10.2.1. Preparation for test¶
Index
This section explains about the setting file used for OSS library to be used, the data setup method and the setting file used in the test implementation, as a preparation for implementing unit test.
10.2.1.1. OSS library setting¶
OSS library used in the test,is set in POM file of project (domain project, web project) executing unit test.
pom.xml
<!-- == Begin Database == -->
<!-- <dependency> -->
<!-- <groupId>org.postgresql</groupId> -->
<!-- <artifactId>postgresql</artifactId> -->
<!-- <scope>test</scope> -->
<!-- </dependency> -->
<!-- == End Database == -->
<!-- == Begin Unit Test == -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hamcrest</groupId>
<artifactId>hamcrest-library</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE DBUnit
<dependency>
<groupId>org.dbunit</groupId>
<artifactId>dbunit</artifactId>
<version>2.5.4</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
-->
<!-- REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE Spring Test DBUnit
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.springtestdbunit</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test-dbunit</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
-->
<!-- == End Unit Test == -->
Note
For setup example of other than dbunit and spring-test-dbunit, since it is assumed that version of
dependency library is managed by parent project - terasoluna-gfw-parent, specifying version in pom.xml is not required.
Further, for hamcrest-core, since junit resolves dependency relation, it is not necessary to define it again.
Tip
Regarding how to add PostgreSQL driver
When PostgreSQL driver is used in the test involving data access, comments for PostgreSQL driver of POM file should be removed.
Note that, if the dependent library is required for test, test is considered appropriate.
10.2.1.2. Database setup¶
10.2.1.2.1. Schema and test data setup (in case of a test when only Spring Test standard function is used)¶
Following methods can be used for setup of database to be used in the unit test.
| Setup method | Characteristics | Use scene |
|---|---|---|
Use
<jdbc:initialize-database>. |
Read and configure setup file which defines
<jdbc:initialize-database> element at the time of test execution. |
It is used to set up in-memory database (H2 Database).
|
Use initdb project.
|
DB can be initialized in advance, separately from test execution.
|
It is used to setup database collectively before test execution.
|
Use
@org.springframework.test.context.jdbc.Sqlannotation. |
Issue a SQL specified in
@Sql annotation argument.
@Sql annotation can be specified at method level and class level.
SQL can be issued by specified method only when it is specified at the method level and
when it is specified at the class level, it can be issued before and after test by all the test methods
without @Sql annotation specification. |
It is used while setting test data for each set.
|
Warning
“COMMIT;” should be explicitly described in SQL file which is set in <jdbc:initialize-database>tag.
It is assumed that setup of schema used in unit test is executed collectively before test, and not executed for each test. Therefore, it is assumed in this chapter that schema is created using initdb project which is separated from the test. For initdb project, refer Structure of Initdb module.
On the other hand, it is assumed that test data setup is executed for each test.
Therefore, it is assumed in this chapter that @Sql annotation which can issue a SQL for each test class or test method is used.
A example to setup test data while assigning @Sql annotation to method level is shown below.
MemberRepositoryTest.java
public class MemberRepositoryTest {
@Test
@Sql(scripts = "classpath:META-INF/sql/setupMemberLogin.sql" // (1)
config = @SqlConfig(encoding = "utf-8")) // (2)
public void testUpdateMemberLogin() {
// omitted
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify SQL file which injects data required for test, in
@Sql annotation. |
(2)
|
Use
@SqlConfig annotation and specify encoding of SQL file. |
Tip
About @Sql
Following can be specified in the argument of @Sqlannotation.
- SQL file (
scriptsorvalue) - SQL statement (
statements) - SQL execution phase (
executionPhase) - SQL analysis meta data (Specify
@SqlConfigannotation inconfig)
Further, @Sqlannotation is executed by SqlScriptsTestExecutionListener which is enabled by default.
For details, refer Executing SQL scripts declaratively with @Sql.
Note that, configuration by using @Sql annotation and @SqlConfigannotation is a superset of
configuration by <jdbc:initialize-database>element.
Note
Omit SQL file path of @Sql
@Sql annotation can omit the SQL file path similar to @ContextConfiguration annotation.
When it is omitted, SQL file is searched based on the location specified by @Sql annotation.
For example, files which are on the default path are thrown.
When com.example.domain.repository.SampleRepositoryTest is specified →
classpath:com/example/domain/repository/SampleRepositoryTest.sql
When SampleRepositoryTest#testUpdate()is specified →
classpath:com/example/domain/repository/SampleRepositoryTest.testUpdate.sql
Note that, if default path is not detected, java.lang.IllegalStateException is thrown.
Note
Multiple specification of @Sql
Since @Repeatable added from Java SE8 is assigned to @Sql, it is possible to specify for multiple
times at same location from Java SE8 onwards. Note that, while using Java SE7 or earlier versions, multiple
@Sql can be specified by using @org.springframework.test.context.jdbc.SqlGroup.
10.2.1.2.2. Test data setup (In case of a test which use Spring Test DBUnit)¶
DBUnit is a JUnit extension framework for performing test of class dependent on database. A method to setup database for test, by using DBUnit and Spring Test DBUnit is explained.
DBUnit provides org.dbunit.dataset.IDataSet interface which abstracts and operates the database information
described in the tabular format as a Java object.
By using IDataSet interface, data definition file which defines test data and expected result data can be read
and a file of Flat XML format is used as a default.
DBUnit consists of an implementation class of IDataSet interface corresponding to Excel format (.xlsx) and CSV format in addition to Flat XML format.
Spring Test DBUnit delegates the function of reading data definition file to the implementation class of
com.github.springtestdbunit.dataset.DataSetLoader interface. Data definition file of XML format is read by default.
When the file format is to be changed, implementation class of IDataSet interface corresponding to format to be changed is generated.
It is executed by creating an implementation class of DataSetLoader interface.
Note that, when data is setup by using Spring Test DBUnit, a file which defines test data can be loaded into test code
by using @DatabaseSetup annotation.
@DatabaseSetup annotation can be specified at the class level and method level. Data can be setup by a specified
method when the annotation is specified at the method level and by the file specified before test execution of each method when the annotation is specified at the class level.
Explanation in this section is given by assuming the use of data definition file of Excel format (.xlsx).
Implementation example of DataSetLoader interface corresponding to Excel format is shown below.
XlsDataSetLoader.java
public class XlsDataSetLoader extends AbstractDataSetLoader { // (1)
@Override
protected IDataSet createDataSet(Resource resource) throws IOException, DataSetException {
try (InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream()) {
return new XlsDataSet(inputStream);
}
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Use
com.github.springtestdbunit.dataset.AbstractDataSetLoader- an abstract base class provided by
Spring Test DBUnit and define XlsDataSetLoader class of data definition file of Excel format. |
MemberRepositoryDbunitTest.java
// omitted
@DbUnitConfiguration(dataSetLoader = XlsDataSetLoader.class) // (1)
@DatabaseSetup("classpath:META-INF/dbunit/setup_MemberLogin.xlsx")
public class MemberRepositoryDbunitTest {
// omitted
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Data definition file of Excel format which use
@DatabaseSetup annotation can be read by specifying
XlsDataSetLoader class in @DbUnitConfiguration annotation. |
- Data definition file of Excel format (setup_MemberLogin.xlsx)
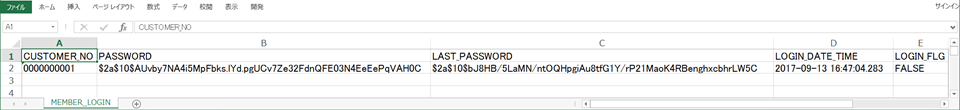
Each sheet corresponds to each table in data definition file of Excel format. Set the table name as sheet name and the column name as the first row of the sheet. Describe the data inserted in the table after the second line.
Note
When data definition file of CSV format is used
When data definition file of CSV format is to be used in DBUnit, it can be achieved by using
org.dbunit.dataset.csv.CsvDataSet.CsvDataSet class as an implementation class of IDataSet interface.
Note
Regarding the format of the file which is read by DBUnit, by default
DBUnit by default supports data definition file of Flat XML format.
When Spring Test DBUnit is used, and if dataSetLoader is not specified in @DbUnitConfiguration,
org.dbunit.dataset.xml.FlatXmlDataSet class - an implementation class of IDataSet interface
corresponding to a file of Flat XML format is used.
Example of data definition file of Flat XML format is shown below.
setup_MemberLogin.xml
<!-- (1) --> <?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?> <dataset> <MEMBER_LOGIN CUSTOMER_NO="0000000001" PASSWORD="$2a$10$AUvby7NA4i5MpFbks.lYd.pgUCv7Ze32FdnQFE03N4EeEePqVAH0C" LAST_PASSWORD="$2a$10$bJ8HB/5LaMN/ntOQHpgiAu8tfG1Y/rP21MaoK4RBenghxcbhrLW5C" LOGIN_DATE_TIME="2017-09-13 16:47:04.283" LOGIN_FLG="FALSE" /> </dataset>
Sr. No. Description datasetelement corresponds to a record in the table and defines table name for element name, column name for attribute name and data to be entered for attribute value. In the example, value is defined inMEMBER_LOGINtable.
10.2.1.3. Setting file used in the implementation example¶
By using DI function of Spring Test, it is possible to read the setting file which defines the Bean used in the test and use it at the time of test. For details, refer Spring Test DI function.
In this section, settings necessary for performing test are defined in test-context.xml and the setting file is set as a common setting at the time of test.
Note that, test-context.xml deletes <import resource="classpath:META-INF/spring/projectName-domain.xml" />from src/test/resources/test-context.xml of domain project and each layer is implemented together with setup
file (sample-infra.xml etc) is retained by the application to implement tests.
Note
Creation unit of setting file used in unit test
In this section, setup file is created as shown above, however, architect should consider business requirements while providing actual setup file and required settings are added to test implementation team based on this.
Setting file used in the implementation example of this chapter is shown below.
test-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder
location="classpath*:/META-INF/spring/*.properties" />
<!-- (1) -->
<bean id="exceptionLogger" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionLogger" />
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<!-- (2) -->
<bean id="passwordEncoder" class="org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder" />
</beans>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Define a Bean for test implementation.
|
(2)
|
Here, Bean definition of
passwordEncoder is added for implementing test example.Bean definition should be added appropriately according to the operation.
|