to “password”.
6.3.2.3. Setting authentication process¶
Define AuthenticationProvider and UserDetailsService in order to set the authentication process in Spring Security.
AuthenticationProvider plays the following roles.
- Returning authenticated user information in case of successful authentication
- Throwing an exception in case of authentication failure.
UserDetailsService fetches authenticated user information from the persistence layer.
These classes may each be used as default or may be used by extending individually. They may also be combined.
6.3.2.3.1. AuthenticationProvider class settings¶
AuthenticationProvider implementation, how to use the provider, org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider that performs DB authentication, is explained here.spring-security.xml
<sec:authentication-manager><!-- (1) --> <sec:authentication-provider user-service-ref="userDetailsService"><!-- (2) --> <sec:password-encoder ref="passwordEncoder" /><!-- (3) --> </sec:authentication-provider> </sec:authentication-manager>
Sr. No. Description (1)Define<sec:authentication-provider>element in<sec:authentication-manager>element. Authentication methods can be combined by specifying multiple elements. However it is not explained here.(2)DefineAuthenticationProviderin<sec:authentication-provider>element.DaoAuthenticationProvideris enabled by default. To specifyAuthenticationProviderother than this, specify the Bean ID of target AuthenticationProvider, in `ref attribute <http://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/3.2.7.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#nsa-authentication-provider>`_.Specify the Bean Id ofUserDetailsServicethat fetches authenticated user information, inuser-service-refattribute. This setting is mandatory when usingDaoAuthenticationProvider.For details, refer to UserDetailsService class settings.(3)Specify the Bean ID of the class that encodes the password entered from Form, at the time of password verification.When it is not specified, password is handled in “Plain Text”. For details, refer to Password Hashing.
DaoAuthenticationProvider may be used.UserDetailsService explained below.6.3.2.3.2. UserDetailsService class settings¶
userDetailsService property of AuthenticationProvider.UserDetailsService is the interface that includes the next method.
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException
By executing this interface, authenticated user information can be fetched from any storage location.
Here, org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.jdbc.JdbcDaoImpl that fetches user information from DB using JDBC, is explained.
In order to use JdbcDaoImpl, it is advisable to perform following Bean definitions in spring-security.xml.
<!-- omitted -->
<bean id="userDetailsService"
class="org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.jdbc.JdbcDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
JdbcDaoImpl defines the default SQL for fetching authenticated user information and authorization information and provides tables corresponding to these. For definitions of assumed tables, refer to Spring Security manual.By creating a table matching with the query that fetches user information, need of specifying the query to configuration file described later, is eliminated.Fields namely, “username”, “password” and “enabled” are mandatoryAlso, by specifying the query to the configuration file described later and by assigning an alias to the query, there is no issue even if table name and column name do not match.For example, while setting the following SQL, “email” column can be used as “username” wherein, “enabled” field is alwaystrue.SELECT email AS username, pwd AS password, true AS enabled FROM customer WHERE email = ?“User ID” described earlier in Creating login form, is specified in query parameter.
User authorities acquisition query
This query fetches authorization information for a user.Group authorities acquisition query
This query fetches authorization information of the group, to which the user belongs. ‘Group authorities’ is disabled by default and is also out of this guideline’s scope.
Table name: account
| Logical name | Physical name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| User ID | username | String | User ID for uniquely identifying the user. |
| Password | password | String | User password. Stored in hashed status. |
| Enabled flag | enabled | Boolean value | Flag indicating invalid user and valid user. The user set to “false” is an invalid user, thus results in throwing an authentication error. |
| Authority name | authority | String | Not required when authorization functionality is unnecessary. |
Following is the example wherein, JdbcDaoImpl is set through customization.
<!-- omitted -->
<bean id="userDetailsService"
class="org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.jdbc.JdbcDaoImpl">
<property name="rolePrefix" value="ROLE_" /><!-- (1) -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="enableGroups" value="false" /><!-- (2) -->
<property name="usersByUsernameQuery"
value="SELECT username, password, enabled FROM account WHERE username = ?" /><!-- (3) -->
<property name="authoritiesByUsernameQuery"
value="SELECT username, authority FROM account WHERE username = ?" /><!-- (4) -->
</bean>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify the prefix of authorization name. When the authorization name stored on DB is “USER”, this authenticated user object has the authorization name as “ROLE_USER”.
It is necessary to set the naming conventions and authorization functionality by combining them. For details of authorization functionality, refer to Authorization.
|
(2)
|
Specify this when the concept of “Group authorities” is to be used in authorization functionality.
Not handled in this guideline.
|
(3)
|
Set the query for fetching user information. Data should be fetched in the order, “User ID”, “Password” and “Enabled flag”.
When authentication is not decided by “Enabled flag”, SELECT result of “Enabled flag” is fixed to “true”.
The query that can uniquely acquire a user, should be described. When multiple records are fetched, the first record is used as user.
|
(4)
|
Set the query that fetches user authority. Data should be acquired in the order, “User ID” and “Authority ID”.
When authorization functionality is not used, “Authority ID” can be any fixed value.
|
Note
Authentication that cannot be implemented just by changing query, is necessary to be implemented by extending UserDetailsService.
For extension methods, refer to Extending UserDetailsService.
6.3.2.4. How to use UserDetails class¶
UserDetails created by UserDetailsService after successful authentication is explained.6.3.2.4.1. Using UserDetails object in Java class¶
UserDetails classorg.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder.Example of fetching UserDetails from SecurityContextHolder is shown below.
public static String getUsername() {
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
.getAuthentication(); // (1)
if (authentication != null) {
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal(); // (2)
if (principal instanceof UserDetails) {
return ((UserDetails) principal).getUsername(); // (3)
}
return (String) principal.toString();
}
return null;
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Fetch
org.springframework.security.core.Authentication object from SecurityContextHolder. |
(2)
|
Fetch
UserDetails object from Authentication object. |
(3)
|
Fetch user name from
UserDetails object. |
While the method for fetching UserDetails object from SecurityContextHolder is convenient as it can be used from anywhere by static method,
it ends up increasing module coupling. Testing is also difficult to execute.
UserDetails object can be fetched using @AuthenticationPrincipal.@AuthenticationPrincipal, it is necessary to set org.springframework.security.web.bind.support.AuthenticationPrincipalArgumentResolver in <mvc:argument-resolvers>.spring-mvc.xml
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:argument-resolvers>
<bean
class="org.springframework.data.web.PageableHandlerMethodArgumentResolver" />
<bean
class="org.springframework.security.web.bind.support.AuthenticationPrincipalArgumentResolver" />
</mvc:argument-resolvers>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
As shown below, UserDetails object can be fetched in Spring MVC Controller without using SecurityContextHolder.
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String view(@AuthenticationPrincipal SampleUserDetails userDetails, // (1)
Model model) {
// get account object
Account account = userDetails.getAccount(); // (2)
model.addAttribute(account);
return "account/view";
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Fetch information of logged-in user using
@AuthenticationPrincipal. |
(2)
|
Fetch account information from
SampleUserDetails. |
Note
The type of argument attached with @AuthenticationPrincipal annotation, needs to be a class that inherits UserDetails type.
Usually, it is better to use UserDetails inheritance class that is created using Extending UserDetailsService.
SampleUserDetails class is a class created using Spring Security Tutorial. For details, refer to Creating Authentication Service.
This method is recommended when accessing UserDetails object in Controller.
Note
It is recommended to use the UserDetails object information fetched from Controller in Service class rather than using SecurityContextHolder.
SecurityContextHolder should be used only in those methods where UserDetails object is not passed as argument.
6.3.2.4.2. Accessing UserDetails in JSP¶
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/security/tags" prefix="sec"%>
Note
It is already set in WEB-INF/views/common/include.jsp when using TERASOLUNA Server Framework for Java (5.x) template.
<sec:authentication property="principal.username" /><!-- (1) -->
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Authentication object can be accessed using <sec:authentication> tag and the property specified in property attribute can be accessed. In this example, result of getPrincipal().getUsername() is output. |
<sec:authentication property="principal" var="userDetails" /> <!-- (1) -->
${f:h(userDetails.username)} <!-- (2) -->
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Property specified in
property attribute can be stored in variable, by changing it to a var attribute name. |
(2)
|
UserDetails can be accessed in JSP once it is stored in variable by step (1). |
Note
UserDetails can also be fetched in Controller and added to Model. However, it is advisable to use JSP tag when displaying it in JSP.
Note
UserDetails created by JdbcDaoImpl which is explained in UserDetailsService class settings, stores only the minimum required information such as “User ID” and “Authority”.
When other information related to the user such as “User name” etc. is required to be displayed as screen fields, it is necessary to extend UserDetails and UserDetailsService.
For extension methods, refer to Extending UserDetailsService.
6.3.2.5. Session management in Spring Security¶
<session-management> tag.<sec:http auto-config="true" create-session="ifRequired" ><!-- (1) -->
<!-- omitted -->
<sec:session-management
invalid-session-url="/"
session-authentication-error-url="/"
session-fixation-protection="migrateSession" /><!-- Steps (2) to (4) in the specified order of attribute -->
<!-- omitted -->
</sec:http>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify the policy for creating session in
create-session attribute of <http> tag.Following values can be specified.
|
(2)
|
Specify the transition path when an invalid session ID is requested (session time-out) in
invalid-session-url attribute.When not specified, a subsequent process is called without executing session existence check.
For details, refer to “Detecting session time-out”.
|
(3)
|
When an exception occurs in
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.session.SessionAuthenticationStrategy, specify the transition path in session-authentication-error-url attribute.When not specified, “401 Unauthorized” is set in response code and error response is sent.
This setting is not used when authentication is performed using
<form-login> tag. An exception occurred in SessionAuthenticationStrategy is handled according to the definition of authentication-failure-handler-ref attribute or authentication-failure-url attribute of <form-login> tag. |
(4)
|
Specify the session management system of successful authentication in
session-fixation-protection attribute.Following values can be specified.
The objective of this functionality is to prevent Session fixation attack by allocating a new session ID for each login. Therefore, it is recommended to use this default setting unless there are other clear reasons for not using it.
|
6.3.2.5.1. Detecting session time-out¶
When session time-out is to be detected,
it is advisable to specify the transition path when session time-out occurs, in invalid-session-url attribute .
When invalid-session-url attribute is specified,
the session existence check (existence check for requested session ID) is performed for all the requests that match with
the path pattern specified in pattern attribute of http element.
Note
When a path that detects session time-out and a path that does not detect session time-out are mixed, http element needs to be defined multiple times.
When http element is defined multiple times, care needs to be taken as the setting becomes redundant reducing maintainability.
When setting to detect session time-out becomes redundant, create a custom filter that can specify an applicable path or an exception path. To create a custom filter, it is advisable to refer to or to use the following classes provided by Spring Security.
org.springframework.security.web.session.SessionManagementFilterProcess to perform session existence check (existence check of requested session ID) is implemented.org.springframework.security.web.session.SimpleRedirectInvalidSessionStrategyProcess after detecting session time-out (invalid session ID) is implemented.By default, it is redirected to the path specified after the session is created.org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.RequestMatcherIt is an interface to determine whether it matches with the request and it can be used in the processes of determining an applicable path or an exception path.Some useful implementation classes have been provided in the same package.
Note
When CSRF Countermeasures is performed by specifying <csrf> element, sometimes the session time-out can be detected using “CSRF measures” functionality.
Following are the conditions for detecting session time-out using “CSRF measures” functionality.
- Destination to store CSRF token is HTTP session (default).
- CSRF token cannot be fetched from HTTP session.
- It is Request for CSRF token check.
When session time-out is detected using “CSRF measures” functionality, any of the following operations is performed.
- When
invalid-session-urlattribute is specified, it is redirected to the path specified ininvalid-session-urlafter the session is created. - When
invalid-session-urlattribute is not specified, it is handled according to the definition oforg.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandlerspecified in<access-denied-handler>element.
Refer to “spring-security.xml settings” for the method to define AccessDeniedHandler.
6.3.2.5.2. Settings of Concurrent Session Control¶
Authentication.getPrincipal().Note
This functionality is valid when single application server is configured, or, session replication is implemented using session server or cluster (i.e. all applications are using the same session area) When multiple servers or multiple instances are configured leading to the existence of different session areas, a care should be taken as concurrent login cannot be controlled using this functionality.
- When a user exceeds the number of maximum sessions, the user having least usage is disabled. (after win)
- When a user exceeds the number of maximum sessions, new login request is not accepted.(first win)
In both cases, following settings need to be added to web.xml, to enable this functionality.
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.security.web.session.HttpSessionEventPublisher</listener-class><!-- (1) -->
</listener>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
When using Concurrent Session Control, it is necessary to define
org.springframework.security.web.session.HttpSessionEventPublisher in listener. |
6.3.2.5.3. Setting <sec:concurrency-control>¶
When using Concurrent Session Control,
specify <sec:concurrency-control> element as a child element of <sec:session-management> element.
<sec:http auto-config="true" >
<sec:session-management>
<sec:concurrency-control
error-if-maximum-exceeded="true"
max-sessions="2"
expired-url="/expiredSessionError.jsp" /><!-- Steps (1) to (3) in the specified order of attribute -->
</sec:session-management>
</sec:http>
| Sr. No. | Attribute name | Description | Default values | Description of default values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
(1)
|
error-if-maximum-exceeded |
Specify behavior if there is a login request in a state where it exceeds maximum number of sessions that a user can log in to.
When set to
true, generate authentication error so that a new login is not accepted. (first win) |
false
|
Login is possible, but a session which is not frequently used is invalidated (session with oldest last access time). When a request is sent by the client using invalidated session, it is transited to the URL specified in
expired-url attribute. (after win) |
(2)
|
max-sessions |
Specify maximum number of sessions that a single user can log in to.
When 2 is set, same user can login with 2 sessions.
|
1
|
Default is 1 session only
|
(3)
|
expired-url |
URL to be transited to when a request is sent by the client using invalidated session.
|
None
|
A fixed message to notify that session is invalidated is sent as response.
|
Note
When a filter (FORM_LOGIN_FILTER) for authentication is to be customized,
it is necessary to disable the following 2 SessionAuthenticationStrategy classes, apart from specifying <sec:concurrency-control> element.
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.session.ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategyA class to check number of sessions for each logged in user after successful authentication.org.springframework.security.web.authentication.session.RegisterSessionAuthenticationStrategyA class to register a session with successful authentication, in session management area.
In version 1.0.x.RELEASE dependent Spring Security 3.1, org.springframework.security.web.authentication.session.ConcurrentSessionControlStrategy class is provided; however,
it is deprecated API from Spring Security 3.2.
When upgrading version from Spring Security 3.1 to Spring Security 3.2 or later versions, changes need to be made so that it can be used with combination of following classes.
ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy(added in Spring Security 3.2)RegisterSessionAuthenticationStrategy(added in Spring Security 3.2)org.springframework.security.web.authentication.session.SessionFixationProtectionStrategy
For specific methods of definition, refer to sample code of Spring Security Reference -Web Application Security (Concurrency Control)-.
6.3.2.6. Setting the handler class in case of authentication error¶
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ExceptionMappingAuthenticationFailureHandler class inauthentication-failure-handler-ref attribute of <sec:form-login> element,spring-security.xml
<sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true">
<sec:form-login login-page="/login"
authentication-failure-handler-ref="authenticationFailureHandler"
authentication-success-handler-ref="authenticationSuccessHandler" />
</sec:http>
<bean id="authenticationFailureHandler"
class="org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ExceptionMappingAuthenticationFailureHandler">
<property name="defaultFailureUrl" value="/login/defaultError" /><!-- (1) -->
<property name="exceptionMappings"><!-- (2) -->
<props>
<prop key=
"org.springframework.security.authentication.BadCredentialsException"><!-- (3) -->
/login/badCredentials
</prop>
<prop key=
"org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException"><!-- (4) -->
/login/usernameNotFound
</prop>
<prop key=
"org.springframework.security.authentication.DisabledException"><!-- (5) -->
/login/disabled
</prop>
<prop key=
"org.springframework.security.authentication.ProviderNotFoundException"><!-- (6) -->
/login/providerNotFound
</prop>
<prop key=
"org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationServiceException"><!-- (7) -->
/login/authenticationService
</prop>
<!-- omitted -->
</props>
</property>
</bean>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify the default destination path in case of an error.
If an exception not defined in the
exceptionMappings property that will be described later occurs, it transits to the destination specified by this property. |
(2)
|
Specify the exceptions to be caught and their corresponding destinations in a list format.
Set the exception class in key and destination in value.
|
Note
If an exception defined into the exceptionMappings property is occurred, the ExceptionMappingAuthenticationFailureHandler redirects the request to the transition destination mapped to a occurred exception.
However a message generated by Spring Security does not display on the screen because the exception object is not stored in the session scope.
Therefore, the message shown on the error screen needs to be created at the processing of redirect destination(controller’s method or view).
In addition, changing of following properties is ignored because the processing which refers those properties are not called in this case.
useForwardallowSessionCreation
A typical exception thrown by Spring Security is shown below.
| Sr. No. | Error type | Description |
|---|---|---|
(3)
|
BadCredentialsException |
It is thrown when authentication error occurs due to failure in password verification. |
(4)
|
UsernameNotFoundException |
It is thrown when authentication error occurs due to an invalid user ID (non-existent user ID).
When specifying the class that inherits
org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider in authentication provider,if
hideUserNotFoundExceptions is not changed to false, the above exception is changed to BadCredentialsException. |
(5)
|
DisabledException |
It is thrown when an authentication error occurs due to invalid user ID. |
(6)
|
ProviderNotFoundException |
It is thrown at the time of undetected error of authentication provider class.
Exception occurs when authentication provider class is invalid due to reasons such as a setting error etc.
|
(7)
|
AuthenticationServiceException |
It is thrown at the time of authentication service error.
It is thrown when certain errors such as DB connection error etc. occur in authentication service.
|
Warning
In this example, transition is made by handling UsernameNotFoundException.
However, if the user is informed that user ID does not exist, presence and absence of specific IDs may be revealed, which is not desirable from the security perspective.
Therefore, it is recommended that the screen transition and notification message to the user is set such that it does not reveal type of exception.
6.3.2.7. Setting <sec:logout> element¶
<sec:logout> element, is explained in this section.spring-security.xml
<sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true">
<!-- omitted -->
<sec:logout
logout-url="/logout"
logout-success-url="/"
invalidate-session="true"
delete-cookies="JSESSIONID"
success-handler-ref="logoutSuccessHandler"
/> <!-- Perform steps (1) to (5) in the specified attribute order -->
<!-- omitted -->
</sec:http>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify the path for executing logout process in
logout-url attribute.When not specified, “/j_spring_security_logout” will be default path.
In this guideline, it is recommended to change it to system specific value instead of using the above default value “/j_spring_security_logout”. In this example, “/logout” is specified.
|
(2)
|
Specify the destination path after logout in
logout-success-url attribute.When not specified, “/” will be default path.
If
success-handler-ref attribute is to be specified while this attribute is specified, error will occur during startup process. |
(3)
|
In
invalidate-session attribute, set whether to discard the session when logging out.By default, it is set to
true.In case of
true, the session is discarded at the time of logout. |
(4)
|
In
delete-cookies attribute, mention the cookie names to be deleted at the time of logout.When multiple cookies are mentioned, use “,” to separate them.
|
(5)
|
Specify the handler class to be called after a successful logout, in
success-handler-ref attribute.If
logout-success-url attribute is to be specified while this attribute is specified, error will occur during startup process. |
Warning
Why it is not recommended to use Spring Security default value, “/j_spring_security_logout”
If default value is used, the fact that the application is using Spring Security is revealed. As a result, if any Spring Security related vulnerability is detected, there is a higher risk of receiving an attack due to the vulnerability. In order to prevent these risks, it is recommended to avoid using default value.
Note
CSRF token check is performed when <sec:csrf> explained in CSRF Countermeasures is used. Therefore, it is necessary to send logout request using POST as well as to send the CSRF token..
How to embed CSRF token is described below.
How to insert CSRF token automatically
<form:form method="POST" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/logout"> <input type="submit" value="Logout" /> </form:form>
Following HTML is output in such cases. CSRF token is set as hidden.
<form id="command" action="/your-context-path/logout" method="POST"> <input type="submit" value="Logout" /> <input type="hidden" name="_csrf" value="5826038f-0a84-495b-a851-c363e501b73b" /> </form>
How to explicitly insert CSRF token
<form method="POST" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/logout"> <sec:csrfInput/> <input type="submit" value="Logout" /> </form>
In this case as well, following HTML is output as before. CSRF token is set as hidden.
<form method="POST" action="/your-context-path/logout"> <input type="hidden" name="_csrf" value="5826038f-0a84-495b-a851-c363e501b73b" /> <input type="submit" value="Logout" /> </form>
6.3.2.8. Setting <sec:remember-me> element¶
<sec:remember-me> elements are shown below.spring-security.xml
<sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true">
<!-- omitted -->
<sec:remember-me key="terasoluna-tourreservation-km/ylnHv"
token-validity-seconds="#{30 * 24 * 60 * 60}" /> <!-- Perform steps (1) to (2) in the specified attribute order-->
<!-- omitted -->
</sec:http>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify the unique key that stores the cookie for Remember Me functionality in
key attribute.When not specified, it is recommended to specify it in cases where improvement in start-up time has been considered as the unique key is generated at the time of start-up.
|
(2)
|
Specify the validity of the cookie for Remember Me functionality in seconds, in
token-validity-seconds attribute. In this example it is set as 30 days.When not specified, it is valid for 14 days by default.
|
For attributes other than the above, refer to Spring Security manual.
Following flag that enables “Remember Me” functionality needs to be provided in login form.
<form method="post"
action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/authentication">
<!-- omitted -->
<label for="_spring_security_remember_me">Remember Me : </label>
<input name="_spring_security_remember_me"
id="_spring_security_remember_me" type="checkbox"
checked="checked"> <!-- (1) -->
<input type="submit" value="LOGIN">
<!-- omitted -->
</form>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
When requested as
true, next authentication can be avoidedby setting
_spring_security_remember_me in HTTP parameter. |
6.3.3. How to extend¶
6.3.3.1. Extending UserDetailsService¶
org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsorg.springframework.security.core.userdetails.userDetailsService
need to be implemented.
When attached information such as login user’s name and division etc. need to be displayed at all times on screen header, fetching it for each request from DB hampers the efficiency.
This extension is necessary to enable its access from SecurityContext or <sec:authentication> tags, by storing it in UserDetails object.
6.3.3.1.1. Extending UserDetails¶
Creating ReservationUserDetails class that also stores customer information other than authentication information.
public class ReservationUserDetails extends User { // (1)
// omitted
private final Customer customer; // (2)
private static final List<? extends GrantedAuthority> DEFAULT_AUTHORITIES = Collections
.singletonList(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER")); // (3)
public ReservationUserDetails(Customer customer) {
super(customer.getCustomerCode(),
customer.getCustomerPassword(), true, true, true, true, DEFAULT_AUTHORITIES); // (4)
this.customer = customer;
}
public Customer getCustomer() { // (5)
return customer;
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Inherit
org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User class which is the default class of UserDetails. |
(2)
|
Store the DomainObject class containing authentication information and customer information.
|
(3)
|
Create authorization information using constructor of
org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority. Here the authority named “ROLE_USER” is provided.This is a simple implementation wherein the authorization information should essentially be fetched from another table in the DB.
|
(4)
|
Set the user ID and password contained in DomainObject, in the constructor of super class.
|
(5)
|
Method to access customer information via
UserDetails. |
Note
When the business requirement cannot be implemented just by inheriting User class, UserDetails interface may be implemented.
6.3.3.1.2. Implementing an independent UserDetailsService¶
UserDetailsService.CustomerSharedService class that implements the process to fetch Customer object.public class ReservationUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Inject
CustomerSharedService customerSharedService;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
Customer customer = customerSharedService.findOne(username);
// omitted
return new ReservationUserDetails(customer);
}
}
6.3.3.1.3. How to use¶
How to use the created ReservationUserDetailsService and ReservationUserDetails, is described here.
spring-security.xml
<sec:authentication-manager> <sec:authentication-provider user-service-ref="userDetailsService"><!-- (1) --> <sec:password-encoder ref="passwordEncoder" /> </sec:authentication-provider> </sec:authentication-manager> <bean id="userDetailsService" class="com.example.domain.service.userdetails.ReservationUserDetailsService"><!-- (2) --> </bean> <!-- omitted -->
Sr. No. Description (1)Define the Bean ID ofReservationUserDetailsServicein ref attribute.(2)Perform Bean definition forReservationUserDetailsService.JSP
Access
Customerobject by using<sec:authentication>tag.<sec:authentication property="principal.customer" var="customer"/><!-- (1) --> ${f:h(customer.customerName)}<!-- (1) -->
Sr. No. Description (1)Customerobject contained inReservationUserDetailsis stored in variable.(2)Display the optional property ofCustomerobject stored in variable.Forf:h(), refer to XSS Countermeasures.Controller
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET) public String view(@AuthenticationPrincipal ReservationUserDetails userDetails, Model model) { // get Customer Customer customer = userDetails.getCustomer(); // (1) // omitted ... }
Sr. No. Description (1)Fetch the logged-inCustomerobject fromReservationUserDetails.Perform business process by passing this object to Service class.
Note
When customer information is changed, Customer object contained in ReservationUserDetails is not changed unless logout is carried out once.
It is recommended not to store the information that may undergo frequent changes or the information which is changed by a user other than the login user (administrator etc.).
6.3.3.2. Extending AuthenticationProvider¶
In case of business requirements that cannot be supported by Spring Security’s authentication provider,
it is necessary to create a class that implements org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider interface.
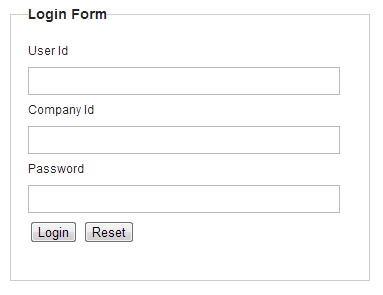
Here, the extended example of DB authentication using 3 parameters such as user name, password and Company identifier (independent authentication parameter) is given below.
To implement the above requirements, it is necessary to create a class given below.
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Implementation class of Here, it is created by inheriting |
(2)
|
Implementation class of Here, it is created by inheriting |
(3)
|
Servlet filter class to create Here, it is created by inheriting |
Tip
Here, as the example considers addition of independent parameter as an authentication parameter,
it is necessary to extend servlet filter class to generate Authentication and implementation class of Authentication interface.
To authenticate only by user name and password, the authentication process can be extended
only by creating implementation class of AuthenticationProvider interface.
6.3.3.2.1. Extending UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken¶
Here, by inheriting UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken class,
create a class that stores company identifier (independent authentication parameter) in addition to user name and password.
// import omitted
public class CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken extends
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken {
private static final long serialVersionUID = SpringSecurityCoreVersion.SERIAL_VERSION_UID;
// (1)
private final String companyId;
// (2)
public CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
Object principal, Object credentials, String companyId) {
super(principal, credentials);
this.companyId = companyId;
}
// (3)
public CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
Object principal, Object credentials, String companyId,
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(principal, credentials, authorities);
this.companyId = companyId;
}
public String getCompanyId() {
return companyId;
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Create a field to store company identifier. |
(2)
|
Create a constructor to be used while creating instances for storing the information (information specified in request parameter) before authentication. |
(3)
|
Create a constructor to be used while creating instances for storing the authenticated information.
Authentication completion status is reached by passing authorization information to the constructor argument of parent class.
|
6.3.3.2.2. Extending DaoAuthenticationProvide¶
Here, by inheriting DaoAuthenticationProvider class,
create a class that performs DB authentication using user name, password and company identifier.
// import omitted
public class CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationProvider extends
DaoAuthenticationProvider {
// omitted
@Override
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
// (1)
super.additionalAuthenticationChecks(userDetails, authentication);
// (2)
CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken companyIdUsernamePasswordAuthentication =
(CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication;
String requestedCompanyId = companyIdUsernamePasswordAuthentication.getCompanyId();
String companyId = ((SampleUserDetails) userDetails)
.getAccount().getCompanyId();
if (!companyId.equals(requestedCompanyId)) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
}
@Override
protected Authentication createSuccessAuthentication(Object principal,
Authentication authentication, UserDetails user) {
String companyId = ((SampleUserDetails) user).getAccount()
.getCompanyId();
// (3)
return new CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(user,
authentication.getCredentials(), companyId,
user.getAuthorities());
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
// (4)
return CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class
.isAssignableFrom(authentication);
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Call parent class method and execute check process provided by Spring Security. Password authentication is performed at this time. |
(2)
|
When password authentication is successful, validate company identifier (independent authentication parameter). In the above example, it is checked whether requested company identifier matches with the company identifier stored in the table. |
(3)
|
When password authentication and independent authentication is successful, create and return authenticated CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken. |
(4)
|
When Authenticationthat can be casted is specified in CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,
perform the authentication process using this class. |
Tip
User existence check, user status check (check for invalid users, locked users, validity expired users, etc.),
are performed as processes of parent class before the additionalAuthenticationChecks method is called.
6.3.3.2.3. Extending UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter¶
Here, by inheriting UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter class,
create a servlet filter class to pass the authentication information (user name, password, company identifier) to AuthenticationProvider.
Implementation of attemptAuthentication method is customized by copying UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilterclass method.
// import omitted
public class CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter {
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (!request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: "
+ request.getMethod());
}
// (1)
// Obtain UserName, Password, CompanyId
String username = super.obtainUsername(request);
String password = super.obtainPassword(request);
String companyId = obtainCompanyId(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
} else {
username = username.trim();
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest =
new CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password, companyId);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest); // (2)
}
// (3)
protected String obtainCompanyId(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameter("companyid");
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Create an instance of CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken from authentication information (user name, password, company identifier) fetched from request parameter. |
(2)
|
Call If |
(3)
|
Company identifier is fetched from the request parameter called "companyid". |
Note
Authentication information input check
Sometimes, a check needs to be performed in advance for the obvious input errors that occur due to load reduction on DB server.
In such cases, input check process can be performed by extending UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter, similar to
Extending UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.
Input check is not performed in the above mentioned example.
Todo
Input check of authentication information can also be performed using Bean Validation by handling the request in Controller class.
Input check method using Bean Validation will be added later.
6.3.3.2.4. Application of extended authentication process¶
Apply the DB authentication function using user name, password, company identifier (independent authentication parameter) in Spring Security.
spring-security.xml
<!-- omitted -->
<!-- (1) -->
<sec:http
auto-config="false"
use-expressions="true"
entry-point-ref="loginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint">
<!-- omitted -->
<!-- (2) -->
<sec:custom-filter
position="FORM_LOGIN_FILTER"
ref="companyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter" />
<!-- omitted -->
<sec:csrf token-repository-ref="csrfTokenRepository" />
<sec:logout
logout-url="/logout"
logout-success-url="/login"
delete-cookies="JSESSIONID" />
<!-- omitted -->
<sec:intercept-url pattern="/login" access="permitAll" />
<sec:intercept-url pattern="/**" access="isAuthenticated()" />
<!-- omitted -->
</sec:http>
<!-- (3) -->
<bean id="loginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint"
class="org.springframework.security.web.authentication.LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint">
<constructor-arg value="/login" />
</bean>
<!-- (4) -->
<bean id="companyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter"
class="com.example.app.common.security.CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter">
<!-- (5) -->
<property name="requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher">
<bean class="org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.AntPathRequestMatcher">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="/authentication" />
<constructor-arg index="1" value="POST" />
</bean>
</property>
<!-- (6) -->
<property name="authenticationManager" ref="authenticationManager" />
<!-- (7) -->
<property name="sessionAuthenticationStrategy" ref="sessionAuthenticationStrategy" />
<!-- (8) -->
<property name="authenticationFailureHandler">
<bean class="org.springframework.security.web.authentication.SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler">
<constructor-arg value="/login?error=true" />
</bean>
</property>
<!-- (9) -->
<property name="authenticationSuccessHandler">
<bean class="org.springframework.security.web.authentication.SimpleUrlAuthenticationSuccessHandler" />
</property>
</bean>
<!-- (6') -->
<sec:authentication-manager alias="authenticationManager">
<sec:authentication-provider ref="companyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationProvider" />
</sec:authentication-manager>
<bean id="companyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationProvider"
class="com.example.app.common.security.CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationProvider">
<property name="userDetailsService" ref="sampleUserDetailsService" />
<property name="passwordEncoder" ref="passwordEncoder" />
</bean>
<!-- (7') -->
<bean id="sessionAuthenticationStrategy"
class="org.springframework.security.web.authentication.session.CompositeSessionAuthenticationStrategy">
<constructor-arg>
<util:list>
<bean class="org.springframework.security.web.csrf.CsrfAuthenticationStrategy">
<constructor-arg ref="csrfTokenRepository" />
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.security.web.authentication.session.SessionFixationProtectionStrategy" />
</util:list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="csrfTokenRepository"
class="org.springframework.security.web.csrf.HttpSessionCsrfTokenRepository" />
<!-- omitted -->
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
To replace “FORM_LOGIN_FILTER” using
|
(2)
|
Replace “FORM_LOGIN_FILTER” by using Specify |
(3)
|
Define bean of Here, bean of |
(4)
|
Define bean of servlet filter to be used as “FORM_LOGIN_FILTER”. Here, bean of extended servlet filter class ( |
(5)
|
Specify Here, if there is a request in |
(6)
|
Specify the value which was set in If |
(6’)
|
Set extended AuthenticationProvider (CompanyIdUsernamePasswordAuthenticationProvider) to AuthenticationManager generated by Spring Security. |
(7)
|
Specify bean of component (SessionAuthenticationStrategy) to control the session handling at the time of successful authentication, in sessionAuthenticationStrategy property. |
(7’)
|
Define bean of component ( Here, the following features provided by Spring Security are enabled.
|
(8)
|
Specify handler class, called at the time of authentication failure, in
authenticationFailureHandler. |
(9)
|
Specify handler class, called at the time of successful authentication, in
authenticationSuccessHandler. |
Note
When auto-config="false" is specified, <sec:http-basic> element and <sec:logout> element will not be enabled if not defined explicitly.
6.3.3.2.5. Creating login form¶
Here, add company identifier for the screen (JSP), introduced in Creating login form.
<form:form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/authentication" method="post">
<!-- omitted -->
<span>User Id</span><br>
<input type="text" id="username" name="j_username"><br>
<span>Company Id</span><br>
<input type="text" id="companyid" name="companyid"><br> <!-- (1) -->
<span>Password</span><br>
<input type="password" id="password" name="j_password"><br>
<!-- omitted -->
</form:form>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify
"companyid" in the input field name of company identifier. |
6.3.4. Appendix¶
6.3.4.1. Authentication Success handler for which destination can be specified¶
In case of authentication using Spring Security, user is transited to the following two paths if authentication is successful.
- Path described in bean definition file (
spring-security.xml) (path specified indefault-target-urlattribute of<form-login>element) - Path for displaying “Secure page for which authentication is necessary” which is accessed before the login.
In common library, in addition to the functionality provided by Spring Security,
a class (org.terasoluna.gfw.security.web.RedirectAuthenticationHandler) is provided which can specify the destination path in request parameter.
RedirectAuthenticationHandler is a class, created for implementing the mechanism given below.
- For performing login for page display
- For specifying destination page after login at JSP side (source JSP)
RedirectAuthenticationHandler is shown below.Description example of source screen JSP
<form:form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login" method="get">
<!-- omitted -->
<input type="hidden" name="redirectTo"
value="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/reservetour/read?
${f:query(reserveTourForm)}&page.page=${f:h(param['page.page'])}
&page.size=${f:h(param['page.size'])}" /> <!-- (1) -->
</form:form>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
As hidden field, set the “URL of destination page after successful login”.
Specify “
redirectTo ” as hidden field name (request parameter name).Field name (request parameter name) should match with
targetUrlParameter property value of RedirectAuthenticationHandler. |
Description example of login screen JSP
<form:form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/authentication" method="post">
<!-- omitted -->
<input type="submit"
value="Login">
<input type="hidden" name="redirectTo" value="${f:h(param.redirectTo)}" /> <!-- (1) -->
<!-- omitted -->
</form:form>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
As hidden field, set the “URL of destination page after successful login”, passed by request parameter from source screen.
Specify “
redirectTo ” as hidden field name (request parameter name).Field name (request parameter name) should match with
targetUrlParameter property value of RedirectAuthenticationHandler. |
Spring Security configuration file
<sec:http auto-config="true">
<!-- omitted -->
<!-- (1) -->
<sec:form-login
login-page="/login"
login-processing-url="/authentication"
authentication-failure-handler-ref="authenticationFailureHandler"
authentication-success-handler-ref="authenticationSuccessHandler" />
<!-- omitted -->
</sec:http>
<!-- (2) -->
<bean id="authenticationSuccessHandler"
class="org.terasoluna.gfw.security.web.RedirectAuthenticationHandler">
</bean>
<!-- (3) -->
<bean id="authenticationFailureHandler"
class="org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ExceptionMappingAuthenticationFailureHandler">
<property name="defaultFailureUrl" value="/login?error=true"/> <!-- (4) -->
<property name="useForward" value="true"/> <!-- (5) -->
</bean>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify BeanId of
authentication-failure-handler-ref (handler setting at the time of authentication error) and authentication-success-handler-ref (handler setting in case of successful authentication). |
(2)
|
Define
org.terasoluna.gfw.security.web.RedirectAuthenticationHandleras a bean referred from authentication-success-handler-ref. |
(3)
|
Define
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ExceptionMappingAuthenticationFailureHandler as a bean referred from authentication-failure-handler-ref. |
(4)
|
Specify destination path at the time of authentication failure.
In above example, login screen path and the query (
error=true) to indicate transition after authentication error, is set. |
(5)
|
To use this functionality, useForward should be set to true.
By setting it to
true, Forward is used instead of Redirect, at the time of transiting to the screen (login screen) which would be displayed in case of authentication failure.This is because “URL of destination page after successful login” needs to be included in the request parameter of authentication request.
By using Redirect, if authentication error screen is displayed, “URL of destination page after successful login” cannot be inherited from request parameter. Hence, it is not possible to transit to the specified screen even after login is successful.
To avoid this, it is necessary to ensure that “URL of destination page after successful login” is inherited from request parameter using Forward.
|
Tip
Measures against Open Redirector vulnerability are implemented in RedirectAuthenticationHandler.
Therefore, user cannot transit to external sites such as “http://google.com”.
In order to transit to an external site, it is necessary to create a class that implements org.springframework.security.web.RedirectStrategy,
and it is to be injected to targetUrlParameterRedirectStrategy property of RedirectAuthenticationHandler.
As a precaution while extending, it is necessary to have a structure that does not pose any problems even if redirectTovalue is tampered with.
For example, the measures given below can be considered.
- Specifying the ID of page number etc. instead of directly specifying the destination URL and redirecting to the URL corresponding to that ID.
- Checking the destination URL, and redirecting only the URL that matches with white list.