10.2.3. Implementation of tests by functions¶
Index
This chapter explains about test methods for functions which cannot be applied to each layer.
10.2.3.1. Unit test of input check¶
Unit test implementation method for following input check is explained here.
| Types of Validation | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Bean Validation | Test for Validator which is implemented by using Hibernate validator |
| Bean Validation | Test for Validator which is implemented by using Spring DI container |
| Spring Validation | Test for Validator which is implemented by using Spring Validation |
Unit test for Validator is originally performed as test for Controller, however, it results in many test patterns.
Hence, considering implementation cost for tests, the test can performed as Validator unit by isolating it from Controller.
Test implementation method as a Validator unit is explained here.
This section explains implementation methods while using Bean Validation and Spring Validation respectively.
10.2.3.1.1. Unit test of Validator implemented by Bean Validation¶
While performing the test of Bean Validation, required dependent libraries must be added since libraries are
not provided by application server. For how to add libraries, refer Adding dependent libraries.
Note that, input check function provided by Hibernate Validator is not within the scope of this test.
Test methods for Bean Validation are explained as shown below.
Bean Validationusing Hibernate validatorBean Validationusing Spring DI container
10.2.3.1.1.1. Bean Validationtest using Hibernate validator¶
Files to be created in unit test of Bean Validation using Hibernate validator are shown below.
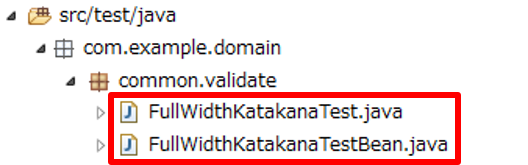
| Names of files to be created | Description |
|---|---|
FullWidthKatakanaTest.java |
Test class of @FullWidthKatakana annotation |
FullWidthKatakanaTestBean.java |
Bean class wherein @FullWidthKatakana annotation is assigned to the field |
Bean class which uses @FullWidthKatakana for the test (FullWidthKatakanaTestBean)is created here and
the validation check is performed by using implementation class of javax.validation.Validator generated
from javax.validation.ValidatorFactory.
How to create a Bean class wherein @FullWidthKatakana annotation is assigned to the field is shown below.
FullWidthKatakanaTestBean.java
public class FullWidthKatakanaTestBean {
@FullWidthKatakana
private String testString;
public FullWidthKatakanaTestBean() {
// constructor
}
public String getTestString() {
return testString;
}
public void setTestString(String testString) {
this.testString = testString;
}
}
FullWidthKatakanaTest.java
public class FullWidthKatakanaTest {
private static Validator validator;
@BeforeClass
public static void setUpBeforeClass() {
// setup
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
// (1)
validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
}
@Test
public void testFullWidthKatakana() {
// setup
FullWidthKatakanaTestBean form = new FullWidthKatakanaTestBean();
form.setTestString("テスト");
// run the test
Set<ConstraintViolation<FullWidthKatakanaTestBean>> violations = validator.validate(form); // (2)
// assert
assertThat(violations, is(empty())); // (3)
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Fetch
Validator by using getValidator method.Input check by using
validate method can be performed, by fetching Validator |
(2)
|
Perform input check by using
validate method.Set of ConstrainViolation is returned only for number of input check errors, by executing validate method.
Specify an object of FullWidthKatakanaBean class in the argument of validate method. |
(3)
|
Confirm whether an error has occurred from the
Set fetched in (2).Since there are no errors at this time, an empty
Set is returned. |
Note
Test using validation group
When validation group is to be set, it can be executed only by applying Validatorof specified group by specifying java.lang.Class object which points to a group
in validate method argument while performing input check.
For validation group, refer Grouped validation.
Form example which use validation group is shown below.
FullWidthKatakanaTestBean.javafor testpublic class FullWidthKatakanaTestBean { public interface Search {}; public interface Register {}; // (1) @Size(min = 5, max = 10, groups = Search.class) @FullWidthKatakana(groups = Register.class) @NotNull private String testString; public FullWidthKatakanaTestBean() { // constructor } public String getTestString() { return testString; } public void setTestString(String testString) { this.testString = testString; } }
Sr. No. Description Validatorset in the field are grouped.
FullWidthKatakanaTest.javapublic class FullWidthKatakanaTest { // omitted @Test public void testFullWidthKatakana() { // setup FullWidthKatakanaTestBean form = new FullWidthKatakanaTestBean(); form.setTestString("テスト"); // run the test // (1) Set<ConstraintViolation<FullWidthKatakanaTestBean>> violations = validator.validate(form, Default.class, Search.class); // assert assertThat(violations, is(empty())); // (2) } }
Sr. No. Description java.lang.Classobject, invalidatemethod argument. Further, multiplejava.lang.Classobjects can be specified as shown in the example.
10.2.3.1.1.2. Bean Validationtest using Spring DI container¶
Files to be created in unit test of Bean Validationby using Spring DI container are shown below.
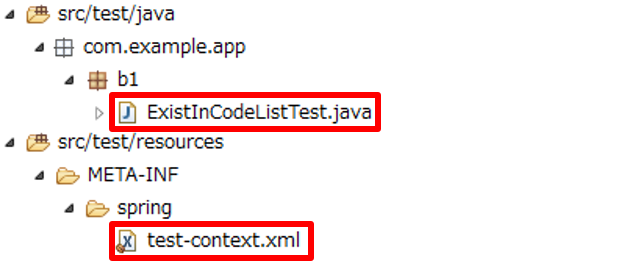
| Names of files to be created | Description |
|---|---|
ExistInCodeListTest.java |
Test class of Bean Validationusing Spring DI container |
test-context.xml |
Settings file for supplementing settings necessary for performing unit test by using Spring Test. |
Bean Validation using Spring DI container can perform the test by generating Validator object
from org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.LocalValidatorFactoryBean.
An implementation method of testing is explained here by using @ExistInCodeList as an input check using Spring DI container.
For details of @ExistInCodeList, refer Input validation of code value using codelist.
A Bean is defined for LocalValidatorFactoryBean in settings file to be used in the test in order to generate Validator object.
test-context.xml
<!-- (1) -->
<bean id="validator" class="org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.LocalValidatorFactoryBean" />
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
A
Validator generated from LocalValidatorFactoryBean for which a Bean is defined in
test-context.xml must be used to fetch a code list Bean from DI container by using @ExistInCodeList. |
An implementation example of Formclass which uses @ExistInCodeList is shown below.
TicketSearchForm.java
public class TicketSearchForm implements Serializable {
@NotNull
@ExistInCodeList(codeListId = "CL_AIRPORT") // (1)
private String depAirportCd;
// omitted
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Verify whether a value exists in the code list, for
depAirportCd field. |
A method to create test class of @ExistInCodeList is explained here.
Here, a value not defined in the defined codelist (CL_AIRPORT) is set in sample-codelist.xml and it is
confirmed whether a validation check error occurs by injected implementation class of javax.validation.Validator.
ExistInCodeListTest.java
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {
"classpath:META-INF/spring/sample-infra.xml",
"classpath:META-INF/spring/sample-codelist.xml",
"classpath:META-INF/spring/test-context.xml" })
public class ExistInCodeListTest {
// (1)
@Inject
private Validator validator;
@Test
public void testExistInCodeList() {
// setup
TicketSearchForm ticketSearchForm = new TicketSearchForm();
// (2)
ticketSearchForm.setDepAirportCd("AAA");
// omitted
// run the test
Set<ConstraintViolation<TicketSearchForm>> violations = validator
.validate(ticketSearchForm);
// assert
// (3)
assertThat(violations.size(), is(1));
ConstraintViolation<TicketSearchForm> violation = violations.iterator().next();
// (4)
assertThat(violation.getPropertyPath().toString(), is("depAirportCd"));
// (5)
assertThat((String) violation.getInvalidValue(), is("AAA"));
// (6)
assertThat(violation.getMessage(), is("Does not exist in CL_AIRPORT"));
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Apply DI of
Validator generated from LocalValidatorFactoryBean of Spring, to Validator.Validator generated from LocalValidatorFactoryBean operates on Spring DI container and a Bean
of codelist read by @ContextConfiguration can be fetched.
Accordingly, @ExistInCodeList operates as per expected operation. |
(2)
|
Enter code which does not exist in the codelist and anticipate an error in the
@ExistInCodeList. |
(3)
|
Use
size method to fetch the number of input check errors and verify whether the error has occurred. |
(4)
|
Verify whether the violated field is the assumed location.
|
(5)
|
Verify whether the violated input value is the assumed value.
|
(6)
|
Verify error message thus generated.
|
10.2.3.1.2. Unit test of Validator implemented by Spring Validator¶
Files to be created in unit test of Validator(Spring Validation) are shown below.
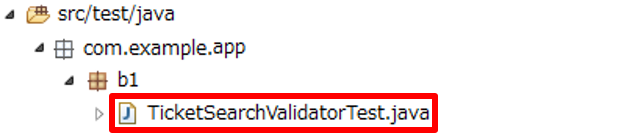
| Names of files to be created | Description |
|---|---|
TicketSearchValidatorTest.java |
Test class of TicketSearchValidator.java |
A class for test is shown below.
TicketSearchValidator.java
@Component
public class TicketSearchValidator implements Validator {
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
return (TicketSearchForm.class).isAssignableFrom(clazz);
}
@Override
public void validate(Object target, Errors errors) {
TicketSearchForm form = (TicketSearchForm) target;
if (!errors.hasFieldErrors("depAirportCd")
&& !errors.hasFieldErrors("arrAirportCd")) {
String depAirport = form.getDepAirportCd();
String arrAirport = form.getArrAirportCd();
if (depAirport.equals(arrAirport)) {
errors.reject(TicketSearchErrorCode.E_AR_B1_5001.code());
}
}
// omitted
}
}
How to create a test class of Validator(Spring Validation) is explained below.
Here, a value causing an error in TicketSearchValidator which is a target for testing is set in
TicketSearchForm and it is verified that it causes a validation error and the resulting error message is correct.
TicketSearchValidatorTest.java
public class TicketSearchValidatorTest {
private TicketSearchValidator validator;
private TicketSearchForm ticketSearchForm;
private BindingResult result;
@BeforeClass
public void setUpBeforeClass() {
// setup
validator = new TicketSearchValidator();
}
@Test
public void testTicketSearchValidator() {
// setup
ticketSearchForm = new TicketSearchForm();
result = new DirectFieldBindingResult(ticketSearchForm, "TicketSearchForm");
ticketSearchForm.setFlightType(FlightType.RT);
ticketSearchForm.setDepAirportCd("HND");
ticketSearchForm.setArrAirportCd("HND");
// omitted
// run the test
// (1)
validator.validate(ticketSearchForm, result);
// (2)
assertThat(result.hasErrors(), is(true));
// (3)
ObjectError error = result.getGlobalError();
// (4)
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
// (5)
messageSource.setBasename("i18n/sample-messages");
// (6)
messageSource.setUseCodeAsDefaultMessage(true);
String code = error.getCode();
// assert
// (7)
assertThat(code, is(TicketSearchErrorCode.E_AR_B1_5001.code()));
assertThat(messageSource.getMessage(error, Locale.JAPAN),
is("出発空港と到着空港に同じ空港は指定できません。区間をご確認ください。"));
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
By specifying
ticketSearchForm and BindingResult interface object in validatemethod argument, input check results for ticketSearchForm are stored in object
of BindingResult class. |
(2)
|
Use
hasErrors method and determine whether an error has occurred.true is returned in case of an error and false is returned when error does not occur.
|
(3)
|
Fetch error details by
getGlobalError method. |
(4)
|
Generate an object of
org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource- an implementation class of MessageSourceto check details of error message.
For class details, refer
Javadoc of ResourceBundleMessageSource. |
(5)
|
Specify a property file in which the message is defined, in
setBasename method and load the same. |
(6)
|
When true is specified in
setUseCodeAsDefaultMessage method, error code is returned when error message corresponding to error code is not defined.
If false is specified, NoSuchMessageException is returned when error message corresponding to error code is not defined.
false is applied by default. |
(7)
|
Verify error code and message details.
|