5.16. RESTful Web Service¶
Caution
This version is already obsolete. Please check the latest guideline.
Table of Contents
- Overview
- Architecture
- How to design
- How to use
- Web application configuration
- Application settings
- REST API implementation
- Creating REST API packages
- Creating Resource class
- Creating Controller class
- Implementing REST API that fetches collection of resources
- Implementing REST API that adds a resource to collection
- Implementing REST API that fetches specified resource
- Implementing REST API that updates specified resource
- Implementing REST API that deletes specified resource
- Implementing exception handling
- Implementation to output error information in response Body
- Implementing input error exception handling
- Implementing exception handling for “Resource not found” error
- Implementing exception handling for business errors
- Implementing exception handling for exclusive errors
- Implementing exception handling for system errors
- Resolving error codes and messages using ExceptionCodeResolver
- Implementing the error handling notified to Servlet Container
- Security measures
- Conditional operations for resource
- Cache control for resource
- Appendix
- Settings when RESTful Web Service and client application are operated as the same Web application
- Implementing hypermedia link
- Creating RESTful Web Service conforming to HTTP specifications
- Disabling CSRF measures
- Enabling XXE Injection measures
- How to copy Joda-Time classes using Dozer
- Source code for application layer
- Source code of the domain layer class created at the time of REST API implementation
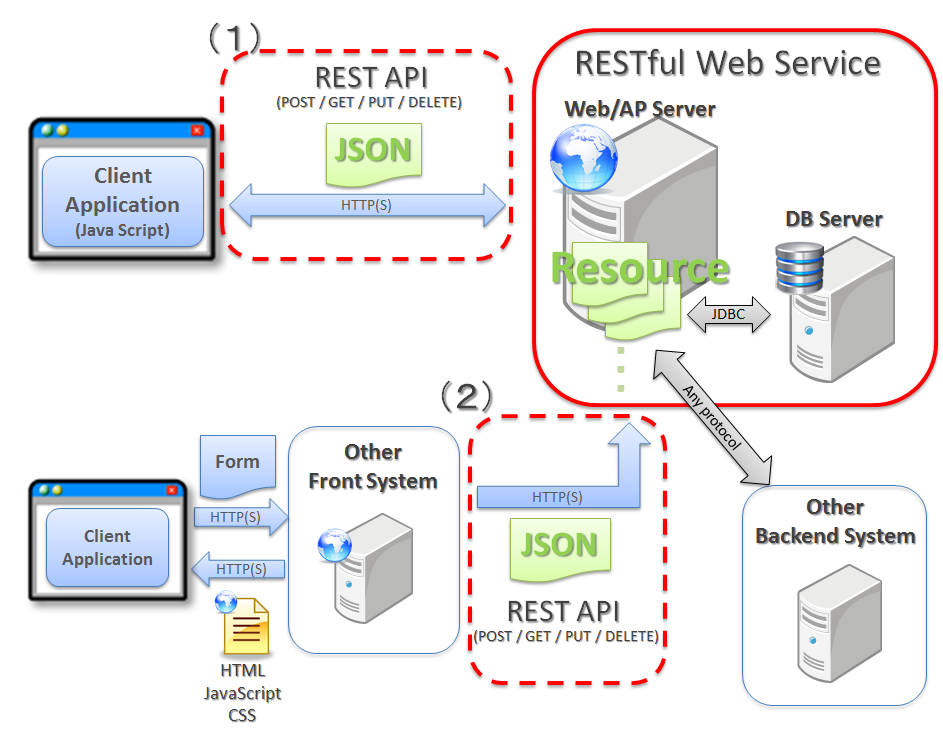
5.16.1. Overview¶
This section explains the basic concept of RESTful Web Service and its development by using Spring MVC.
Refer to the following for basic description of architecture, design and implementation of RESTful Web Service
- Basic architecture of RESTful Web Service is explained.
- Points to be considered while designing a RESTful Web Service are explained.
- Application structure of RESTful Web Service and API implementation methods are explained.
5.16.1.1. What is RESTful Web Service¶
Sr. No. Description
5.16.1.2. RESTful Web Service development¶
RESTful Web Service is developed in TERASOLUNA Server Framework for Java (5.x) using Spring MVC functionalities.
Sr. No. Function overview Note
Exception handling
It is necessary to implement exception handling for each project since a generic functionality for the same is not provided by Spring MVC. For details on exception handling, refer to “Implementing exception handling”.
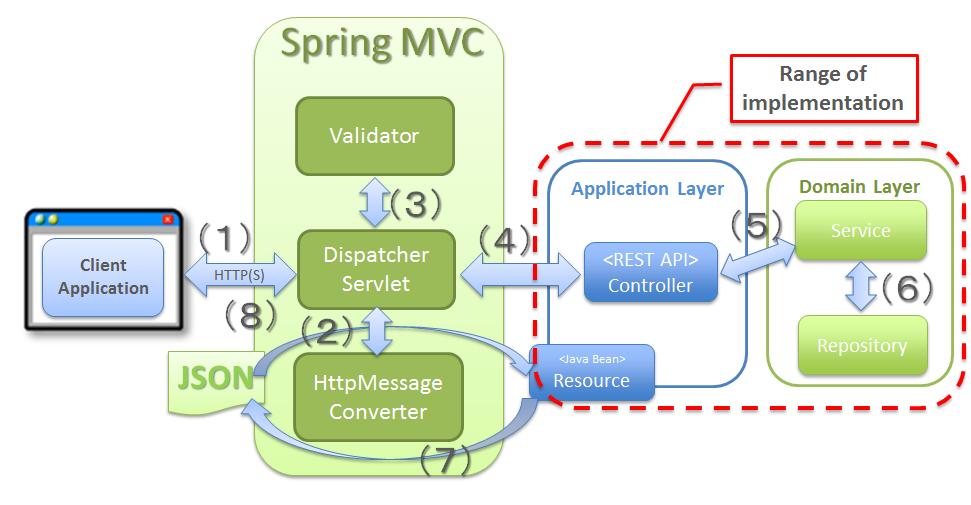
Sr. No. Process layer Description HttpMessageConverter.Validator.HttpMessageConverter.
5.16.1.2.1. Configuration for RESTful Web Service module¶
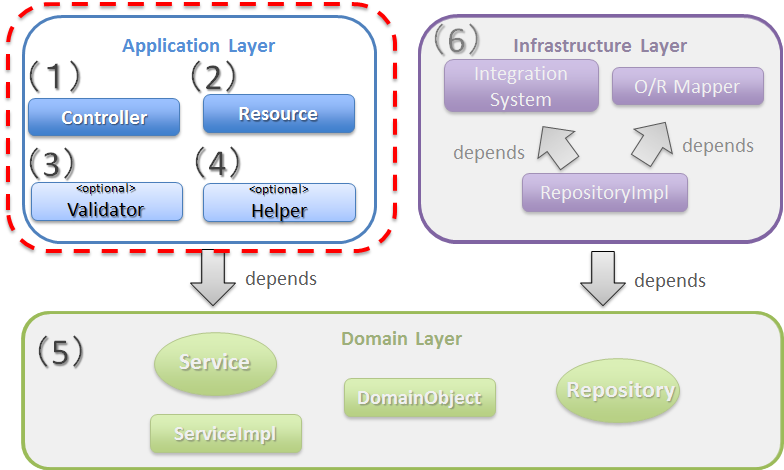
Module for application layer
Sr. No. Module name Description (1)Controller classA class that provides REST API.Controller class is created by resource unit and specifies end points (URI) of REST API for each resource.CRUD process for the resource is implemented by delegating it to the Service of domain layer.(2)Resource classJava Bean representing JSON (or XML) that acts as I/O for REST API.Annotation for Bean Validation and annotation for controlling JSON or XML format are specified in this class.(3)Validator Class(Optional)Class that implements correlation validation for input value.If the correlation validation for input value is unnecessary, this class need not be created. Hence, it is considered as optional.For input value correlation validation, refer to “Input Validation”.(4)Helper Class(Optional)Class which implements the process that assists the process to be performed by the Controller.This class is created with the aim of simplifying the Controller processing.Basically, it implements a method that performs conversion of Resource object and DomainObject models.If the model can be converted simply by using copy of the value, “Bean Mapping (Dozer)” may be used without creating the Helper class. Hence, it is considered as optional.
Domain layer module
Sr. No. Description (5)The description is beyond the scope of this section since the module implemented in the domain layer is independent of application type.For role of each module, refer to “Application Layering” and for domain layer development, refer to “Domain Layer Implementation”.
Infrastructure layer module
Sr. No Description (6)The description is beyond the scope of this section since the module implemented in the infrastructure layer is independent of application type.Refer to “Application Layering” for role of each module and “Implementation of Infrastructure Layer” for development of infrastructure layer.
5.16.1.2.2. REST API implementation sample¶
Note
It is strongly recommended to practice **:doc:`../TutorialREST/index`** first, before reading the detailed explanation.
Aim of the tutorial is to emphasize the saying “Practice makes one perfect”. Prior to detailed explanation, the user can gain the experience of actually practicing RESTful Web Service development using TERASOLUNA Server Framework for Java (5.x), with the help of this tutorial. When this firsthand experience of RESTful Web Service development is followed by reading the detailed explanation, the user gains a deeper understanding of the development.
Especially when the user does not have any experience of RESTful Web Service development, it is recommended to follow a process in the order namely, “Tutorial practice” –> “Detailed explanation of architecture, design and development (described in subsequent sections) –> “Tutorial revision (Re-practice)”.
- Resources handled in implementation sample
Resources handled in the implementation sample (Todo resources) are set in following JSON format.
{ "todoId" : "9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558", "todoTitle" : "Hello World!", "finished" : false, "createdAt" : "2014-02-25T02:21:48.493+0000" }
- Resource class implementation sample
Resource class is created as the JavaBean representing the Todo resources shown above.
package todo.api.todo; import java.util.Date; import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; import javax.validation.constraints.Size; public class TodoResource { private String todoId; @NotNull @Size(min = 1, max = 30) private String todoTitle; private boolean finished; private Date createdAt; public String getTodoId() { return todoId; } public void setTodoId(String todoId) { this.todoId = todoId; } public String getTodoTitle() { return todoTitle; } public void setTodoTitle(String todoTitle) { this.todoTitle = todoTitle; } public boolean isFinished() { return finished; } public void setFinished(boolean finished) { this.finished = finished; } public Date getCreatedAt() { return createdAt; } public void setCreatedAt(Date createdAt) { this.createdAt = createdAt; } }
- Implementation sample for Controller class (REST API)
Following five REST APIs (Controller processing methods) are created for Todo resource.
/api/v1/todos/api/v1/todos/api/v1/todos/{todoId}/api/v1/todos/{todoId}/api/v1/todos/{todoId}
5.16.2. Architecture¶
Following five architectural elements must be applied regardless of the application characteristics.
Sr. No. Architecture Architecture overview
Following two architectural elements are applied depending on the characteristics of an application.
Sr. No. Architecture Architectural elements
5.16.2.1. Publishing as a resource on Web¶
For example, following information is published on the Web as resource, for a Web system providing shopping site.
- Product information
- Stock information
- Order information
- Member information
- Authentication information for each member (Login ID and password etc.)
- Order history information for each member
- Authentication history information for each member
- and more …
5.16.2.2. Identifying the resource using URI¶
- http://example.com/api/v1/items“items” portion is the “noun that represents the type of resource”. If there are multiple resources, a plural noun is used.In the above example, a plural noun is specified to indicate the product information. It forms the URI for batch operation of product information. If replaced to a file system, it corresponds to a directory.
- http://example.com/api/v1/items/I312-535-01216The part “I312-535-01216” in the above URI, represents “the value that identifies the resource” and varies for each resource.In the above example, product ID is specified as the value for uniquely identifying product information. It acts as the URI used to handle specific product information. If replaced by a file system, it corresponds to the files stored in a directory.
Warning
Verbs that indicate operations cannot be included in the URI assigned to RESTful Web Service are as shown below.
- http://example.com/api/v1/items?get&itemId=I312-535-01216
- http://example.com/api/v1/items?delete&itemId=I312-535-01216
URI mentioned in the above example is not suitable to be assigned to RESTful Web Service since it includes verbs like get or delete.
In RESTful Web Service, Resource related operations are represented by using HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT and DELETE).
5.16.2.3. Resource operations using HTTP methods¶
The association of resource operations assigned to HTTP methods and the post-conditions ensured by each operation, are explained below.
Sr. No. HTTP method Resource operations Post-conditions that the operation should ensure Note
Ensuring safety and idempotency
When resource operation is performed using HTTP method, it is necessary to ensure “safety” and “idempotency” as post conditions.
[Safety]
It ensures that even if a particular value is multiplied several times by 1, the value does not change. (for example, if 10 is multiplied several times by 1, result remains 10). This guarantees that even if an operation is carried out for several times, resource status does not change.[Idempotency]
It ensures that even if a value is multiplied a number of times by 0, the value remains 0 (for example, if 10 is multiplied a number of times or just once by 0, the result remains 0). This signifies that once an operation is performed, resource status does not change even if the same operation is performed later for a number of times. However, when another client is modifying the status of the same resource, idempotency need not be ensured and can be handled as a precondition error.Tip
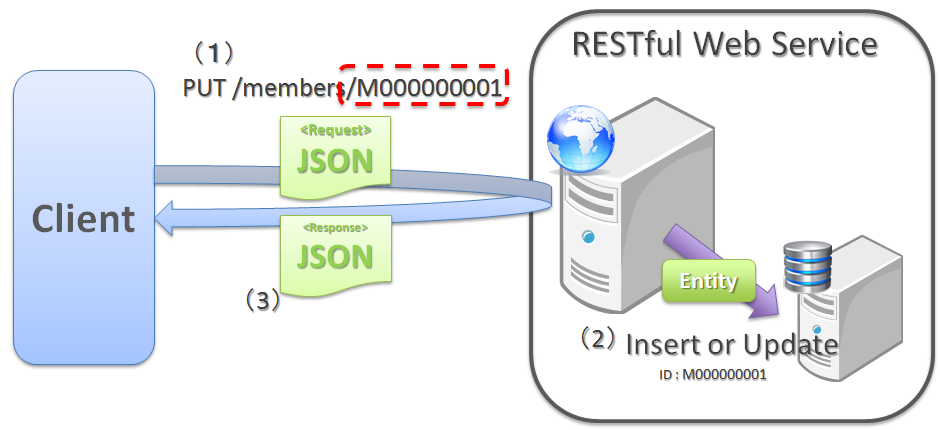
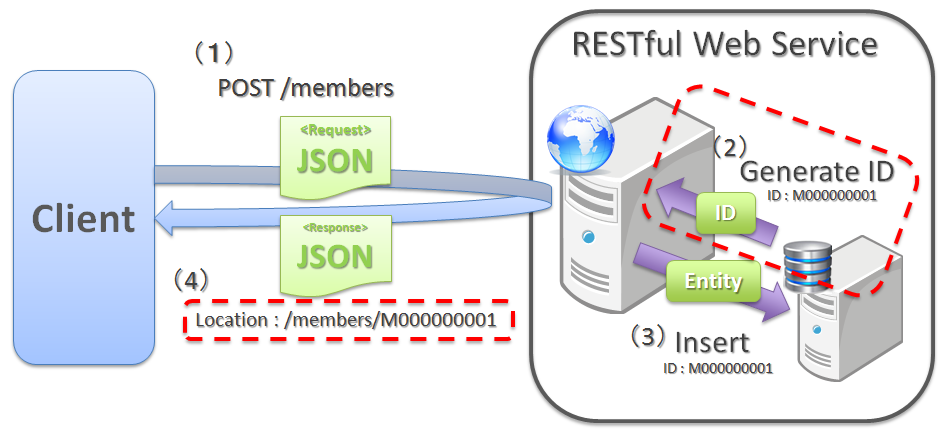
When client specifies the URI assigned to a resource for creating a resource
To create a resource, when the URI to be assigned to the resource is specified by client, PUT method is called for the URI assigned to the resource to be created.
When creating a resource using PUT method, the general operation is to,
- Create a resource when no resource exists in the specified URI
- Modify resource status when a resource already exists
Following is the difference in process images while creating a resource using PUT and POST methods.
[Process image while creating a resource using PUT method]
[Process image while creating a resource using POST method]
5.16.2.4. Using an appropriate format¶
JSON or XML that indicate data structure, are used for resource format.
Changing the format using an extension.
Response format can be changed by specifying the extension.This guideline recommends changing the format using extension.The reasons for recommending this format are, responding format can be easily specified and as the responding format is included in URI, it results in an intuitive URI.
Note
Examples of URI where format is changed using extension
- http://example.com/api/v1/items.json
- http://example.com/api/v1/items.xml
- http://example.com/api/v1/items/I312-535-01216.json
- http://example.com/api/v1/items/I312-535-01216.xml
Changing format by using the MIME type in Accept header of request.
A typical MIME type used in RESTful Web Service is shown below.
Sr. No. Format MIME type (1)JSONapplication/json(2)XMLapplication/xml
5.16.2.5. Using the appropriate HTTP status code¶
Appropriate HTTP status code is set in the response to be returned to the client.
Tip
HTTP Specifications
Refer to RFC 2616 (Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.1) - 6.1.1 Status Code and Reason Phrase.
"200 OK" was returned as the response and process results were displayed in entity body (HTML),
Sr. No. Potential issues
5.16.2.6. Stateless communication between client and server¶
Note
Application status
Web page transition status, selection status for input value, pull down/checkbox/radio buttons and authentication status etc. are included in application status.
Note
Relation with CSRF measures
Please note that the “Stateless” state between client and server cannot be retained when the CSRF measures described in this guideline are implemented for RESTful Web Service as, the token values for CRSF measures are stored in HTTP sessions.
As a result, system availability must be considered while implementing CSRF measures.
Following measures need to be implemented for a system that requires high availability.
- Perform AP server clustering and session replication.
- Use a destination other than AP server memory for storing a session.
However, above measures may affect the performance. Hence, it is necessary to consider performance requirements as well.
For CSRF measures, refer to CSRF Countermeasures.
Todo
TBD
When high availability is required, it is advisable to review an architecture wherein, “token values for CSRF measures are stored in a destination other than the AP server memory (HTTP session)”.
Basic architecture is currently under review and will be documented in subsequent versions.
5.16.3. How to design¶
This section explains the design of RESTful Web Service.
5.16.3.1. Resource extraction¶
First, the resource published on the Web is extracted.
Precautions while extracting a resource are as given below.
Sr. No. Precautions while extracting a resource
5.16.3.2. Assigning URI¶
URI is assigned to the extracted resource for identifying it.
It is recommended to use following formats for the URI.
http(s)://{Domain name (:Port number)}/{A value indicating REST API}/{API version}/{path for identifying a resource}http(s)://{Domain name indicating REST API(:Port number)}/{API version}/{path for identifying a resource}
A typical example is given below.
http://example.com/api/v1/members/M000000001http://api.example.com/v1/members/M000000001
5.16.3.2.1. Assigning a URI that indicates the API as REST API¶
It is recommended to include api within the URI domain or path, to clearly indicate that the URI is intended for RESTful Web Service (REST API).
Typically, the URI is as given below.
http://example.com/api/...http://api.example.com/...
5.16.3.2.2. Assigning a URI for identifying the API version¶
It is recommended to include a value that identifies the API version, in the URI to be published to the client, since it may be necessary to run RESTful Web Service in multiple versions.
Typically, the URI format is as follows.
http://example.com/api/{API version}/{path for identifying a resource}http://api.example.com/{API version}/{path for identifying a resource}
Todo
TBD
Whether API version should be included in URI, is currently being investigated.
5.16.3.2.3. Assigning a path for identifying resource¶
Sr. No. URI format Typical example of URI Description
Sr. No. URI format Typical example of URI Description
Sr. No. URI format Typical example of URI Description
5.16.3.3. Assigning HTTP methods¶
CRUD operation for resources is published as REST API by assigning the following HTTP methods for the URI assigned to each resource.
Note
HEAD and OPTIONS method
Hereafter, HEAD and OPTIONS methods are described as well. However, providing them for REST API is optional.
While creating the REST API conforming to HTTP specifications, it is necessary to provide the HEAD and OPTIONS methods as well. However, it is actually used very rarely and is not required in most of the cases.
5.16.3.3.1. Assigning HTTP methods for resource collection URI¶
Sr. No. HTTP methods Overview of the REST API to be implemented
5.16.3.3.2. Assigning HTTP methods for URI of specific resources¶
Sr. No. HTTP methods Overview of REST API to be implemented
5.16.3.4. Resource format¶
5.16.3.4.1. JSON Field name¶
{ "memberId" : "M000000001" }
5.16.3.4.2. NULL and blank characters¶
{ "dateOfBirth" : null, "address1" : "" }
5.16.3.4.3. Date format¶
Basically, there are following three formats.
- yyyy-MM-dd
{ "dateOfBirth" : "1977-03-12" }
- yyyy-MM-dd’T’HH:mm:ss.SSSZ
{ "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-12T22:22:36.637+09:00" }
- yyyy-MM-dd’T’HH:mm:ss.SSS’Z’ (format for UTC)
{ "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-12T13:11:27.356Z" }
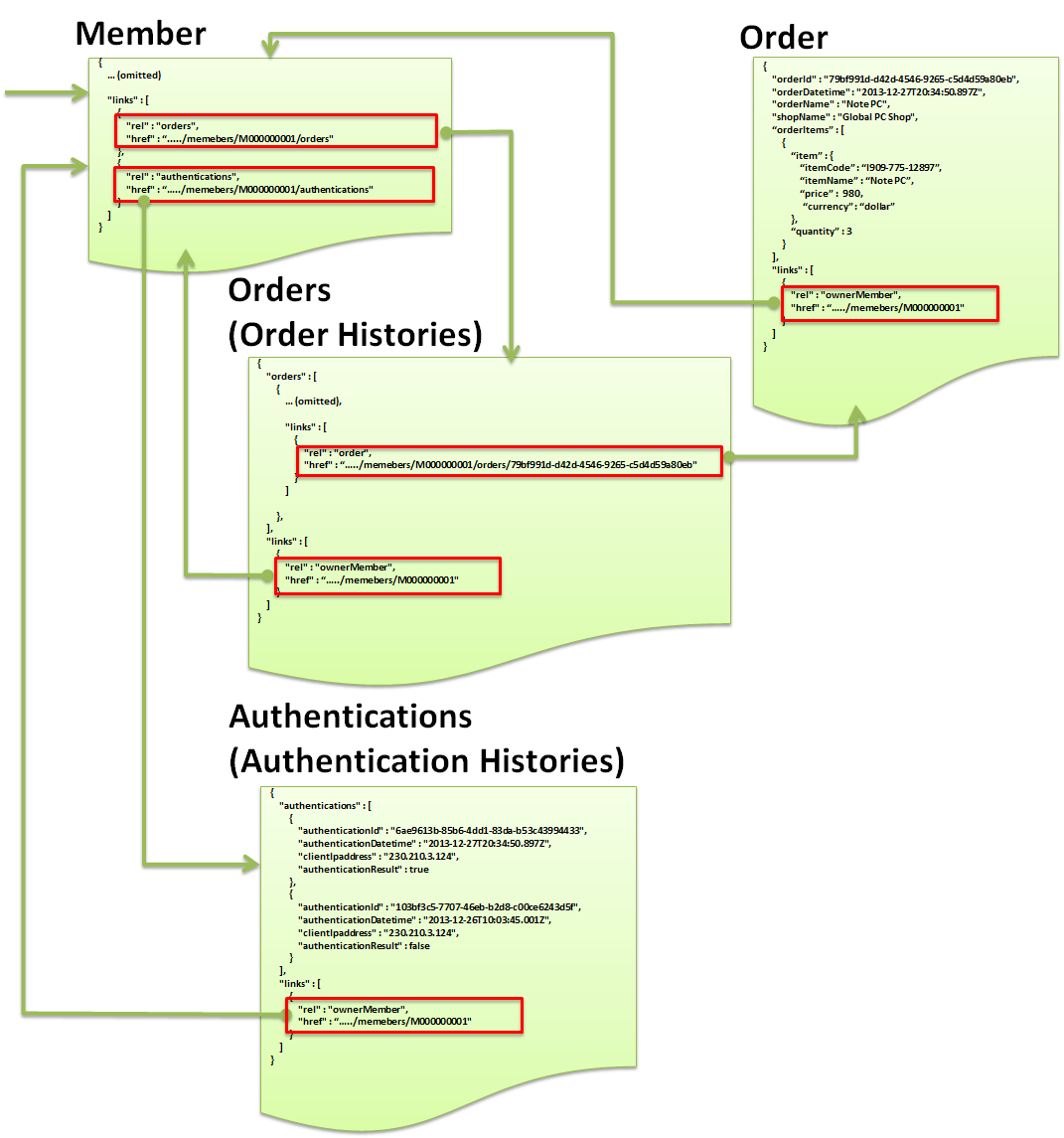
5.16.3.4.4. Hypermedia link format¶
{ "links" : [ { "rel" : "ownerMember", "href" : "http://example.com/api/v1/memebers/M000000001" } ] }
- Link object consisting of 2 fields -
"rel"and"href"is retained in collection format.- Link name for identifying the link is specified in
"rel".- URI to access the resource is specified in
"href"."links"is the field which retains the Link object in collection format.
5.16.3.4.5. Format at the time of error response¶
Following is an example of the response format when error is detected.
{ "code" : "e.ex.fw.7001", "message" : "Validation error occurred on item in the request body.", "details" : [ { "code" : "ExistInCodeList", "message" : "\"genderCode\" must exist in code list of CL_GENDER.", "target" : "genderCode" } ] }
In the above example,
- Error code (code)
- Error message (message)
- Error details list (details)
5.16.3.5. HTTP Status Code¶
HTTP status code is sent as the response, in accordance with the following guidelines.
Sr. No. Objectives
5.16.3.5.1. HTTP status codes when the request is successful¶
When the request is successful, following HTTP status codes are sent as responses, depending on status.
Tip
The difference between
"200 OKand"204 No Content"is whether the resource information is output/not output in the response body.
5.16.3.5.2. HTTP status code when the cause of request failure lies at client side¶
When the cause of request failure lies at client side, following HTTP status codes are sent as responses depending on the status.
Status codes that must be identified by individual REST APIs handling the resources, are as given below.
5.16.3.5.3. HTTP status code when the cause of request failure lies at server side¶
When the cause of request failure lies at server side, HTTP status codes given below are sent as responses, depending on the status.
5.16.3.6. Authentication and Authorization¶
Todo
TBD
The guidelines for authentication and authorization control are explained here.
Performing authentication and authorization using OAuth2 protocol will be described in subsequent versions.
5.16.3.7. Conditional update control of resource¶
Todo
TBD
The process for conditional update (exclusive control) of a resource using HTTP header is explained here.
Conditional update using headers like Etag/Last-Modified-Since etc. will be described in subsequent versions.
5.16.3.8. Conditional acquisition control of resource¶
Todo
TBD
The process for conditional acquisition (304 not modified control) of resource using HTTP header is explained here.
Conditional acquisition using headers like Etag/Last-Modified etc. will be described in subsequent versions.
5.16.3.9. Cache control of resource¶
Todo
TBD
Cache control of resources which use HTTP header, is explained here.
Cache control of resources that use headers such as Cache-Control/Pragma/Expires etc. shall be described in subsequent versions.
5.16.3.10. Versioning¶
Todo
TBD
Version control of RESTful Web Service and details on performing parallel operations in multiple versions, will be described in subsequent versions.
5.16.4. How to use¶
This section explains the basic method to create RESTful Web Service.
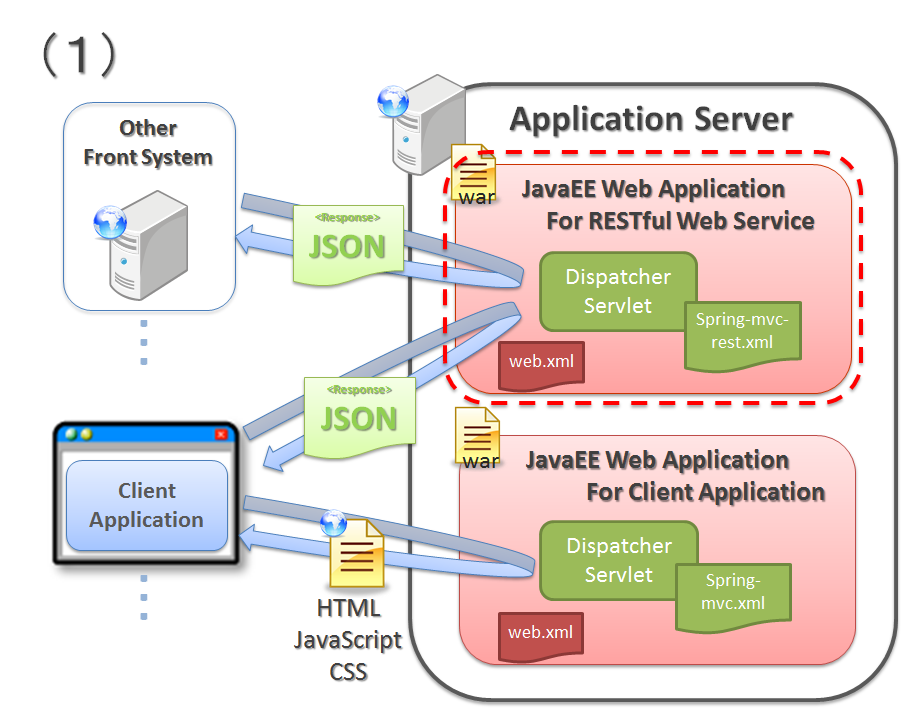
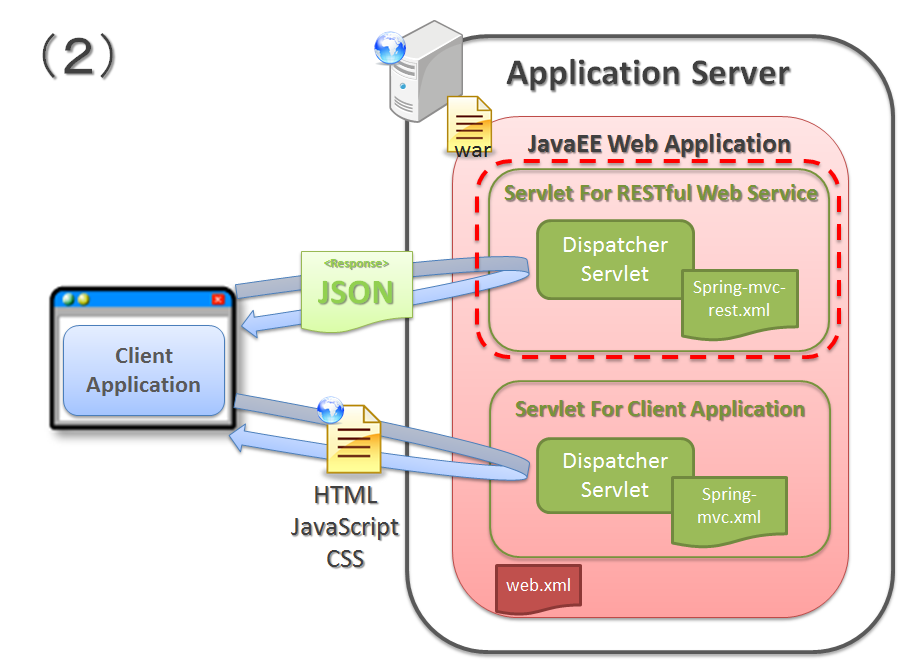
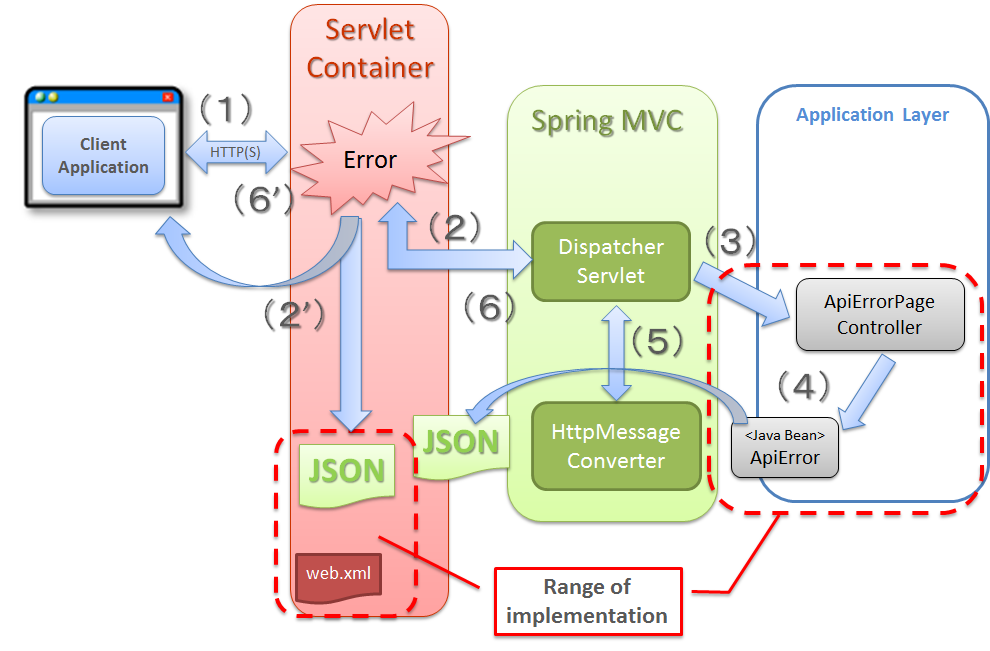
5.16.4.1. Web application configuration¶
Sr. No. Configuration Description DispatcherServletfor RESTful Web Service.DispatcherServletthat receives the requests for RESTful Web Service andDispatcherServletthat receives client application requests.Note
Client application (UI layer application)
Client application (UI layer application) described here refers to the application that responds with client layer (UI layer) component called CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) and scripts like HTML, JavaScript etc. HTML generated by template engine such as JSP, is also considered.
Note
Why division of DispatcherServlet is recommended
In Spring MVC, operation settings of the application are defined for each
DispatcherServlet. Therefore, when the requests of RESTful Web Service and client application (UI layer application) are configured to be received from the sameDispatcherServlet, specific operation settings for RESTful Web Service or client application cannot be defined, thus resulting in complex or cumbersome settings.In this guideline, when RESTful Web Service and client application are to be configured as same Web application, it is recommended to divide
DispatcherServletto avoid occurrence of the issues described above.
Configuration image when building a Web application exclusive to RESTful Web Service, is as follows:
Configuration image when building RESTful Web Service and client application as a single application, is as follows:
5.16.4.2. Application settings¶
Application settings for RESTful Web Service are explained below.
5.16.4.2.1. Settings for activating the Spring MVC components necessary for RESTful Web Service¶
spring-mvc-rest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd "> <!-- Load properties files for placeholder. --> <!-- (1) --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:/META-INF/spring/*.properties" /> <bean id="jsonMessageConverter" class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter"> <property name="objectMapper"> <bean id="objectMapper" class="com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper"> <!-- (2) --> <property name="dateFormat"> <bean class="com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.util.StdDateFormat" /> </property> </bean> </property> </bean> <!-- Register components of Spring MVC. --> <!-- (3) --> <mvc:annotation-driven> <mvc:message-converters register-defaults="false"> <ref bean="jsonMessageConverter" /> </mvc:message-converters> <!-- (4) --> <mvc:argument-resolvers> <bean class="org.springframework.data.web.PageableHandlerMethodArgumentResolver" /> </mvc:argument-resolvers> </mvc:annotation-driven> <!-- Register components of interceptor. --> <!-- (5) --> <mvc:interceptors> <mvc:interceptor> <mvc:mapping path="/**" /> <bean class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.logging.TraceLoggingInterceptor" /> </mvc:interceptor> <!-- omitted --> </mvc:interceptors> <!-- Scan & register components of RESTful Web Service. --> <!-- (6) --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.example.project.api" /> <!-- Register components of AOP. --> <!-- (7) --> <bean id="handlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor"> <property name="exceptionLogger" ref="exceptionLogger" /> </bean> <aop:config> <aop:advisor advice-ref="handlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor" pointcut="execution(* org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver.resolveException(..))" /> </aop:config> </beans>
Sr. No. Description <context:property-placeholder>element.For the details of fetching a value from property file, refer to “Properties Management”.<mvc:message-converters> element is set asfalse.To use XML as resource format,MessageConverterfor XML, that performs the XXE Injection countermeasure, should be specified. For details on designated methods, refer to “Enabling XXE Injection measures” .TraceLoggingInterceptorprovided by common library is defined. However, when using JPA as data access,OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptorsetting needs to be added separately.Refer to Database Access (JPA) forOpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor."com.example.project.api"part is the package name for each project.HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor.
Note
Points to be noted when changing the jackson version from 1.x.x to 2.x.x
- Changed package
version package
- Please note that configuration of subordinate package also is also changed.
- Deprecated List
5.16.4.2.2. Servlet settings for RESTful Web Service¶
web.xml
<!-- omitted --> <servlet> <!-- (1) --> <servlet-name>restAppServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <!-- (2) --> <param-value>classpath*:META-INF/spring/spring-mvc-rest.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <!-- (3) --> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>restAppServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/api/v1/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <!-- omitted -->
Sr. No. Description <servlet-name>element.In the above example,"restAppServlet"is specified as the servlet name.DispatcherServletfor RESTful Web Service.In the above example,META-INF/spring/spring-mvc-rest.xmlin class path, is specified as the Spring MVC bean definition file.DispatcherServletof RESTful Web Service.In the above example, the servlet path under"/api/v1/"is mapped with theDispatcherServletfor RESTful Web Service.Typically, servlet paths like"/api/v1/""/api/v1/members""/api/v1/members/xxxxx"are mapped in theDispatcherServlet("restAppServlet") for RESTful Web Service.Tip
Value specified in the value attribute of @RequestMapping annotation
For the value to be specified in value attribute of
@RequestMappingannotation, specify the value assigned to the part of wild card (*) in<url-pattern>element.For example, when
@RequestMapping(value = "members")is specified, it is deployed as the method to perform a process for path"/api/v1/members". Therefore, it is not necessary to specify the path ("api/v1") in value attribute of@RequestMappingannotation for mapping to divided servlets.When
@RequestMapping(value = "api/v1/members")is specified, it gets deployed as the method that performs a process for the"/api/v1/api/v1/members"path. Hence, please take note of same.
5.16.4.3. REST API implementation¶
Note
Domain layer implementation is not explained in this section, however, it is sent as attachment “Source code of the domain layer class created at the time of REST API implementation”.
Please refer if required.
REST API specifications used in this explanation are as shown below.
Resource format
The resource format of member information should be the following JSON format.In the following example, although all the fields are displayed, they are not used in the requests and responses of all API.For example,"password"is used only in requests whereas"createdAt"or"lastModifiedAt"are used only in responses.{ "memberId" : "M000000001", "firstName" : "Firstname", "lastName" : "Lastname", "genderCode" : "1", "dateOfBirth" : "1977-03-13", "emailAddress" : "user1@test.com", "telephoneNumber" : "09012345678", "zipCode" : "1710051", "address" : "Tokyo", "credential" : { "signId" : "user1@test.com", "password" : "zaq12wsx", "passwordLastChangedAt" : "2014-03-13T04:39:14.831Z", "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-13T04:39:14.831Z" }, "createdAt" : "2014-03-13T04:39:14.831Z", "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-13T04:39:14.831Z" }Note
This section illustrates an example wherein a hypermedia link for related resource is not provided. For details on implementation with hypermedia link, refer to “Implementing hypermedia link”.
Specifications of resource fields
The specifications for each field of a resource (JSON) are as shown below.
Sr. No. Item name Type I/O specifications Number of digits (min-max) Other specifications memberId String I/O 10-10 It should be “Unspecified” (NULL) at the time of request for POST Members. firstName String I/O 1-128 - lastName String I/O 1-128 - genderCode I/O 1-1 "0": UNKNOWN"1": MEN"2": WOMENdateOfBirth Date I/O - emailAddress I/O 1-256 - telephoneNumber String I/O 0-20 - zipCode String I/O 0-20 - address String I/O 0-256 - credential I/O - It is specified at the time of request for POST Members. credential/signId I/O 0-256 emailAddress value is applied when not specified. String I 8-32 - O - O - createdAt O - lastModifiedAt O -
REST APIs List
APIs given below are used as the REST API to be implemented.
GET Members GET /api/v1/membersPOST Members POST /api/v1/membersOne Member resource is created. GET Member GET /api/v1/members/{memberId}One Member resource is fetched. PUT Member PUT /api/v1/members/{memberId}One Member resource is updated. DELETE Member DELETE /api/v1/members/{memberId}One Member resource is deleted. Note
This section focuses on the details of CRUD operation for a resource. Hence, HEAD and OPTIONS methods are not explained. To create the RESTful Web Service conforming to HTTP specifications, refer to “Creating RESTful Web Service conforming to HTTP specifications”.
5.16.4.3.1. Creating REST API packages¶
Create a package to store REST API class.
api as the package name for the route package that stores REST API class and to create a package for each resource (lower case of resource name) under the same.Member. Hence, the package name is org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.member.Note
Usually, following 4 types of classes are stored in the created package. It is recommended to use the following naming rules for name of the class to be created.
[Resource name]Resource[Resource name]RestController[Resource name]Validator(created when required)[Resource name]Helper(created when required)In the explanation, name of the resource is
Member. As a result, the respective names will be as below.
MemberResourceMemberRestControllerMemberValidatorMemberHelperWhen handling a related resource, it is advisable to place the class for related resource also in the same package.
common that stores common parts for REST API just under the route package that stores the REST API class and to create sub packages at functionality level.error.org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.common.error.Note
As long as it is clear that the package is storing common parts, it can have a name other than
common.
5.16.4.3.2. Creating Resource class¶
Note
Reasons for creating a Resource class
The reason for creating a Resource class regardless of DomainObject class (for example, Entity class) being available is, user interface information (UI) which is used in the I/O with client and information handled by business process do not necessarily match.
If these are mixed and then used, the application layer may affect the domain layer, resulting in deteriorated maintainability. It is recommended to create the DomainObject and Resource class separately and convert data by using BeanMapper like Dozer etc.
Role of Resource class is as follows:
Sr. No. Roles Description Warning
Measures to circular reference
When you serialize a Resource class (JavaBean) in JSON or XML format and if property holds an object of cross reference relationship, the
StackOverflowErrorandOutOfMemoryErroroccur due to circular reference, hence it is necessary to exercise caution.In order to avoid a circular reference,
@com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreannotation to exclude the property from serialization in case of serialized in JSON format using the Jackson@javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlTransientannotation to exclude the property from serialization in case of serialized in XML format using the JAXBcan be added.
An example to exclude specific field from serialization while serializing in JSON format using Jackson is given below.
public class Order { private String orderId; private List<OrderLine> orderLines; // ... }public class OrderLine { @JsonIgnore private Order order; private String itemCode; private int quantity; // ... }
Sr. No. Description Add @JsonIgnoreannotation to exclude the property from serialization.
Example of Resource class creation is shown below.
MemberResource.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.member; import java.io.Serializable; import javax.validation.Valid; import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; import javax.validation.constraints.Null; import javax.validation.constraints.Past; import javax.validation.constraints.Size; import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email; import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotEmpty; import org.joda.time.DateTime; import org.joda.time.LocalDate; import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.codelist.ExistInCodeList; // (1) public class MemberResource implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; // (2) interface PostMembers { } interface PutMember { } @Null(groups = PostMembers.class) @NotEmpty(groups = PutMember.class) @Size(min = 10, max = 10, groups = PutMember.class) private String memberId; @NotEmpty @Size(max = 128) private String firstName; @NotEmpty @Size(max = 128) private String lastName; @NotEmpty @ExistInCodeList(codeListId = "CL_GENDER") private String genderCode; @NotNull @Past private LocalDate dateOfBirth; @NotEmpty @Size(max = 256) @Email private String emailAddress; @Size(max = 20) private String telephoneNumber; @Size(max = 20) private String zipCode; @Size(max = 256) private String address; @NotNull(groups = PostMembers.class) @Null(groups = PutMember.class) @Valid // (3) private MemberCredentialResource credential; @Null private DateTime createdAt; @Null private DateTime lastModifiedAt; // omitted setter and getter }
Sr. No. Description
MemberCredentialResource.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.member; import java.io.Serializable; import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; import javax.validation.constraints.Null; import javax.validation.constraints.Size; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude; import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email; import org.joda.time.DateTime; // (4) public class MemberCredentialResource implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Size(max = 256) @Email private String signId; // (5) @JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL) @NotNull @Size(min = 8, max = 32) private String password; @Null private DateTime passwordLastChangedAt; @Null private DateTime lastModifiedAt; // omitted setter and getter }
Sr. No. Description null.It is specified so that the field ‘password’ is not output in responding JSON.In the above example, it is restricted to (Inclusion.NON_NULL) for NULL value, however it can also be specified as (Inclusion.NON_EMPTY) in case of an empty value.
- Adding the mapping definition of BeanIn the subsequent implementations, Entity class and Resource class are copied by using “Bean Mapping (Dozer)” .Joda-Time classes namely,
org.joda.time.DateTimeandorg.joda.time.LocalDateare included in the JavaBean shown above. However, Joda-Time objects are not correctly copied if “Bean Mapping (Dozer)” is used for copying.Therefore, it is necessary to apply “How to copy Joda-Time classes using Dozer” to copy the objects correctly.
5.16.4.3.3. Creating Controller class¶
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.member; // omitted import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; // omitted @RequestMapping("members") // (1) @RestController // (2) public class MemberRestController { // omitted ... }
Sr. No. Description @RequestMappingannotation.In the above example, a servlet path called/api/v1/membersis mapped.Assign
@RestControllerannotation for Controller.Assigning
@RestControllerannotation has same meaning of:
- Assigning
org.springframework.stereotype.Controllerannotation in a class- Assigning
@org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBodyannotation in Controller method which is described later.By assigning
@ResponseBodyto Controller method, the returned Resource object is marshalled in JSON or XML and set in response body.Tip
@RestControlleris an annotation added from Spring Framework 4.0.Due to
@RestControllerannotation, it is not necessary to assign@ResponseBodyannotation to each method of Controller. Hence, it is possible to create Controller for REST API in a simple way. For details about@RestControllerannotation refer to: Here.An example to create a Controller for REST API by combining
@Controllerannotation and@ResponseBodyannotation in a conventional way is given below.@RequestMapping("members") @Controller public class MemberRestController { @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) @ResponseBody public Page<MemberResource> getMembers() { // ... } // ... }
5.16.4.3.4. Implementing REST API that fetches collection of resources¶
Example to implement the REST API wherein a page search is performed for member resource collection specified by URI.
- Creating the JavaBean for receiving search conditionsWhen search conditions are necessary to fetch resource collection, create a JavaBean for receiving the search conditions.
// (1) public class MembersSearchQuery implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; // (2) @NotEmpty private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
Sr. No. Description "John"is set in the name property of JavaBean for request/api/v1/members?name=John.
- REST API implementationImplement a process wherein page search is performed for a collection of Member resources.
@RequestMapping("members") @RestController public class MemberRestController { // omitted @Inject MemberService memberService; @Inject Mapper beanMapper; // (3) @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET) // (4) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) public Page<MemberResource> getMembers( // (5) @Validated MembersSearchQuery query, // (6) Pageable pageable) { // (7) Page<Member> page = memberService.searchMembers(query.getName(), pageable); // (8) List<MemberResource> memberResources = new ArrayList<>(); for (Member member : page.getContent()) { memberResources.add(beanMapper.map(member, MemberResource.class)); } Page<MemberResource> responseResource = new PageImpl<>(memberResources, pageable, page.getTotalElements()); // (9) return responseResource; } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description RequestMethod.GETin method attribute of@RequestMappingannotation.@org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatusas method annotation and specify the status code returned as response.Set 200 (OK) in the value attribute of@ResponseStatusannotation.Tip
How to specify the status code
A fixed status code sent as response is specified in this example using
@ResponseStatusannotation. However, it can also be specified in Controller logic.public ResponseEntity<Page<MemberResource>> getMembers( @Validated MembersSearchQuery query, Pageable pageable) { // omitted return ResponseEntity.ok().body(responseResource); }When it is necessary to change the responding status codes based on process details or process results,
org.springframework.http.ResponseEntityis used, as shown in the above implementation.@Validatedas argument annotation. For input validation details, refer to “Input Validation”.org.springframework.data.domain.Pageableas an argument.For page search details, refer to “Pagination”.org.springframework.data.domain.PageImplclass while sending page search result as response, the fields that are necessary as response at the time of page search, can be sent to the client.In the above example, a Resource object is being generated from Entity by using Bean mapping library. For details on Bean mapping library, refer to “Bean Mapping (Dozer)” .When the quantity of code for generating Resource objects is more, it is recommended to create a method for generating Resource object in Helper class.PageImplclass is as below.Highlighted portion shows the fields specific for page search.{ "content" : [ { "memberId" : "M000000001", "firstName" : "John", "lastName" : "Smith", "genderCode" : "1", "dateOfBirth" : "1977-03-07", "emailAddress" : "john.smith@test.com", "telephoneNumber" : "09012345678", "zipCode" : "1710051", "address" : "Tokyo", "credential" : { "signId" : "john.smit@test.com", "passwordLastChangedAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z", "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z" }, "createdAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z", "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z" }, { "memberId" : "M000000002", "firstName" : "Sophia", "lastName" : "Smith", "genderCode" : "2", "dateOfBirth" : "1977-03-07", "emailAddress" : "sophia.smith@test.com", "telephoneNumber" : "09012345678", "zipCode" : "1710051", "address" : "Tokyo", "credential" : { "signId" : "sophia.smith@test.com", "passwordLastChangedAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z", "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z" }, "createdAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z", "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z" } ], "last" : false, "totalPages" : 13, "totalElements" : 25, "size" : 2, "number" : 1, "sort" : [ { "direction" : "DESC", "property" : "lastModifiedAt", "ignoreCase" : false, "nullHandling": "NATIVE", "ascending" : false } ], "numberOfElements" : 2, "first" : false }Note
Points to be noted due to changes in API specifications of Spring Data Commons
In case of “terasoluna-gfw-common 5.0.0.RELEASE or later version” dependent spring-data-commons (1.9.1 RELEASE or later), there is a change in API specifications of interface for page search functionality (
org.springframework.data.domain.Page) and class (org.springframework.data.domain.PageImplandorg.springframework.data.domain.Sort.Order).Specifically,
- In
Pageinterface andPageImplclass,isFirst()andisLast()methods are added in spring-data-commons 1.8.0.RELEASE, andisFirstPage()andisLastPage()methods are deleted from spring-data-commons 1.9.0.RELEASE.- In
Sort.Orderclass,nullHandlingproperty is added in spring-data-commons 1.8.0.RELEASE.When using
Pageinterface (PageImplclass) as resource object of REST API, that application may also need to be modified, as JSON and XML format get changed.
- Adding Bean mapping definitionIn the above implementation,
Memberobject andMemberResourceobject are copied by using “Bean Mapping (Dozer)” .It is not necessary to add Bean mapping definition when simply a copy of field value can be used. However, in the above implementation, the setting needs to be such thatcredential.passwordis not copied while copyingMemberobject details toMemberResourceobject.It is necessary to add Bean mapping definition so that specific fields are not copied.
<!-- (11) --> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <mappings xmlns="http://dozer.sourceforge.net" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://dozer.sourceforge.net http://dozer.sourceforge.net/schema/beanmapping.xsd"> <mapping type="one-way"> <class-a>org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.model.MemberCredential</class-a> <class-b>org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.member.MemberCredentialResource</class-b> <!-- (12) --> <field-exclude> <a>password</a> <b>password</b> </field-exclude> </mapping> </mappings>
Sr. No. Description Memberobject andMemberResourceobject.It is recommended to create a mapping definition file of Dozer for each resource.In this implementation, it is stored in/xxx-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/dozer/memberResource-mapping.xml.passwordfield is not copied while copying the details ofMemberCredentialwhich is a related entity ofMember, toMemberCredentialResource, a related resource ofMemberResource.For Bean mapping definition methods, refer to “Bean Mapping (Dozer)” .
- Request example
GET /rest-api-web/api/v1/members?name=Smith&page=0&size=2 HTTP/1.1 Accept: text/plain, application/json, application/*+json, */* User-Agent: Java/1.7.0_51 Host: localhost:8080 Connection: keep-alive
- Response Example
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: fb63a6d446f849feb8ccaa4c9a794333 Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked Date: Thu, 13 Mar 2014 11:10:43 GMT {"content":[{"memberId":"M000000001","firstName":"John","lastName":"Smith","genderCode":"1","dateOfBirth":"2013-03-13","emailAddress":"user1394709042120@test.com","telephoneNumber":"09012345678","zipCode":"1710051","address":"Tokyo","credential":{"signId":"user1394709042120@test.com","passwordLastChangedAt":"2014-03-13T11:10:43.066Z","lastModifiedAt":"2014-03-13T11:10:43.066Z"},"createdAt":"2014-03-13T11:10:43.066Z","lastModifiedAt":"2014-03-13T11:10:43.066Z"},{"memberId":"M000000002","firstName":"Sophia","lastName":"Smith","genderCode":"2","dateOfBirth":"2013-03-13","emailAddress":"user1394709043663@test.com","telephoneNumber":"09012345678","zipCode":"1710051","address":"Tokyo","credential":{"signId":"user1394709043663@test.com","passwordLastChangedAt":"2014-03-13T11:10:43.678Z","lastModifiedAt":"2014-03-13T11:10:43.678Z"},"createdAt":"2014-03-13T11:10:43.678Z","lastModifiedAt":"2014-03-13T11:10:43.678Z"}],"last":true,"totalPages":1,"totalElements":2,"size":2,"number":0,"sort":null,"numberOfElements":2,"first":true}
Tip
When page search is not necessary, Resource class list may be handled directly.
Following is the definition of the Controller method used when handling the list of Resource class directly.
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) public List<MemberResource> getMembers( @Validated MembersSearchQuery query) { // omitted }JSON is as follows when list of Resource class is directly handled.
[ { "memberId" : "M000000001", "firstName" : "John", "lastName" : "Smith", "genderCode" : "1", "dateOfBirth" : "1977-03-07", "emailAddress" : "john.smith@test.com", "telephoneNumber" : "09012345678", "zipCode" : "1710051", "address" : "Tokyo", "credential" : { "signId" : "john.smit@test.com", "passwordLastChangedAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z", "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z" }, "createdAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z", "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z" }, { "memberId" : "M000000002", "firstName" : "Sophia", "lastName" : "Smith", "genderCode" : "2", "dateOfBirth" : "1977-03-07", "emailAddress" : "sophia.smith@test.com", "telephoneNumber" : "09012345678", "zipCode" : "1710051", "address" : "Tokyo", "credential" : { "signId" : "sophia.smith@test.com", "passwordLastChangedAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z", "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z" }, "createdAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z", "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-13T10:18:08.003Z" } ]
5.16.4.3.5. Implementing REST API that adds a resource to collection¶
Example of implementation of REST API wherein a specified Member resource is created and added to the collection is given below.
- REST API implementationImplement a process that creates specified Member resource and adds it to the collection.
@RequestMapping("members") @RestController public class MemberRestController { // omitted // (1) @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST) // (2) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED) public MemberResource postMember( // (3) @RequestBody @Validated({ PostMembers.class, Default.class }) MemberResource requestedResource) { // (4) Member inputMember = beanMapper.map(requestedResource, Member.class); Member createdMember = memberService.createMember(inputMember); MemberResource responseResource = beanMapper.map(createdMember, MemberResource.class); return responseResource; } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description RequestMethod.POSTin the method attribute of@RequestMappingannotation.@ResponseStatusannotation as method annotation and specify responding status code.Set 201(Created) in the value attribute of@ResponseStatusannotation.@org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBodyas argument annotation.By assigning@RequestBodyannotation, JSON or XML data set in request Body is unmarshalled in Resource object.Assign@Validatedannotation as argument annotation to enable input validation. For details on input validation, refer to “Input Validation” .
- Request example
POST /rest-api-web/api/v1/members HTTP/1.1 Accept: text/plain, application/json, application/*+json, */* Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 User-Agent: Java/1.7.0_51 Host: localhost:8080 Connection: keep-alive Content-Length: 248 {"firstName":"John","lastName":"Smith","genderCode":"1","dateOfBirth":"2013-03-13","emailAddress":"user1394708306056@test.com","telephoneNumber":"09012345678","zipCode":"1710051","address":"Tokyo","credential":{"signId":null,"password":"zaq12wsx"}}
- Response example
HTTP/1.1 201 Created Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: c7e9c8a9aa4f40ff87f3acdb77baccdf Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked Date: Thu, 13 Mar 2014 10:58:26 GMT {"memberId":"M000000023","firstName":"John","lastName":"Smith","genderCode":"1","dateOfBirth":"2013-03-13","emailAddress":"user1394708306056@test.com","telephoneNumber":"09012345678","zipCode":"1710051","address":"Tokyo","credential":{"signId":"user1394708306056@test.com","passwordLastChangedAt":"2014-03-13T10:58:26.324Z","lastModifiedAt":"2014-03-13T10:58:26.324Z"},"createdAt":"2014-03-13T10:58:26.324Z","lastModifiedAt":"2014-03-13T10:58:26.324Z"}
5.16.4.3.6. Implementing REST API that fetches specified resource¶
Implementation of REST API that fetches the Member resource specified by URI, is shown below.
- REST API implementationImplement a process that fetches the Member resource specified by URI.
@RequestMapping("members") @RestController public class MemberRestController { // omitted // (1) @RequestMapping(value = "{memberId}", method = RequestMethod.GET) // (2) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) public MemberResource getMember( // (3) @PathVariable("memberId") String memberId) { // (4) Member member = memberService.getMember(memberId); MemberResource responseResource = beanMapper.map(member, MemberResource.class); return responseResource; } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description {memberId}in the example above) in value attribute whereasRequestMethod.GETin method attribute of@RequestMappingannotation.A value that uniquely identifies the resource is specified in{memberId}.@ResponseStatusannotation as method annotation and specify the responding status code.Set 200 (OK) in value attribute of@ResponseStatusannotation.{memberId}) can be received as method argument by specifying@PathVariable("memberId")as argument annotation.For details on path variable, refer to “Retrieving values from URL path”.In the above example, when URI is/api/v1/members/M12345,"M12345"is stored inmemberIdof argument.
- Request example
GET /rest-api-web/api/v1/members/M000000003 HTTP/1.1 Accept: text/plain, application/json, application/*+json, */* User-Agent: Java/1.7.0_51 Host: localhost:8080 Connection: keep-alive
- Response Example
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: 275b4e7a61f946eea47672f272315ac2 Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked Date: Thu, 13 Mar 2014 11:25:13 GMT {"memberId":"M000000003","firstName":"John","lastName":"Smith","genderCode":"1","dateOfBirth":"2013-03-13","emailAddress":"user1394709913496@test.com","telephoneNumber":"09012345678","zipCode":"1710051","address":"Tokyo","credential":{"signId":"user1394709913496@test.com","passwordLastChangedAt":"2014-03-13T11:25:13.762Z","lastModifiedAt":"2014-03-13T11:25:13.762Z"},"createdAt":"2014-03-13T11:25:13.762Z","lastModifiedAt":"2014-03-13T11:25:13.762Z"}
5.16.4.3.7. Implementing REST API that updates specified resource¶
Implementation of REST API that updates the Member resource specified in URI, is shown below.
- REST API implementationImplement a process that updates the Member resource specified in URI.
@RequestMapping("members") @RestController public class MemberRestController { // omitted // (1) @RequestMapping(value = "{memberId}", method = RequestMethod.PUT) // (2) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) public MemberResource putMember( @PathVariable("memberId") String memberId, // (3) @RequestBody @Validated({ PutMember.class, Default.class }) MemberResource requestedResource) { // (4) Member inputMember = beanMapper.map( requestedResource, Member.class); Member updatedMember = memberService.updateMember( memberId, inputMember); MemberResource responseResource = beanMapper.map(updatedMember, MemberResource.class); return responseResource; } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description {memberId}in the example above) in value attribute whereasRequestMethod.PUTin “method” attribute of@RequestMappingannotation.Value that uniquely identifies the resource is specified in{memberId}.@ResponseStatusannotation as method annotation and specify the responding status code.Set 200 (OK) in value attribute of@ResponseStatusannotation.@RequestBodyannotation as argument annotation, JSON or XML data set in request Body is unmarshalled in Resource object.Assign@Validatedannotation as argument annotation to enable input validation.For details on input validation, refer to “Input Validation” .
- Request example
PUT /rest-api-web/api/v1/members/M000000004 HTTP/1.1 Accept: text/plain, application/json, application/*+json, */* Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 User-Agent: Java/1.7.0_51 Host: localhost:8080 Connection: keep-alive Content-Length: 221 {"memberId":"M000000004","firstName":"John","lastName":"Smith","genderCode":"1","dateOfBirth":"2013-03-08","emailAddress":"user1394710559584@test.com","telephoneNumber":"09012345678","zipCode":"1710051","address":"Tokyo"}
- Response example
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: 5e8fea3aae044e94bf20a293e155af57 Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked Date: Thu, 13 Mar 2014 11:35:59 GMT {"memberId":"M000000004","firstName":"John","lastName":"Smith","genderCode":"1","dateOfBirth":"2013-03-08","emailAddress":"user1394710559584@test.com","telephoneNumber":"09012345678","zipCode":"1710051","address":"Tokyo","credential":{"signId":"user1394710559584@test.com","passwordLastChangedAt":"2014-03-13T11:35:59.847Z","lastModifiedAt":"2014-03-13T11:35:59.847Z"},"createdAt":"2014-03-13T11:35:59.847Z","lastModifiedAt":"2014-03-13T11:36:00.122Z"}
5.16.4.3.8. Implementing REST API that deletes specified resource¶
Implementation of REST API that deletes the Member resource specified by URI is as follows:
- REST API implementationImplement a process that deletes the Member resource specified by URI.
@RequestMapping("members") @RestController public class MemberRestController { // omitted // (1) @RequestMapping(value = "{memberId}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE) // (2) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) public void deleteMember( @PathVariable("memberId") String memberId) { // (3) memberService.deleteMember(memberId); } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description {memberId}in the example above) in value attribute andRequestMethod.DELETEin method attribute of@RequestMappingannotation.@ResponseStatusannotation as method annotation and specify the responding status code.Set 204 (NO_CONTENT) in value attribute of@ResponseStatusannotation.Note
To set deleted resource information in response BODY, set (200) OK in the status code.
- Request example
DELETE /rest-api-web/api/v1/members/M000000005 HTTP/1.1 Accept: text/plain, application/json, application/*+json, */* User-Agent: Java/1.7.0_51 Host: localhost:8080 Connection: keep-alive
- Response example
HTTP/1.1 204 No Content Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: e06c5bd40c864a299c48d9be3f12b2c0 Date: Thu, 13 Mar 2014 11:40:05 GMT
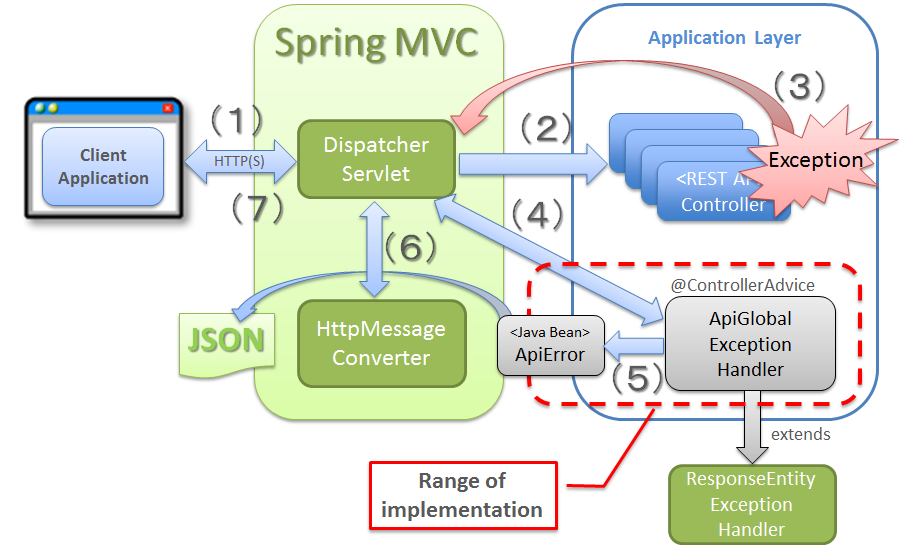
5.16.4.4. Implementing exception handling¶
How to handle the exceptions occurring in RESTful Web Service is explained below.
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler) is provided as the class that assists in implementing exception handling for RESTful Web Service.@ControllerAdvice annotation to this exception handling class.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler by using @ExceptionHandler annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler are set by the same specifications as DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler, it can be extended so as to output error information in the response Body.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler is created and common exception handling is performed, is described before explaining the typical implementation.
Sr. No. Processing layer Description HttpMessageConverter.
5.16.4.4.1. Implementation to output error information in response Body¶
- Error information should be in the following JSON format.
{ "code" : "e.ex.fw.7001", "message" : "Validation error occurred on item in the request body.", "details" : [ { "code" : "ExistInCodeList", "message" : "\"genderCode\" must exist in code list of CL_GENDER.", "target" : "genderCode" } ] }
- Create JavaBean that retains error information.
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.common.error; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude; // (1) public class ApiError implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private final String code; private final String message; @JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_EMPTY) private final String target; // (2) @JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_EMPTY) private final List<ApiError> details = new ArrayList<>(); // (3) public ApiError(String code, String message) { this(code, message, null); } public ApiError(String code, String message, String target) { this.code = code; this.message = message; this.target = target; } public String getCode() { return code; } public String getMessage() { return message; } public String getTarget() { return target; } public List<ApiError> getDetails() { return details; } public void addDetail(ApiError detail) { details.add(detail); } }
Sr. No. Description Tip
When the value is
nullor empty, it is possible to avoid fields being output to JSON by specifying@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_EMPTY)in the field. When the condition to disable field output is to be restricted tonull, it is advisable to specify@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL).
- Create a class for generating JavaBean that retains error information.
Refer to Appendix for the source code when implementation of all exception handling is completed.
// (4) @Component public class ApiErrorCreator { @Inject MessageSource messageSource; public ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request, String errorCode, String defaultErrorMessage, Object... arguments) { // (5) String localizedMessage = messageSource.getMessage(errorCode, arguments, defaultErrorMessage, request.getLocale()); return new ApiError(errorCode, localizedMessage); } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description MessageSource.For message management methods, refer to “Message Management”.Tip
In the above example,
org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequestis received as an argument to support localization of messages.WebRequestis not necessary when message localization is not required.The reason for using
WebRequestas an argument instead ofjava.util.Localeis due to an additional requirement wherein, HTTP request details are to be embedded in the error message. When there is no such requirement to embed HTTP request details in error,Localecan also be used.
ResponseEntityExceptionHandlermethod is extended and the implementation to output error information in response Body is carried out.
Refer to Appendix for the source code when implementation for all exception handling is completed.
@ControllerAdvice // (6) public class ApiGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler { @Inject ApiErrorCreator apiErrorCreator; @Inject ExceptionCodeResolver exceptionCodeResolver; // (7) @Override protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(Exception ex, Object body, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) { final Object apiError; // (8) if (body == null) { String errorCode = exceptionCodeResolver.resolveExceptionCode(ex); apiError = apiErrorCreator.createApiError(request, errorCode, ex .getLocalizedMessage()); } else { apiError = body; } // (9) return ResponseEntity.status(status).headers(headers).body(apiError); } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description ResponseEntityExceptionHandlerprovided by Spring MVC and assign@ControllerAdviceannotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler.ExceptionCodeResolverprovided by common library.For setting example ofExceptionCodeResolver, refer to “Resolving error codes and messages using ExceptionCodeResolver” .When the JavaBean output to response Body is specified, use the specified JavaBean as it is.This process is implemented considering that error information is generated individually in the error handling process for each exception.ResponseEntityExceptionHandlerprovided by Spring MVC.Refer to “HTTP response code set by DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver” for status codes that are set.Tip
Attribute of @ControllerAdvice annotation added in Spring Framework 4.0
By specifying an attribute of
@ControllerAdviceannotation, it has been improved to allow flexibility in specifying Controller to apply a method implemented in the class wherein@ControllerAdviceis assigned. For details about attribute refer to: Attribute of @ControllerAdvice.Note
Points to be noted while using an attribute of @ControllerAdvice annotation
By using an attribute of@ControllerAdviceannotation, it is possible to share exception handling in respective granularity, however, it is advisable not to specify attribute of@ControllerAdviceannotation for exception handling of common application (class corresponding toApiGlobalExceptionHandlerclass in the above example).When an attribute is specified in
@ControllerAdviceannotation assigned inApiGlobalExceptionHandler, a part of exception handling may not be possible that occurs in framework process provided by Spring MVC.Specifically, inApiGlobalExceptionHandlerclass, exception handling is not possible for the exceptions that occur when REST API (process method of Controller) corresponding to the request could not be found, hence, it is not possible to correctly respond to errors such as “405 Method Not Allowed”, etc.
- Response example
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: e60b3b6468194e22852c8bfc7618e625 Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked Date: Thu, 13 Mar 2014 12:16:55 GMT Connection: close {"code":"e.ex.fw.7001","message":"Validation error occurred on item in the request body.","details":[{"code":"ExistInCodeList","message":"\"genderCode\" must exist in code list of CL_GENDER.","target":"genderCode"}]}
5.16.4.4.2. Implementing input error exception handling¶
Implementation for responding to input errors (syntax error, unit item check error, correlated field check error) is explained here.
Following three exceptions need to be handled in order to respond to input errors.
Sr. No. Exception Description Note
org.springframework.beans.TypeMismatchExceptionoccurs when there is a type conversion error for value while fetching values from request parameter, request header and path variable, by using annotation provided by Spring Framework.When following annotations are specified as arguments of Controller processing method (argument other than
String),TypeMismatchExceptionmay occur.
@org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam@org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestHeader@org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.Pathvariable@org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.MatrixVariable
TypeMismatchExceptionis handled byResponseEntityExceptionHandlerresulting in 400 (Bad Request). As a result, individual handling is not required.Refer to “Resolving error codes and messages using ExceptionCodeResolver” in order to resolve the error codes and error messages to be set in error information.
- Method is created to generate error information for input validation errors.
@Component public class ApiErrorCreator { @Inject MessageSource messageSource; // omitted // (1) public ApiError createBindingResultApiError(WebRequest request, String errorCode, BindingResult bindingResult, String defaultErrorMessage) { ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, errorCode, defaultErrorMessage); for (FieldError fieldError : bindingResult.getFieldErrors()) { apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, fieldError, fieldError .getField())); } for (ObjectError objectError : bindingResult.getGlobalErrors()) { apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, objectError, objectError .getObjectName())); } return apiError; } // (2) private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request, DefaultMessageSourceResolvable messageResolvable, String target) { String localizedMessage = messageSource.getMessage(messageResolvable, request.getLocale()); return new ApiError(messageResolvable.getCode(), localizedMessage, target); } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description FieldError) and correlated field check error (ObjectError) are added to detailed error information.This method need not be provided when it is not necessary to output error information for each item.FieldError) and correlation check error (ObjectError).
ResponseEntityExceptionHandlermethod is extended and the implementation to output input validation error information in response Body, is performed.
@ControllerAdvice public class ApiGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler { @Inject ApiErrorCreator apiErrorCreator; @Inject ExceptionCodeResolver exceptionCodeResolver; // omitted // (3) @Override protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid( MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) { return handleBindingResult(ex, ex.getBindingResult(), headers, status, request); } // (4) @Override protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleBindException(BindException ex, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) { return handleBindingResult(ex, ex.getBindingResult(), headers, status, request); } // (5) @Override protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleHttpMessageNotReadable( HttpMessageNotReadableException ex, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) { if (ex.getCause() instanceof Exception) { return handleExceptionInternal((Exception) ex.getCause(), null, headers, status, request); } else { return handleExceptionInternal(ex, null, headers, status, request); } } // omitted // (6) protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleBindingResult(Exception ex, BindingResult bindingResult, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) { String code = exceptionCodeResolver.resolveExceptionCode(ex); String errorCode = exceptionCodeResolver.resolveExceptionCode(ex); ApiError apiError = apiErrorCreator.createBindingResultApiError( request, errorCode, bindingResult, ex.getMessage()); return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request); } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description ResponseEntityExceptionHandlerand extend error handling forMethodArgumentNotValidException.In the above example, the process is delegated to a common method (6) that handles input validation errors.When it is not necessary to output error information for each item, overriding is not required.400 (Bad Request) is set in the status code and presence of some flaw in the field value of the specified resource is notified.ResponseEntityExceptionHandlerand extend error handling forBindException.In the above example, the process is delegated to a common method (6) that handles input validation error.When it is not necessary to output error information for each item, overriding is not required.400 (Bad Request) is set in the status code and presence of flaw in the specified request parameter is notified.ResponseEntityExceptionHandlerand extend error handling forHttpMessageNotReadableException.In the above example, detailed error handling is performed by using cause exception.If a detailed error handling is not necessary, overriding is not required.400 (Bad Request) is set in the status code and presence of flaw in the specified resource format etc. is notifiedTip
Error handling when using JSON
When JSON is used as the resource format, following exception is stored as cause exception of
HttpMessageNotReadableException.
Sr. No. Exception class Description
- Following error response is sent when an input validation error (single field check error, correlated field check error) occurs.
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: 13522b3badf2432ba4cad0dc7aeaee80 Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked Date: Wed, 19 Feb 2014 05:08:28 GMT Connection: close {"code":"e.ex.fw.7002","message":"Validation error occurred on item in the request parameters.","details":[{"code":"NotEmpty","message":"\"{0}\" may not be empty.","target":"name"}]}
- Following error response is sent when JSON errors (format error etc.) occur.
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: ca4c742a6bfd49e5bc01cd0b124738a1 Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked Date: Wed, 19 Feb 2014 13:32:24 GMT Connection: close {"code":"e.ex.fw.7003","message":"Request body format error occurred."}
5.16.4.4.3. Implementing exception handling for “Resource not found” error¶
When a resource does not exist, implementation for responding to the “resource not found” error, is explained below.
org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException is provided by common library as an exception notifying “resource not found”.- When a resource matching with the ID fetched from path variable is not found, generate
ResourceNotFoundException.
public Member getMember(String memberId) { Member member = memberRepository.findOne(memberId); if (member == null) { throw new ResourceNotFoundException(ResultMessages.error().add( "e.ex.mm.5001", memberId)); } return member; }
- Create a method to generate error information for
ResultMessages.
@Component public class ApiErrorCreator { // omitted // (1) public ApiError createResultMessagesApiError(WebRequest request, String rootErrorCode, ResultMessages resultMessages, String defaultErrorMessage) { ApiError apiError; if (resultMessages.getList().size() == 1) { ResultMessage resultMessage = resultMessages.iterator().next(); String errorCode = resultMessage.getCode(); String errorText = resultMessage.getText(); if (errorCode == null && errorText == null) { errorCode = rootErrorCode; } apiError = createApiError(request, errorCode, errorText, resultMessage.getArgs()); } else { apiError = createApiError(request, rootErrorCode, defaultErrorMessage); for (ResultMessage resultMessage : resultMessages.getList()) { apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, resultMessage .getCode(), resultMessage.getText(), resultMessage .getArgs())); } } return apiError; } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description ResultMessagesis set in error information.Note
In the above example, as
ResultMessagescan retain multiple messages, the process is divided as per when a single message is stored and when multiple messages are stored.When it is not necessary to support multiple messages, the process wherein the message at the start is generated as error information, may be implemented.
- Create a method for handling the exception that notifies “resource not found” error, in the class that performs error handling.
@ControllerAdvice public class ApiGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler { @Inject ApiErrorCreator apiErrorCreator; @Inject ExceptionCodeResolver exceptionCodeResolver; // omitted // (2) @ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class) public ResponseEntity<Object> handleResourceNotFoundException( ResourceNotFoundException ex, WebRequest request) { return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(), HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, request); } // omitted // (3) private ResponseEntity<Object> handleResultMessagesNotificationException( ResultMessagesNotificationException ex, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) { String errorCode = exceptionCodeResolver.resolveExceptionCode(ex); ApiError apiError = apiErrorCreator.createResultMessagesApiError( request, errorCode, ex.getResultMessages(), ex.getMessage()); return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request); } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description ResourceNotFoundException.ResourceNotFoundExceptionexception can be handled if@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)is specified as method annotation.In the above example, the process is delegated to method that handles exception of the parent class (ResultMessagesNotificationException) ofResourceNotFoundException.Set 404 (Not Found) in the status code and notify a message stating, ‘specified resource does not exist in the server’.
- When resource is not found, following error response is generated.
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: 5ee563877f3140fd904d0acf52eba398 Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked Date: Wed, 19 Feb 2014 08:46:18 GMT {"code":"e.ex.mm.5001","message":"Specified member not found. member id : M000000001"}
5.16.4.4.4. Implementing exception handling for business errors¶
An implementation wherein business error is sent as a response on detecting violation of business rule, is explained here.
Perform business rule check as Service process and generate business exception when a business rule violation is detected. For details on how to detect business error, refer to “Notifying business error”.
- Create a method to handle business exception in the class that performs error handling.
@ControllerAdvice public class ApiGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler { // omitted // (1) @ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class) public ResponseEntity<Object> handleBusinessException(BusinessException ex, WebRequest request) { return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(), HttpStatus.CONFLICT, request); } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description BusinessException.BusinessExceptioncan be handled if@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)is specified as method annotation.In the above example, the process is delegated to the method that handles the exception of parent class (ResultMessagesNotificationException) ofBusinessException.Set 409 (Conflict)in the status code and send a message notifying although there are no errors in the resource itself specified by client, all the conditions necessary for operating the resource stored by the server are not in place.
- Following error response is generated when a business error occurs.
HTTP/1.1 409 Conflict Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: 37c1a899d5f74e7a9c24662292837ef7 Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked Date: Wed, 19 Feb 2014 09:03:26 GMT {"code":"e.ex.mm.8001","message":"Cannot use specified sign id. sign id : user1@test.com"}
5.16.4.4.5. Implementing exception handling for exclusive errors¶
- Create a method for exclusive error handling in the class that performs error handling.
@ControllerAdvice public class ApiGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler { // omitted // (1) @ExceptionHandler({ OptimisticLockingFailureException.class, PessimisticLockingFailureException.class }) public ResponseEntity<Object> handleLockingFailureException(Exception ex, WebRequest request) { return handleExceptionInternal(ex, null, new HttpHeaders(), HttpStatus.CONFLICT, request); } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description OptimisticLockingFailureExceptionandPessimisticLockingFailureException).If@ExceptionHandler({ OptimisticLockingFailureException.class, PessimisticLockingFailureException.class })is specified as method annotation, exception handling of exclusive errors (OptimisticLockingFailureExceptionandPessimisticLockingFailureException) can be performed.Set 409(Conflict) in status code and send a message notifying that, ‘although there are no flaws in the resource itself specified by client, the conditions for operating the resource could not be fulfilled due to conflict in the process’.
- When an exclusive error occurs, following error response is generated.
HTTP/1.1 409 Conflict Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: 85200b5a51be42b29840e482ee35087f Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked Date: Wed, 19 Feb 2014 16:32:45 GMT {"code":"e.ex.fw.8002","message":"Conflict with other processing occurred."}
5.16.4.4.6. Implementing exception handling for system errors¶
An implementation wherein system error is sent as a response on detecting system abnormality, is explained here.
Generate system exception when any system abnormality is detected. Refer to “Notifying system error” for the details on how to detect system errors.
- Create a method to handle system exceptions in the class that performs error handling.
@ControllerAdvice public class ApiGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler { // omitted // (1) @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) public ResponseEntity<Object> handleSystemError(Exception ex, WebRequest request) { return handleExceptionInternal(ex, null, new HttpHeaders(), HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, request); } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description Exception.Exceptioncan be handled if@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)is specified as method annotation.In the above example, the system exceptions generated from dependent libraries being used, are also handled.Set 500 (Internal Server Error) in status code.
- Following error response is generated when a system error occurs.
HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server Error Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: 3625d5a040a744e49b0a9b3763a24e9c Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked Date: Wed, 19 Feb 2014 12:22:33 GMT Connection: close {"code":"e.ex.fw.9003","message":"System error occurred."}Warning
Error message at the time of system error
When system error occurs, it is recommended that a simple error message that does not specify the error cause, is set as the message to be returned to the client. If an error message specifying the cause of error is set, it may expose system vulnerabilities to the client resulting in security issues.
Cause of error is output to a log, for error analysis. This log is output by
ExceptionLoggerprovided by common library as the default setting of Blank project. As a result, the settings and implementation for log output are not required.
5.16.4.4.7. Resolving error codes and messages using ExceptionCodeResolver¶
ExceptionCodeResolver provided by common library is used, error codes can be resolved from the exception class.applicationContext.xmlMapping exception class and error code (exception code).
<!-- omitted --> <bean id="exceptionCodeResolver" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.SimpleMappingExceptionCodeResolver"> <property name="exceptionMappings"> <map> <!-- omitted --> <entry key="ResourceNotFoundException" value="e.ex.fw.5001" /> <entry key="HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException" value="e.ex.fw.6001" /> <entry key="MediaTypeNotAcceptableException" value="e.ex.fw.6002" /> <entry key="HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException" value="e.ex.fw.6003" /> <entry key="MethodArgumentNotValidException" value="e.ex.fw.7001" /> <entry key="BindException" value="e.ex.fw.7002" /> <entry key="JsonParseException" value="e.ex.fw.7003" /> <entry key="UnrecognizedPropertyException" value="e.ex.fw.7004" /> <entry key="JsonMappingException" value="e.ex.fw.7005" /> <entry key="TypeMismatchException" value="e.ex.fw.7006" /> <entry key="BusinessException" value="e.ex.fw.8001" /> <entry key="OptimisticLockingFailureException" value="e.ex.fw.8002" /> <entry key="PessimisticLockingFailureException" value="e.ex.fw.8002" /> <entry key="DataAccessException" value="e.ex.fw.9002" /> <!-- omitted --> </map> </property> <property name="defaultExceptionCode" value="e.ex.fw.9001" /> </bean> <!-- omitted -->
xxx-web/src/main/resources/i18n/application-messages.propertiesMessage corresponding to error code (exception code) is set for the error that occurs in application layer.
# --- # Application common messages # --- e.ex.fw.5001 = Resource not found. e.ex.fw.6001 = Request method not supported. e.ex.fw.6002 = Specified representation format not supported. e.ex.fw.6003 = Specified media type in the request body not supported. e.ex.fw.7001 = Validation error occurred on item in the request body. e.ex.fw.7002 = Validation error occurred on item in the request parameters. e.ex.fw.7003 = Request body format error occurred. e.ex.fw.7004 = Unknown field exists in JSON. e.ex.fw.7005 = Type mismatch error occurred in JSON field. e.ex.fw.7006 = Type mismatch error occurred in request parameter or header or path variable. e.ex.fw.8001 = Business error occurred. e.ex.fw.8002 = Conflict with other processing occurred. e.ex.fw.9001 = System error occurred. e.ex.fw.9002 = System error occurred. e.ex.fw.9003 = System error occurred. # omitted
xxx-web/src/main/resources/ValidationMessages.propertiesSet a message corresponding to error code for the error that occurs in the input validation performed using Bean Validation.
# --- # Bean Validation common messages # --- # for bean validation of standard javax.validation.constraints.AssertFalse.message = "{0}" must be false. javax.validation.constraints.AssertTrue.message = "{0}" must be true. javax.validation.constraints.DecimalMax.message = "{0}" must be less than ${inclusive == true ? 'or equal to ' : ''}{value}. javax.validation.constraints.DecimalMin.message = "{0}" must be greater than ${inclusive == true ? 'or equal to ' : ''}{value}. javax.validation.constraints.Digits.message = "{0}" numeric value out of bounds (<{integer} digits>.<{fraction} digits> expected). javax.validation.constraints.Future.message = "{0}" must be in the future. javax.validation.constraints.Max.message = "{0}" must be less than or equal to {value}. javax.validation.constraints.Min.message = "{0}" must be greater than or equal to {value}. javax.validation.constraints.NotNull.message = "{0}" may not be null. javax.validation.constraints.Null.message = "{0}" must be null. javax.validation.constraints.Past.message = "{0}" must be in the past. javax.validation.constraints.Pattern.message = "{0}" must match "{regexp}". javax.validation.constraints.Size.message = "{0}" size must be between {min} and {max}. # for bean validation of hibernate org.hibernate.validator.constraints.CreditCardNumber.message = "{0}" invalid credit card number. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.EAN.message = "{0}" invalid {type} barcode. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email.message = "{0}" not a well-formed email address. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Length.message = "{0}" length must be between {min} and {max}. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.LuhnCheck.message = "{0}" The check digit for ${validatedValue} is invalid, Luhn Modulo 10 checksum failed. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Mod10Check.message = "{0}" The check digit for ${validatedValue} is invalid, Modulo 10 checksum failed. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Mod11Check.message = "{0}" The check digit for ${validatedValue} is invalid, Modulo 11 checksum failed. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.ModCheck.message = "{0}" The check digit for ${validatedValue} is invalid, ${modType} checksum failed. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotBlank.message = "{0}" may not be empty. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotEmpty.message = "{0}" may not be empty. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.ParametersScriptAssert.message = "{0}" script expression "{script}" didn't evaluate to true. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Range.message = "{0}" must be between {min} and {max}. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.SafeHtml.message = "{0}" may have unsafe html content. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.ScriptAssert.message = "{0}" script expression "{script}" didn't evaluate to true. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.URL.message = "{0}" must be a valid URL. org.hibernate.validator.constraints.br.CNPJ.message = "{0}" invalid Brazilian corporate taxpayer registry number (CNPJ). org.hibernate.validator.constraints.br.CPF.message = "{0}" invalid Brazilian individual taxpayer registry number (CPF). org.hibernate.validator.constraints.br.TituloEleitoral.message = "{0}" invalid Brazilian Voter ID card number. # for common library org.terasoluna.gfw.common.codelist.ExistInCodeList.message = "{0}" must exist in code list of {codeListId}.
xxx-domain/src/main/resources/i18n/domain-messages.propertiesSet a message corresponding to error code (exception code) for the error in domain layer.
# omitted e.ex.mm.5001 = Specified member not found. member id : {0} e.ex.mm.8001 = Cannot use specified sign id. sign id : {0} # omitted
5.16.4.5. Implementing the error handling notified to Servlet Container¶
When an error occurs in Filter or when error responses are sent by using HttpServletResponse#sendError, the errors cannot be handled using exception handling feature of Spring MVC.
Hence, these errors are notified to Servlet Container.
This section explains how to handle the errors notified to Servlet Container.
Sr. No. Processing layer Description web.xml.If the error is not fatal, Controller for error handling is called and the error is handled.HttpMessageConverter.
5.16.4.5.1. Implementing the Controller that sends error response¶
Create a controller that sends the error response for the error notified to Servlet Container.
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.common.error; import javax.inject.Inject; import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestAttributes; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest; // (1) @RequestMapping("error") @RestController public class ApiErrorPageController { @Inject ApiErrorCreator apiErrorCreator; // (2) // (3) @RequestMapping public ResponseEntity<ApiError> handleErrorPage( @RequestParam("errorCode") String errorCode, // (4) WebRequest request) { // (5) HttpStatus httpStatus = HttpStatus.valueOf((Integer) request .getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE, RequestAttributes.SCOPE_REQUEST)); // (6) ApiError apiError = apiErrorCreator.createApiError(request, errorCode, httpStatus.getReasonPhrase()); // (7) return ResponseEntity.status(httpStatus).body(apiError); } }
Sr. No. Description /api/v1/error”.<error-code>).Therefore, separate consideration is required for the case where an error page that is handled by using exception type (<exception-type>) is to be processed using this method.
5.16.4.5.2. Creating a static JSON file to be sent as response when a fatal error occurs¶
Create a static JSON file to be sent as a response when a fatal error occurs.
unhandledSystemError.json
{"code":"e.ex.fw.9999","message":"Unhandled system error occurred."}
5.16.4.5.3. Settings for handling an error that is notified to Servlet Container¶
Settings for handling an error that is notified to Servlet Container are explained here.
web.xml
<!-- omitted --> <!-- (1) --> <error-page> <error-code>404</error-code> <location>/api/v1/error?errorCode=e.ex.fw.5001</location> </error-page> <!-- (2) --> <error-page> <exception-type>java.lang.Exception</exception-type> <location>/WEB-INF/views/common/error/unhandledSystemError.json</location> </error-page> <!-- (3) --> <mime-mapping> <extension>json</extension> <mime-type>application/json;charset=UTF-8</mime-type> </mime-mapping> <!-- omitted -->
Sr. No. Description "404 Not Found"occurs, Controller (`` ApiErrorPageController``) that is mapped in request “/api/v1/error?errorCode=e.ex.fw.5001” is called and error response is sent./WEB-INF/views/common/error/unhandledSystemError.json” is sent as response.charset=UTF-8is not specified.When there are no multi byte characters in the JSON file, this setting is not mandatory. However, it is always safe to incorporate this setting.
- When the request is sent to a non-existing path, following error response is sent.
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: 2ad50fb5ba2441699c91a5b01edef83f Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked Date: Wed, 19 Feb 2014 23:24:20 GMT {"code":"e.ex.fw.5001","message":"Resource not found."}
- When a fatal error occurs, following error response is sent.
HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server Error Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: 69db3854a19f439781584321d9ce8336 Content-Type: application/json Content-Length: 68 Date: Thu, 20 Feb 2014 00:13:43 GMT Connection: close {"code":"e.ex.fw.9999","message":"Unhandled system error occurred."}
5.16.4.6. Security measures¶
5.16.4.6.1. Authentication and Authorization¶
Todo
TBD
How to implement authentication and authorization using OAuth2 (Spring Security OAuth2), will be explained in subsequent versions.
5.16.4.6.2. CSRF measures¶
- Refer to CSRF Measures for the setting methods when CSRF measures are carried out for RESTful Web Service.
- Refer to Disabling CSRF measures for the setting methods when CSRF measures are not carried out for RESTful Web Service.
5.16.4.7. Conditional operations for resource¶
Todo
TBD
How to implement conditional process control using headers like Etag etc. will be explained in subsequent versions.
5.16.4.8. Cache control for resource¶
Todo
TBD
How to implement cache control using headers like Cache-Control/Expires/Pragma etc. will be explained in subsequent versions.
5.16.5. Appendix¶
5.16.5.1. Settings when RESTful Web Service and client application are operated as the same Web application¶
5.16.5.1.1. How to set DispatcherServlet for RESTful Web Service¶
DispatcherServlet that receives the requests for RESTful Web Service and DispatcherServlet that receives client application requests.DispatcherServlet is explained below.web.xml
<!-- omitted --> <!-- (1) --> <servlet> <servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath*:META-INF/spring/spring-mvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <!-- (2) --> <servlet> <servlet-name>restAppServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <!-- (3) --> <param-value>classpath*:META-INF/spring/spring-mvc-rest.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup> </servlet> <!-- (4) --> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>restAppServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/api/v1/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <!-- omitted -->
Sr. No. Description DispatcherServletthat receives request for client application.DispatcherServlet) that receives the request for RESTful Web Service.Specify a name indicating it as RESTful Web Service Servlet in<servlet-name>element.In the above example,"restAppServlet"is specified as the Servlet name.DispatcherServletfor RESTful Web Service.In the above example,META-INF/spring/spring-mvc-rest.xmlin class path, is specified as the Spring MVC bean definition file.DispatcherServletfor RESTful Web Service.In the above example, the Servlet path under"/api/v1/"is mapped in theDispatcherServletfor RESTful Web Service.Typically, Servlet paths like"/api/v1/""/api/v1/members""/api/v1/members/xxxxx"are mapped in theDispatcherServlet("restAppServlet") for RESTful Web Service.Tip
Value to be specified in the value attribute of @RequestMapping annotation
Value in the wild card (
*) part specified in<url-pattern>element, is specified as the value in “value” attribute of@RequestMappingannotation.For example, when
@RequestMapping(value = "members")is specified, it is deployed as the method that performs process for path"/api/v1/members". Therefore, it is not necessary to specify the path ("api/v1") that performs mapping in divided Servlets, in the value attribute of@RequestMappingannotation.When specified as
@RequestMapping(value = "api/v1/members"), it ends up being deployed as the method performing the process for path"/api/v1/api/v1/members". Hence, please take note of same.
5.16.5.2. Implementing hypermedia link¶
Implementation for including a hypermedia link to a related resource in JSON, is explained here.
5.16.5.2.1. Implementing common parts¶
- Create a JavaBean that retains the link information.
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.common.resource; import java.io.Serializable; // (1) public class Link implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private final String rel; private final String href; public Link(String rel, String href) { this.rel = rel; this.href = href; } public String getRel() { return rel; } public String getHref() { return href; } }
Sr. No. Description
- Create an abstract class of Resource that retains collection of link information.
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.common.resource; import java.net.URI; import java.util.LinkedHashSet; import java.util.Set; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude; // (2) public abstract class AbstractLinksSupportedResource { // (3) @JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_EMPTY) private final Set<Link> links = new LinkedHashSet<>(); public Set<Link> getLinks() { return links; } // (4) public AbstractLinksSupportedResource addLink(String rel, URI href) { links.add(new Link(rel, href.toString())); return this; } // (5) public AbstractLinksSupportedResource addSelf(URI href) { return addLink("self", href); } // (5) public AbstractLinksSupportedResource addParent(URI href) { return addLink("parent", href); } }
Sr. No. Description @JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_EMPTY)is specified to prevent output to JSON when link is not specified."self") and to add link information for accessing parent resource ("parent") are created.
5.16.5.2.2. Implementation for each resource¶
- Inherit an abstract class of Resource that retains collection of link information in Resource class.
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.member; // (1) public class MemberResource extends AbstractLinksSupportedResource implements Serializable { // omitted }
Sr. No. Description links) that retains collection of link information is imported, thus making it a Resource class that supports hypermedia link.
- Adding hypermedia link by REST API process.
@RequestMapping("members") @RestController public class MemberRestController { // omitted @RequestMapping(value = "{memberId}", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) public MemberResource getMember( @PathVariable("memberId") String memberId // (2) UriComponentsBuilder uriBuilder) { Member member = memberService.getMember(memberId); MemberResource responseResource = beanMapper.map(member, MemberResource.class); // (3) responseResource.addSelf(uriBuilder.path("/members").pathSegment(memberId) .build().toUri()); return responseResource; } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilderclass, provided by Spring MVC, in method argument in order to build URI set in link information.WhenUriComponentsBuilderclass is specified in method argument of Controller, instance oforg.springframework.web.servlet.support.ServletUriComponentsBuilderclass,that has inheritedUriComponentsBuilderclass in Spring MVC, is passed at the time of method execution.UriComponentsBuilderclass method is called to build URI set in link information and URI to access to one’s resource is added to resource.ServletUriComponentsBuilderinstances passed as method argument of Controller are initiated based on the information of<servlet-mapping>element described in web.xml. It is not resource dependent.By using URI Template Patterns ,etc. provided in Spring Framework,an URI can be built based on the request information. Thus, a generic build process which is independent of a resource, can be implemented.In the above example, when GET is done forhttp://example.com/api/v1/members/M000000001, built URI is same as the requested URI(http://example.com/api/v1/members/M000000001).Method that builds an URI to be set in link information should be implemented as required.Tip
When building an URL in
ServletUriComponentsBuilder, by referring to “X-Forwarded-Host” header, a configuration with a load balancer or Web server between client and the application server is considered. However, it should be noted that the expected URI will not be built if it does not match with the path configuration.
- Response exampleFollowing response is obtained in actual operation.
GET /rest-api-web/api/v1/members/M000000001 HTTP/1.1 Accept: text/plain, application/json, application/*+json, */* User-Agent: Java/1.7.0_51 Host: localhost:8080 Connection: keep-alive{ "links" : [ { "rel" : "self", "href" : "http://localhost:8080/rest-api-web/api/v1/members/M000000001" } ], "memberId" : "M000000001", "firstName" : "John", "lastName" : "Smith", "genderCode" : "1", "dateOfBirth" : "2013-03-14", "emailAddress" : "user1394794959984@test.com", "telephoneNumber" : "09012345678", "zipCode" : "1710051", "address" : "Tokyo", "credential" : { "signId" : "user1394794959984@test.com", "passwordLastChangedAt" : "2014-03-14T11:02:41.477Z", "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-14T11:02:41.477Z" }, "createdAt" : "2014-03-14T11:02:41.477Z", "lastModifiedAt" : "2014-03-14T11:02:41.477Z" }
5.16.5.3. Creating RESTful Web Service conforming to HTTP specifications¶
5.16.5.3.1. Settings for location header at the time of POST¶
5.16.5.3.2. Implementation for each resource¶
- The URI of created resource is set in Location header by REST API process.
@RequestMapping("members") @RestController public class MemberRestController { // omitted @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST) public ResponseEntity<MemberResource> postMembers( @RequestBody @Validated({ PostMembers.class, Default.class }) MemberResource requestedResource, // (1) UriComponentsBuilder uriBuilder) { Member creatingMember = beanMapper.map(requestedResource, Member.class); Member createdMember = memberService.createMember(creatingMember); MemberResource responseResource = beanMapper.map(createdMember, MemberResource.class); // (2) URI createdUri = uriBuilder.path("/members/{memberId}") .buildAndExpand(responseResource.getMemberId()).toUri(); // (3) return ResponseEntity.created(createdUri).body(responseResource); } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilderclass provided by Spring MVC, in method argument in order to build an URI of created resource.WhenUriComponentsBuilderclass is specified in method argument of Controller, an instance oforg.springframework.web.servlet.support.ServletUriComponentsBuilderclass,that has inheritedUriComponentsBuilderclass by Spring MVC, is passed at the time of method execution.pathmethod, a path using URI Template Patterns is added toServletUriComponentsBuilderinstance passed as argument,buildAndExpandmethod is called and an URI of created resource is built by binding the ID of created resource.ServletUriComponentsBuilderinstances passed as method argument of Controller are initiated based on the information of<servlet-mapping>element described in web.xml. It is not resource dependent.By using URI Template Patterns ,etc. provided by Spring Framework,an URI can be built based on the request information. Thus, a generic build process which is independent of a resource, can be implemented.For example, if POST method is used forhttp://example.com/api/v1/members, the built URI will be “requested URI +"/"+ ID of created resource”.Typically, if"M000000001"is specified in ID, it becomeshttp://example.com/api/v1/members/M000000001.Method that builds an URI to be set in link information should be implemented as required.org.springframework.http.ResponseEntityinstance using following parameters, and return it.
- Status code : 201(Created)
- Location header : Created resource’s URI
- Response body : Created resource object
Tip
When building an URL in
ServletUriComponentsBuilder, by referring to “X-Forwarded-Host” header, a configuration with a load balancer or Web server between client and the application server is considered. However, it should be noted that the expected URI will not be built if it does not match with the path configuration.
- Response exampleFollowing response header is obtained in the actual operation.
HTTP/1.1 201 Created Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: 693e132312d64998a7d8d6cabf3d13ef Location: http://localhost:8080/rest-api-web/api/v1/members/M000000001 Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Transfer-Encoding: chunked Date: Fri, 14 Mar 2014 12:34:31 GMT
5.16.5.3.3. Setting to dispatch OPTIONS method request to the Controller¶
DispatcherServlet default setting, the request for OPTIONS method is not dispatched in the Controller with the list of methods allowed by DispatcherServlet being set in the Allow header.web.xml
<!-- omitted --> <servlet> <servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath*:META-INF/spring/spring-mvc-rest.xml</param-value> </init-param> <!-- (1) --> <init-param> <param-name>dispatchOptionsRequest</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <!-- omitted -->
DispatcherServletthat receives RESTful Web Service request totrue.
5.16.5.3.4. Implementing OPTIONS method¶
- REST API implementationImplement a process wherein, list of HTTP methods (REST API) supported by the resource specified in URI is sent as response.
@RequestMapping("members") @RestController public class MembersRestController { // omitted @RequestMapping(value = "{memberId}", method = RequestMethod.OPTIONS) public ResponseEntity<Void> optionsMember( @PathVariable("memberId") String memberId) { // (1) memberService.getMember(memberId); // (2) return ResponseEntity .ok() .allow(HttpMethod.GET, HttpMethod.HEAD, HttpMethod.PUT, HttpMethod.DELETE, HttpMethod.OPTIONS).build(); } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description
- Request example
OPTIONS /rest-api-web/api/v1/members/M000000004 HTTP/1.1 Accept: text/plain, application/json, application/*+json, */* User-Agent: Java/1.7.0_51 Host: localhost:8080 Connection: keep-alive
- Response example
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: 6d7bbc818c7f44e7942c54bc0ddc15bb Allow: GET,HEAD,PUT,DELETE,OPTIONS Content-Length: 0 Date: Mon, 17 Mar 2014 01:54:27 GMT
5.16.5.3.5. Implementing HEAD method¶
- REST API implementationA process is implemented wherein meta information of the resource specified in URI is fetched.
@RequestMapping("members") @RestController public class MemberRestController { // omitted @RequestMapping(value = "{memberId}", method = { RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.HEAD }) // (1) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) public MemberResource getMember( @PathVariable("memberId") String memberId) { // omitted } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description RequestMethod.HEADto the method attribute of REST API@RequestMappingannotation that processes the GET method.HEAD method needs to respond only the header information, by performing the same process as GET method. Therefore,RequestMethod.HEADis also specified in the method attribute of@RequestMappingannotation.It is advisable to perform a process similar to GET process as the Controller process since, the process for emptying response BODY is performed by standard functionality of Servlet API.
- Request example
HEAD /rest-api-web/api/v1/members/M000000001 HTTP/1.1 Accept: text/plain, application/json, application/*+json, */* User-Agent: Java/1.7.0_51 Host: localhost:8080 Connection: keep-alive
- Response example
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1 X-Track: 71093a551e624c149867b6bfec486d2c Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8 Content-Length: 452 Date: Thu, 13 Mar 2014 13:25:23 GMT
5.16.5.4. Disabling CSRF measures¶
Settings that prevent CSRF measures implementation for RESTful Web Service requests, are explained below.
Tip
Need to use session is eliminated when CSRF measures are not to be implemented.
In the following configuration example, session will not be used in Spring Security process.
CSRF measures are enabled as per the default settings of Blank project. By adding following settings, the process for CSRF measures is prevented for RESTful Web Service requests.
spring-security.xml
<!-- omitted --> <!-- (1) --> <sec:http pattern="/api/v1/**" auto-config="true" use-expressions="true" create-session="stateless"> <sec:headers /> </sec:http> <sec:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true"> <sec:headers> <sec:cache-control /> <sec:content-type-options /> <sec:hsts /> <sec:frame-options /> <sec:xss-protection /> </sec:headers> <sec:csrf /> <sec:access-denied-handler ref="accessDeniedHandler"/> <sec:custom-filter ref="userIdMDCPutFilter" after="ANONYMOUS_FILTER"/> <sec:session-management /> </sec:http> <!-- omitted -->
Sr. No. Description patternattribute of<sec:http>element.In the above example, request path starting with/api/v1/is handled as the REST API request path.Further, session is no longer used in Spring Security process by settingcreate-sessionattribute tostateless.<sec: csrf>element is not specified to disable the CSRF measures.
5.16.5.5. Enabling XXE Injection measures¶
Warning
XXE (XML External Entity) Injection measures
When using terasoluna-gfw-web 1.0.0.RELEASE, a class provided by Spring-oxm should be used, as this version is dependent on the Spring MVC version (3.2.4.RELEASE), that does not implement XXE Injection measures.
Adding Spring-oxm as dependent artifact.
pom.xml
<!-- omitted --> <!-- (1) --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-oxm</artifactId> <version>${org.springframework-version}</version> <!-- (2) --> </dependency> <!-- omitted -->
pom.xmlof terasoluna-gfw-parent.
Perform Bean definition for mutual conversion between XML and object by using the class provided by Spring-oxm.
spring-mvc-rest.xml
<!-- omitted --> <!-- (1) --> <bean id="xmlMarshaller" class="org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Jaxb2Marshaller"> <property name="packagesToScan" value="com.examples.app" /> <!-- (2) --> </bean> <!-- omitted --> <mvc:annotation-driven> <mvc:message-converters> <!-- (3) --> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.xml.MarshallingHttpMessageConverter"> <property name="marshaller" ref="xmlMarshaller" /> <!-- (4) --> <property name="unmarshaller" ref="xmlMarshaller" /> <!-- (5) --> </bean> </mvc:message-converters> <!-- omitted --> </mvc:annotation-driven> <!-- omitted -->
Jaxb2Marshallerprovided by Spring-oxm.ForJaxb2Marshaller, XXE injection measures are carried out by default.javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElementannotation) stored inpackagesToScanproperty.JAXB JavaBean stored under the specified package is scanned and is registered as JavaBean for marshalling and unmarshalling.JavaBean is scanned by the mechanism same as base-package attribute of<context:component-scan>.MarshallingHttpMessageConverterto<mvc:message-converters>element which is the child element of<mvc:annotation-driven>element.Jaxb2Marshallerbean defined in (1) inmarshallerproperty.Jaxb2Marshallerbean defined in (1) inunmarshallerproperty.
5.16.5.6. How to copy Joda-Time classes using Dozer¶
How to copy Joda-Time classes (org.joda.time.DateTime, org.joda.time.LocalDate etc.) using Dozer is explained here.
JodaDateTimeConverter.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.infra.dozer.converter; import org.dozer.DozerConverter; import org.joda.time.DateTime; public class JodaDateTimeConverter extends DozerConverter<DateTime, DateTime> { public JodaDateTimeConverter() { super(DateTime.class, DateTime.class); } @Override public DateTime convertTo(DateTime source, DateTime destination) { // This method not called, because type of from/to is same. return convertFrom(source, destination); } @Override public DateTime convertFrom(DateTime source, DateTime destination) { return source; } }
JodaLocalDateConverter.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.infra.dozer.converter; import org.dozer.DozerConverter; import org.joda.time.LocalDate; public class JodaLocalDateConverter extends DozerConverter<LocalDate, LocalDate> { public JodaLocalDateConverter() { super(LocalDate.class, LocalDate.class); } @Override public LocalDate convertTo(LocalDate source, LocalDate destination) { // This method not called, because type of from/to is same. return convertFrom(source, destination); } @Override public LocalDate convertFrom(LocalDate source, LocalDate destination) { return source; } }
<!-- (1) --> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <mappings xmlns="http://dozer.sourceforge.net" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://dozer.sourceforge.net http://dozer.sourceforge.net/schema/beanmapping.xsd "> <configuration> <custom-converters> <!-- (2) --> <converter type="org.terasoluna.examples.rest.infra.dozer.converter.JodaDateTimeConverter"> <class-a>org.joda.time.DateTime</class-a> <class-b>org.joda.time.DateTime</class-b> </converter> <converter type="org.terasoluna.examples.rest.infra.dozer.converter.JodaLocalDateConverter"> <class-a>org.joda.time.LocalDate</class-a> <class-b>org.joda.time.LocalDate</class-b> </converter> </custom-converters> </configuration> </mappings>
Sr. No. Description /xxx-domain/src/main/resources/META-INF/dozer/dozer-configration-mapping.xml.org.joda.time.DateTimeandorg.joda.time.LocalDate) are added.Note
When Dozer is used in domain layer as well, it is recommended to store the file defining Dozer operation settings, in domain layer project (
xxx-domain).When Dozer is used only in application layer, it may be stored in application layer project (
xxx-web).
5.16.5.7. Source code for application layer¶
Following files are excluded.
- JavaBean
- Configuration file
5.16.5.7.1. MemberRestController.java¶
java/org/terasoluna/examples/rest/api/member/MemberRestController.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.member;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import javax.validation.groups.Default;
import org.dozer.Mapper;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.PageImpl;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.member.MemberResource.PostMembers;
import org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.member.MemberResource.PutMember;
import org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.model.Member;
import org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.service.member.MemberService;
@RequestMapping("members")
@RestController
public class MemberRestController {
@Inject
MemberService memberService;
@Inject
Mapper beanMapper;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public Page<MemberResource> getMembers(@Validated MembersSearchQuery query,
Pageable pageable) {
Page<Member> page = memberService.searchMembers(query.getName(), pageable);
List<MemberResource> memberResources = new ArrayList<>();
for (Member member : page.getContent()) {
memberResources.add(beanMapper.map(member, MemberResource.class));
}
Page<MemberResource> responseResource =
new PageImpl<>(memberResources, pageable, page.getTotalElements());
return responseResource;
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public MemberResource postMembers(@RequestBody @Validated({
PostMembers.class, Default.class }) MemberResource requestedResource) {
Member creatingMember = beanMapper.map(requestedResource, Member.class);
Member createdMember = memberService.createMember(creatingMember);
MemberResource responseResource = beanMapper.map(createdMember,
MemberResource.class);
return responseResource;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "{memberId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public MemberResource getMember(@PathVariable("memberId") String memberId) {
Member member = memberService.getMember(memberId);
MemberResource responseResource = beanMapper.map(member,
MemberResource.class);
return responseResource;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "{memberId}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public MemberResource putMember(
@PathVariable("memberId") String memberId,
@RequestBody @Validated({
PutMember.class, Default.class }) MemberResource requestedResource) {
Member updatingMember = beanMapper.map(requestedResource, Member.class);
Member updatedMember = memberService.updateMember(memberId,
updatingMember);
Member updatedMember = memberService.updateMember(memberId,
MemberResource.class);
return responseResource;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "{memberId}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT)
public void deleteMember(@PathVariable("memberId") String memberId) {
memberService.deleteMember(memberId);
}
}
5.16.5.7.2. ApiErrorCreator.java¶
java/org/terasoluna/examples/rest/api/common/error/ApiErrorCreator.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.common.error;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessage;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessages;
@Component
public class ApiErrorCreator {
@Inject
MessageSource messageSource;
public ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request, String errorCode,
String defaultErrorMessage, Object... arguments) {
String localizedMessage = messageSource.getMessage(errorCode,
arguments, defaultErrorMessage, request.getLocale());
return new ApiError(errorCode, localizedMessage);
}
public ApiError createBindingResultApiError(WebRequest request,
String errorCode, BindingResult bindingResult,
String defaultErrorMessage) {
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, errorCode,
defaultErrorMessage);
for (FieldError fieldError : bindingResult.getFieldErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, fieldError, fieldError
.getField()));
}
for (ObjectError objectError : bindingResult.getGlobalErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, objectError, objectError
.getObjectName()));
}
return apiError;
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request,
DefaultMessageSourceResolvable messageResolvable, String target) {
String localizedMessage = messageSource.getMessage(messageResolvable,
request.getLocale());
return new ApiError(messageResolvable.getCode(), localizedMessage, target);
}
public ApiError createResultMessagesApiError(WebRequest request,
String rootErrorCode, ResultMessages resultMessages,
String defaultErrorMessage) {
ApiError apiError;
if (resultMessages.getList().size() == 1) {
ResultMessage resultMessage = resultMessages.iterator().next();
String errorCode = resultMessage.getCode();
String errorText = resultMessage.getText();
if (errorCode == null && errorText == null) {
errorCode = rootErrorCode;
}
apiError = createApiError(request, errorCode, errorText,
resultMessage.getArgs());
} else {
apiError = createApiError(request, rootErrorCode,
defaultErrorMessage);
for (ResultMessage resultMessage : resultMessages.getList()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, resultMessage
.getCode(), resultMessage.getText(), resultMessage
.getArgs()));
}
}
return apiError;
}
}
5.16.5.7.3. ApiGlobalExceptionHandler.java¶
java/org/terasoluna/examples/rest/api/common/error/ApiGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.api.common.error;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.dao.OptimisticLockingFailureException;
import org.springframework.dao.PessimisticLockingFailureException;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotReadableException;
import org.springframework.validation.BindException;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionCodeResolver;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResultMessagesNotificationException;
@ControllerAdvice
public class ApiGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@Inject
ApiErrorCreator apiErrorCreator;
@Inject
ExceptionCodeResolver exceptionCodeResolver;
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(Exception ex,
Object body, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status,
WebRequest request) {
final Object apiError;
if (body == null) {
String errorCode = exceptionCodeResolver.resolveExceptionCode(ex);
apiError = apiErrorCreator.createApiError(request, errorCode, ex
.getLocalizedMessage());
} else {
apiError = body;
}
return ResponseEntity.status(status).headers(headers).body(apiError);
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
return handleBindingResult(ex, ex.getBindingResult(), headers, status,
request);
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleBindException(BindException ex,
HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
return handleBindingResult(ex, ex.getBindingResult(), headers, status,
request);
}
private ResponseEntity<Object> handleBindingResult(Exception ex,
BindingResult bindingResult, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
String errorCode = exceptionCodeResolver.resolveExceptionCode(ex);
ApiError apiError = apiErrorCreator.createBindingResultApiError(
request, errorCode, bindingResult, ex.getMessage());
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleHttpMessageNotReadable(
HttpMessageNotReadableException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
if (ex.getCause() instanceof Exception) {
return handleExceptionInternal((Exception) ex.getCause(), null,
headers, status, request);
} else {
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, null, headers, status, request);
}
}
@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleResourceNotFoundException(
ResourceNotFoundException ex, WebRequest request) {
return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, request);
}
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleBusinessException(BusinessException ex,
WebRequest request) {
return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.CONFLICT, request);
}
private ResponseEntity<Object> handleResultMessagesNotificationException(
ResultMessagesNotificationException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
String errorCode = exceptionCodeResolver.resolveExceptionCode(ex);
ApiError apiError = apiErrorCreator.createResultMessagesApiError(
request, errorCode, ex.getResultMessages(), ex.getMessage());
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
@ExceptionHandler({ OptimisticLockingFailureException.class,
PessimisticLockingFailureException.class })
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleLockingFailureException(Exception ex,
WebRequest request) {
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, null, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.CONFLICT, request);
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleSystemError(Exception ex,
WebRequest request) {
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, null, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, request);
}
}
5.16.5.8. Source code of the domain layer class created at the time of REST API implementation¶
Following files are excluded.
- JavaBean other than Entity
- Configuration files other than Dozer
5.16.5.8.1. Member.java¶
java/org/terasoluna/examples/rest/domain/model/Member.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Access;
import javax.persistence.AccessType;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.Transient;
import javax.persistence.Version;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import org.joda.time.LocalDate;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.CreatedDate;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.LastModifiedDate;
@Table(name = "t_member")
@Entity
public class Member implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Id
private String memberId;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
@Transient
private Gender gender;
private LocalDate dateOfBirth;
private String emailAddress;
private String telephoneNumber;
private String zipCode;
private String address;
@CreatedDate
private DateTime createdAt;
@LastModifiedDate
private DateTime lastModifiedAt;
@Version
private long version;
@OneToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name = "member_id")
private MemberCredential credential;
public String getMemberId() {
return memberId;
}
public void setMemberId(String memberId) {
this.memberId = memberId;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public Gender getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(Gender gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
@Access(AccessType.PROPERTY)
@Column(name = "gender")
public String getGenderCode() {
if (gender == null) {
return null;
} else {
return gender.getCode();
}
}
public void setGenderCode(String genderCode) {
this.gender = Gender.getByCode(genderCode);
}
public LocalDate getDateOfBirth() {
return dateOfBirth;
}
public void setDateOfBirth(LocalDate dateOfBirth) {
this.dateOfBirth = dateOfBirth;
}
public String getEmailAddress() {
return emailAddress;
}
public void setEmailAddress(String emailAddress) {
this.emailAddress = emailAddress;
}
public String getTelephoneNumber() {
return telephoneNumber;
}
public void setTelephoneNumber(String telephoneNumber) {
this.telephoneNumber = telephoneNumber;
}
public String getZipCode() {
return zipCode;
}
public void setZipCode(String zipCode) {
this.zipCode = zipCode;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public DateTime getCreatedAt() {
return createdAt;
}
public void setCreatedAt(DateTime createdAt) {
this.createdAt = createdAt;
}
public DateTime getLastModifiedAt() {
return lastModifiedAt;
}
public void setLastModifiedAt(DateTime lastModifiedAt) {
this.lastModifiedAt = lastModifiedAt;
}
public long getVersion() {
return version;
}
public void setVersion(long version) {
this.version = version;
}
public MemberCredential getCredential() {
return credential;
}
public void setCredential(MemberCredential credential) {
this.credential = credential;
}
}
5.16.5.8.2. MemberCredentia.java¶
java/org/terasoluna/examples/rest/domain/model/MemberCredential.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.Version;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.LastModifiedDate;
@Table(name = "t_member_credential")
@Entity
public class MemberCredential implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Id
private String memberId;
private String signId;
private String password;
private String previousPassword;
private DateTime passwordLastChangedAt;
@LastModifiedDate
private DateTime lastModifiedAt;
@Version
private long version;
public String getMemberId() {
return memberId;
}
public void setMemberId(String memberId) {
this.memberId = memberId;
}
public String getSignId() {
return signId;
}
public void setSignId(String signId) {
this.signId = signId;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getPreviousPassword() {
return previousPassword;
}
public void setPreviousPassword(String previousPassword) {
this.previousPassword = previousPassword;
}
public DateTime getPasswordLastChangedAt() {
return passwordLastChangedAt;
}
public void setPasswordLastChangedAt(DateTime passwordLastChangedAt) {
this.passwordLastChangedAt = passwordLastChangedAt;
}
public DateTime getLastModifiedAt() {
return lastModifiedAt;
}
public void setLastModifiedAt(DateTime lastModifiedAt) {
this.lastModifiedAt = lastModifiedAt;
}
public long getVersion() {
return version;
}
public void setVersion(long version) {
this.version = version;
}
}
5.16.5.8.3. Gender.java¶
java/org/terasoluna/examples/rest/domain/model/Gender.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.model;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
public enum Gender {
UNKNOWN("0"), MEN("1"), WOMEN("2");
private static final Map<String, Gender> genderMap;
static {
Map<String, Gender> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Gender gender : values()) {
map.put(gender.code, gender);
}
genderMap = Collections.unmodifiableMap(map);
}
private final String code;
private Gender(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public static Gender getByCode(String code) {
Gender gender = genderMap.get(code);
Assert.notNull(gender, "gender code is invalid. code : " + code);
return gender;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
}
5.16.5.8.4. MemberRepository.java¶
java/org/terasoluna/examples/rest/domain/repository/member/MemberRepository.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.repository.member;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
import org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.model.Member;
public interface MemberRepository extends JpaRepository<Member, String> {
@Query("SELECT m FROM Member m"
+ " WHERE m.firstName LIKE :name% ESCAPE '~'"
+ " OR m.lastName LIKE :name% ESCAPE '~'")
Page<Member> findPageByContainsName(@Param("name") String name,
Pageable pageable);
}
5.16.5.8.5. MemberService.java¶
java/org/terasoluna/examples/rest/domain/service/member/MemberService.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.service.member;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.model.Member;
public interface MemberService {
Page<Member> searchMembers(String name, Pageable pageable);
Member getMember(String memberId);
Member createMember(Member creatingMember);
Member updateMember(String memberId, Member updatingMember);
void deleteMember(String memberId);
}
5.16.5.8.6. MemberServiceImpl.java¶
java/org/terasoluna/examples/rest/domain/service/member/MemberServiceImpl.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.service.member;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import javax.inject.Named;
import org.dozer.Mapper;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import org.springframework.dao.DataIntegrityViolationException;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.message.DomainMessageCodes;
import org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.model.Member;
import org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.model.MemberCredential;
import org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.repository.member.MemberRepository;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.date.jodatime.JodaTimeDateFactory;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessages;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.query.QueryEscapeUtils;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.sequencer.Sequencer;
@Transactional
@Service
public class MemberServiceImpl implements MemberService {
@Inject
MemberRepository memberRepository;
@Inject
@Named("memberIdSequencer")
Sequencer<String> sequencer;
@Inject
JodaTimeDateFactory dateFactory;
@Inject
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Inject
Mapper beanMapper;
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public Page<Member> searchMembers(String name, Pageable pageable) {
// escape to like condition value
String escapedName = QueryEscapeUtils.toLikeCondition(name);
// find members that matches with search criteria
return memberRepository.findPageByContainsName(escapedName, pageable);
}
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public Member getMember(String memberId) {
// find member
Member member = memberRepository.findOne(memberId);
if (member == null) {
// If member is not exists
throw new ResourceNotFoundException(ResultMessages.error().add(
DomainMessageCodes.E_EX_MM_5001, memberId));
}
return member;
}
public Member createMember(Member creatingMember) {
MemberCredential creatingCredential = creatingMember.getCredential();
// get processing current date time
DateTime currentDateTime = dateFactory.newDateTime();
// set id
String newMemberId = sequencer.getNext();
creatingMember.setMemberId(newMemberId);
creatingCredential.setMemberId(newMemberId);
// decide sign id(email-address)
String signId = creatingCredential.getSignId();
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(signId)) {
signId = creatingMember.getEmailAddress();
creatingCredential.setSignId(signId.toLowerCase());
}
// encrypt password
String rawPassword = creatingCredential.getPassword();
creatingCredential.setPassword(passwordEncoder.encode(rawPassword));
creatingCredential.setPasswordLastChangedAt(currentDateTime);
// save member & member credential
try {
return memberRepository.saveAndFlush(creatingMember);
} catch (DataIntegrityViolationException e) {
// If sign id is already used
throw new BusinessException(ResultMessages.error().add(
DomainMessageCodes.E_EX_MM_8001,
creatingCredential.getSignId()), e);
}
}
public Member updateMember(String memberId, Member updatingMember) {
// get member
Member member = getMember(memberId);
// override updating member attributes
beanMapper.map(updatingMember, member, "member.update");
// save updating member
return memberRepository.save(member);
}
public void deleteMember(String memberId) {
// delete member
memberRepository.delete(memberId);
}
}
5.16.5.8.7. DomainMessageCodes.java¶
java/org/terasoluna/examples/rest/domain/message/DomainMessageCodes.java
package org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.message;
/**
* Message codes of domain layer message.
* @author DomainMessageCodesGenerator
*/
public class DomainMessageCodes {
private DomainMessageCodes() {
// NOP
}
/** e.ex.mm.5001=Specified member not found. member id : {0} */
public static final String E_EX_MM_5001 = "e.ex.mm.5001";
/** e.ex.mm.8001=Cannot use specified sign id. sign id : {0} */
public static final String E_EX_MM_8001 = "e.ex.mm.8001";
}
5.16.5.8.8. member-mapping.xml¶
Member object.memberId, credential, createdAt and version) are not copied.resources/META-INF/dozer/member-mapping.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<mappings xmlns="http://dozer.sourceforge.net" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://dozer.sourceforge.net
http://dozer.sourceforge.net/schema/beanmapping.xsd">
<mapping map-id="member.update">
<class-a>org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.model.Member</class-a>
<class-b>org.terasoluna.examples.rest.domain.model.Member</class-b>
<field-exclude>
<a>memberId</a>
<b>memberId</b>
</field-exclude>
<field-exclude>
<a>credential</a>
<b>credential</b>
</field-exclude>
<field-exclude>
<a>createdAt</a>
<b>createdAt</b>
</field-exclude>
<field-exclude>
<a>lastModifiedAt</a>
<b>lastModifiedAt</b>
</field-exclude>
<field-exclude>
<a>version</a>
<b>version</b>
</field-exclude>
</mapping>
</mappings>