6.5. Authorization¶
Caution
This version is already obsolete. Please check the latest guideline.
Table of contents
6.5.1. Overview¶
- Web (Request URL)
- Authority required to access specific URLs can be set.
- Screen fields (JSP)
- Authority required to display specific elements in a screen can be set.
- Method
- Authority required to execute specific methods in a screen can be set.
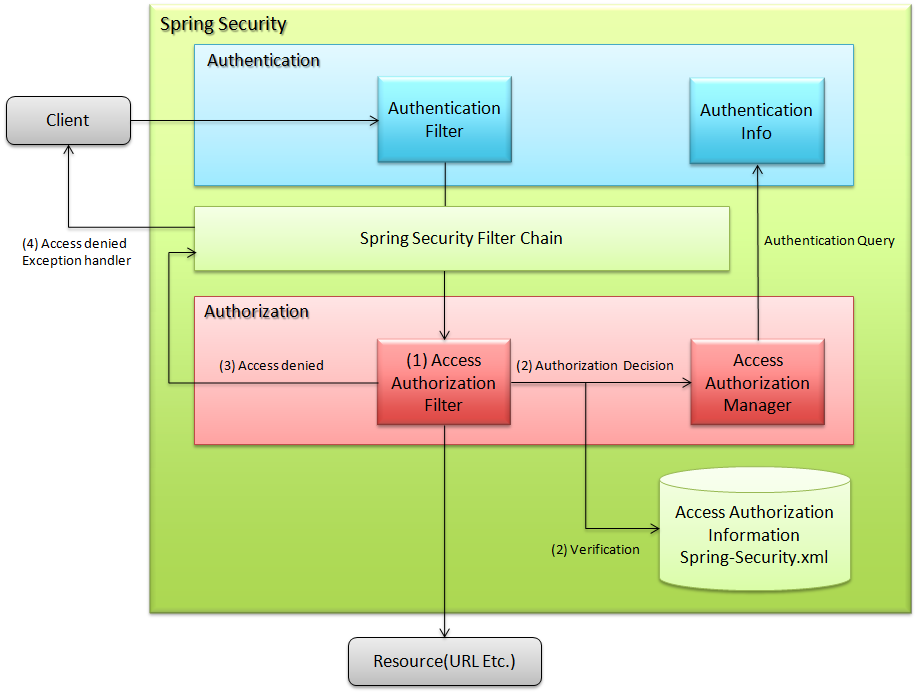
6.5.1.1. Access authorization (Request URL)¶
- Spring Security’s filter chain interrupts the process for user requests.
- Target URL for authorization control and request are matched and a query is sent to access authorization manager regarding decision on access authorization.
- Access authorization manager checks the user authority and access authorization information and throws access denial exception when the required role is not assigned.
- Process is continued if the required role is assigned.
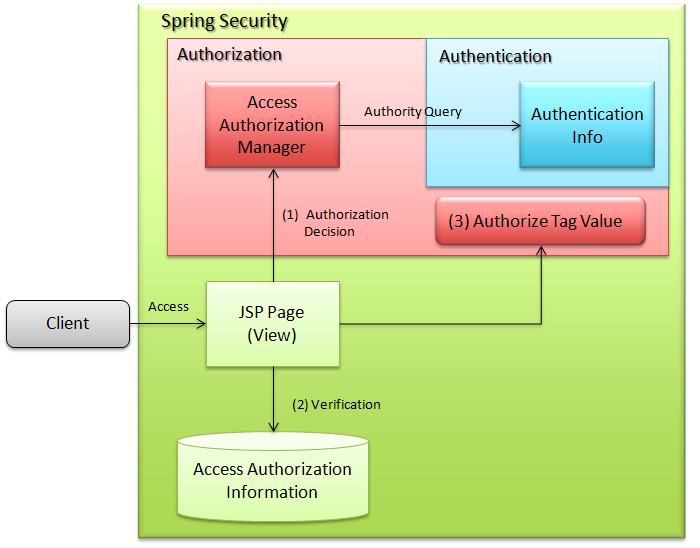
6.5.1.2. Access authorization (JSP)¶
- The servlet generated from JSP inquires with access authorization manager.
- Access authorization manager checks the user authority and access authorization information. If the required role is not assigned, it does not evaluate the internal tag.
- It evaluates internal tag if the required role is assigned.
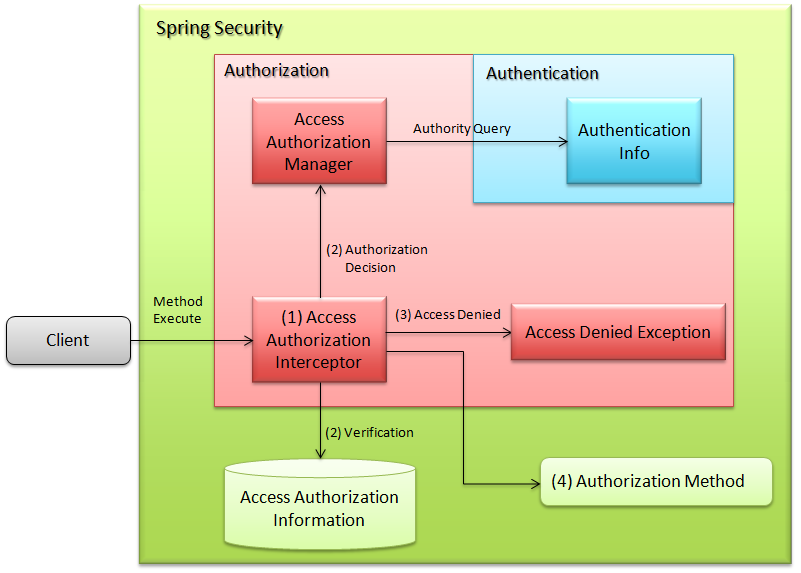
6.5.1.3. Access authorization (Method)¶
- Spring container generates an interceptor for the target object on the basis of access authorization information and interrupts the process.
- Interceptor inquires with access authorization manager on the basis of set roles.
- Access authorization manager checks user authority and access authorization information and throws access denial exception when the required role is not assigned.
- The process is continued if the required role is assigned. (Authority can be checked after executing the process as per the settings).
6.5.2. How to use¶
6.5.2.1. Access authorization (Request URL)¶
6.5.2.1.1. Setting <sec:intercept-url> element¶
<sec:intercept-url> element which is a child element of <sec:http> element,spring-security.xml
<sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true"> <sec:intercept-url pattern="/admin/*" access="hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')"/> <!-- omitted --> </sec:http>
Attribute nameDescriptionpatternDescribes the target URL pattern for access authorization. Wild cards “*” and “**” can be used.“*” is used only for URL patterns of same level while “**” targets all URLs under specified level for authorization setting.accessSpecifies the access control type and accessible role using Spring EL.methodSpecifies the HTTP method (GET, POST etc.). Matches only the specified method with URL pattern.When not specified, any HTTP method is applied. It can be utilized in the Web services that mainly use REST.requires-channelSpecifies “http” or “https”. It enforces access to the specified protocol.When not specified, both protocols can be accessed.For attributes other than the above, refer to <intercept-url>.
spring-security.xml
<sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true"> <sec:intercept-url pattern="/reserve/*" access="hasAnyRole('ROLE_USER','ROLE_ADMIN')" /> <!-- (1) --> <sec:intercept-url pattern="/admin/*" access="hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')" /> <!-- (2) --> <sec:intercept-url pattern="/**" access="denyAll" /> <!-- (3) --> <!-- omitted --> </sec:http>
Sr. No.Description(1)To access “/reserve/*”, either the role “ROLE_USER” or “ROLE_ADMIN” is required.hasAnyRolewill be described later.(2)To access “/admin/*”, the role “ROLE_ADMIN” is required.hasRolewill be described later.(3)denyAllis set for all patternsand it is set such that no user can access the URLs for which authority settings are not performed.denyAllwill be described later.Note
Description order of URL pattern
Match the request received from client with the pattern in intercept-url, starting from the top. Perform access authorization for the matched pattern. Therefore, pattern should be described from restricted patterns.
use-expressions="true" in <sec:http> attribute.spring-security.xml
<sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true"> <sec:intercept-url pattern="/admin/*" access="hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')"/> <!-- (1) --> <!-- omitted --> </sec:http>
Sr. No. Description (1)By specifyinghasRole('role name'), ‘true’ is returned if the login user has the specified role.Example of available expressions listAttribute name Description hasRole('Role name')Returns true if the user has the specified role.hasAnyRole('Role 1','Role 2')Returns true if the user has any of the specified roles.permitAllAlways returns true. Note that it is accessible even if not authenticated.denyAllAlways returns false.isAnonymous()Returns true in case of an anonymous user.isAuthenticated()Returns true in case of an authenticated user.isFullyAuthenticated()Returns false, in case of an anonymous user or authentication by RememberMe functionality.hasIpAddress('IP address')Enabled only by the access authorization to request URL and JSP tag.Returns true if there is a request from specified IP address.For other available Spring EL, refer to Common built-in expressions.Determination can also be performed using operator.In the following example, it can be accessed when it matches with both the role and the requested IP address.spring-security.xml
<sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true"> <sec:intercept-url pattern="/admin/*" access="hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN') and hasIpAddress('192.168.10.1')"/> <!-- omitted --> </sec:http>
Available operators listOperator Description [Expression1] and [Expression2]Returns true when both Expression1 and Expression2 are true.[Expression1] or [Expression2]Returns true when either of the expressions is true.![Expression]Returns false when expression is true and true when the expression is false.
6.5.2.1.2. Setting the URL for which access authorization is not controlled¶
- spring-security.xml
<sec:http pattern="/css/*" security="none"/> <!-- Perform steps (1) and (2) in the specified attribute order --> <sec:http pattern="/login" security="none"/> <sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true"> <!-- omitted --> </sec:http>
patternattribute. When not specifyingpatternattribute, match with all patterns.noneinsecurityattribute, Spring Security filter chain can be avoided for the path stated inpatternattribute.
6.5.2.1.3. Exception handling in URL pattern¶
org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException is thrown when an unauthorized URL is accessed.org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandlerImpl which is set in org.springframework.security.web.access.ExceptionTranslationFilter,spring-security.xml
<sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true"> <!-- omitted --> <sec:access-denied-handler error-page="/accessDeneidPage" /> <!-- (1) --> </sec:http>
Sr. No.Description(1)Specify destination path inerror-pageattribute of<sec:access-denied-handler>element.
6.5.2.2. Access authorization (JSP)¶
<sec:authorize> provided by Spring Security, to control screen display fields.Attributes list of
<sec:authorize>tagAttribute nameDescriptionaccessDescribes the access control expression. If true, tag contents are evaluated.urlTag contents are evaluated when authority is granted to the set URL. It is used to control link display etc.methodSpecifies the HTTP method (GET, POST etc.).It is used by combining with url attribute and only the specified methodis matched with the specified URL pattern. When not specified, GET is applied.ifAllGrantedTag contents are evaluated when all the set roles are granted. Role hierarchy functionality is not effective.ifAnyGrantedTag contents are evaluated when any one of the set roles is granted. Role hierarchy functionality is not effective.ifNotGrantedTag contents are evaluated when the set role is not granted. Role hierarchy functionality is not effective.varDeclares the variables of page scope that stores tag evaluation result. It is used when same authorization check is performed in a page.
<sec:authorize> tag is as follows:spring-security.xml
<div> <sec:authorize access="hasRole('ROLE_USER')"> <!-- (1) --> <p>This screen is for ROLE_USER</p> </sec:authorize> <sec:authorize url="/admin/menu"> <!-- (2) --> <p> <a href="/admin/menu">Go to admin screen</a> </p> </sec:authorize> </div>
Sr. No.Description(1)Tag contents are displayed only when it contains “ROLE_USER”.(2)Tag contents are displayed when access is authorized for “/admin/menu”.Warning
The authorization process using
<sec:authorize>tag can only be controlled by screen display. As a result, even if the link is not displayed by specific authority, the URL of the link can be directly accessed by guessing the URL. Therefore, make sure to use it together with the “Access authorization (request URL)” described earlier or the “Access authorization (Method)” that will be described later and perform the essential access control.
6.5.2.3. Access authorization (Method)¶
org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize annotation for the method to be controlled.spring-security.xml
<sec:global-method-security pre-post-annotations="enabled"/> <!-- (1) -->
Sr. No.Description(1)Specifypre-post-annotationsattribute of<sec:global-method-security>element inenabled.It isdisabledby default.Java code
@Service @Transactional public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { // omitted @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')") // (1) @Override public User create(User user) { // omitted } @PreAuthorize("isAuthenticated()") @Override public User update(User user) { // omitted } }
Sr. No.Description(1)State the access control expression. The expression is evaluated before executing the method and if it is true, the method is executed.If the expression is false,org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedExceptionis thrown.Expression stated in Setting <sec:intercept-url> element andthe expression stated in Spring Expression Language (SpEL) can be set as the value.Tip
Following annotations can also be used in the above setting, other than
org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize.org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PostAuthorizeorg.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreFilterorg.springframework.security.access.prepost.PostFilter
For their details, refer Spring Security manual.
Note
In Spring Security, authorization can also be controlled by using
javax.annotation.security.RolesAllowedannotation of JSR-250 which is a standard Java specification. However, SpEL expressions cannot be stated in@RolesAllowed. By@PreAuthorizeannotation, using SpEL, authorization control can be performed in the same notations as spring-security.xml settings.Note
It is recommended to perform authorization control for request path by carrying out settings in spring-security.xml, instead of assigning annotation to Controller method.
If Service is executed only via Web and if authorization control is performed for all the request path patterns, authorization control for Service need not be performed. It is advisable to use annotation when it is not known from where Service will be executed and thus authorization control is necessary.
6.5.3. How to extend¶
6.5.3.1. Role hierarchy functionality¶
Spring Security configuration file
<sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true">
<sec:intercept-url pattern="/user/*" access="hasAnyRole('ROLE_USER')" />
<!-- omitted -->
</sec:http>
6.5.3.1.1. Common settings¶
org.springframework.security.access.hierarchicalroles.RoleHierarchy class that stores the hierarchical relation.spring-security.xml
<bean id="roleHierarchy" class="org.springframework.security.access.hierarchicalroles.RoleHierarchyImpl"> <!-- (1) --> <property name="hierarchy"> <value> <!-- (2) --> ROLE_ADMIN > ROLE_STAFF ROLE_STAFF > ROLE_USER </value> </property> </bean>
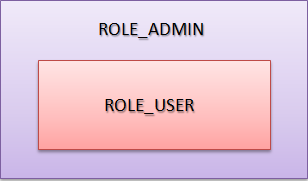
Sr. No.Description(1)Specify the default class ofRoleHierarchynamely,org.springframework.security.access.hierarchicalroles.RoleHierarchyImpl.(2)Define the hierarchical relation inhierarchyproperty.Format:[Higher role] > [Lower role]In the example, STAFF can access all the USER authorized resources.ADMIN can access all the resources authorized by USER and STAFF.
6.5.3.1.2. How to use it in access authorization (request URL) and access authorization (JSP)¶
spring-security.xml
<bean id="webExpressionHandler" class="org.springframework.security.web.access.expression.DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler"> <!-- (1) --> <property name="roleHierarchy" ref="roleHierarchy"/> <!-- (2) --> </bean> <sec:http auto-config="true" use-expression="true"> <!-- omitted --> <sec:expression-handler ref="webExpressionHandler" /> <!-- (3) --> </sec:http>
Sr. No.Explanation(1)Specifyorg.springframework.security.web.access.expression.DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandlerin class.(2)Set the Bean ID ofRoleHierarchyinroleHierarchyproperty.(3)Specify the Bean ID of handler class that implementedorg.springframework.security.access.expression.SecurityExpressionHandlerinexpression-handlerelement.
6.5.3.1.3. How to use it in access authorization (Method)¶
spring-security.xml
<bean id="methodExpressionHandler" class="org.springframework.security.access.expression.method.DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler"> <!-- (1) --> <property name="roleHierarchy" ref="roleHierarchy"/> <!-- (2) --> </bean> <sec:global-method-security pre-post-annotations="enabled"> <sec:expression-handler ref="methodExpressionHandler" /> <!-- (3) --> </sec:global-method-security>
Sr. No.Description(1)Specifyorg.springframework.security.access.expression.method.DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandlerin class.(2)Set the Bean ID ofRoleHierarchyinroleHierarchyproperty.(3)Specify the Bean ID of handler class that implementsorg.springframework.security.access.expression.SecurityExpressionHandlerinexpression-handlerelement.