11.2. チュートリアル(Todoアプリケーション REST編)¶
Caution
本バージョンの内容は既に古くなっています。最新のガイドラインはこちらからご参照ください。
目次
11.2.1. はじめに¶
11.2.1.1. このチュートリアルで学ぶこと¶
- TERASOLUNA Server Framework for Java (5.x)による基本的なRESTful Webサービスの構築方法
11.2.1.2. 対象読者¶
- チュートリアル(Todoアプリケーション)を実施している。
11.2.1.3. 検証環境¶
| 種別 | プロダクト |
|---|---|
| REST Client | DHC REST Client 1.2.3 |
| 上記以外のプロダクト | チュートリアル(Todoアプリケーション)と同様 |
Note
上記のDHC REST Clientのリンク先はTalend API Testerに置き換わっている。 以降の記述ではDHC REST ClientをTalend API Testerに読み替えられたい。
11.2.2. 環境構築¶
Java, STS, Maven, Google Chromeについては、チュートリアル(Todoアプリケーション)を実施する事でインストール済みの状態である事を前提とする。
11.2.2.1. DHCのインストール¶
RESTクライアントとして、Chromeの拡張機能である「DHC」をインストールする。
DHC REST Client にアクセスし、「+ ADD TO CHROME」ボタンを押下する。
「Add app」ボタンを押下する。

Chromeの拡張機能一覧を開く(ブラウザのアドレスバーに「chrome://extensions/」を指定して開く)と、DHCが追加されている。
11.2.2.2. プロジェクト作成¶
本チュートリアルでは、「チュートリアル(Todoアプリケーション)」で作成したプロジェクトに対して、 RESTful Webサービスを追加する手順となっている。
そのため、「チュートリアル(Todoアプリケーション)」で作成したプロジェクトが残っていない場合は、 再度「チュートリアル(Todoアプリケーション)」を実施してプロジェクトを作成してほしい。
Note
再度「チュートリアル(Todoアプリケーション)」を実施する場合は、 ドメイン層の作成まで行えば本チュートリアルを進める事ができる。
11.2.3. REST APIの作成¶
本チュートリアルでは、todoテーブルで管理しているデータ(以降、「Todoリソース」呼ぶ)をWeb上に公開するためのREST APIを作成する。
API名
|
HTTP
メソッド
|
パス
|
ステータス
コード
|
説明
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
GET Todos
|
GET
|
/api/v1/todos |
200
(OK)
|
Todoリソースを全件取得する。
|
POST Todos
|
POST
|
/api/v1/todos |
201
(Created)
|
Todoリソースを新規作成する。
|
GET Todo
|
GET
|
/api/v1/todos/{todoId} |
200
(OK)
|
Todoリソースを一件取得する。
|
PUT Todo
|
PUT
|
/api/v1/todos/{todoId} |
200
(OK)
|
Todoリソースを完了状態に更新する。
|
DELETE Todo
|
DELETE
|
/api/v1/todos/{todoId} |
204
(No Content)
|
Todoリソースを削除する。
|
Tip
パス内に含まれている{todoId}は、パス変数と呼ばれ、任意の可変値を扱う事ができる。
パス変数を使用する事で、GET /api/v1/todos/123とGET /api/v1/todos/456を同じAPIで扱う事ができる。
本チュートリアルでは、Todoを一意に識別するためのID(Todo ID)をパス変数として扱っている。
11.2.3.1. API仕様¶
11.2.3.1.1. GET Todos¶
[リクエスト]
> GET /todo/api/v1/todos HTTP/1.1
[レスポンス]
作成済みのTodoリソースのリストをJSON形式で返却する。
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
[{"todoId":"9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558","todoTitle":"Hello World!","finished":false,"createdAt":"2014-02-25T02:21:48.493+0000"}]
11.2.3.1.2. POST Todos¶
[リクエスト]
新規作成するTodoリソースの内容(タイトル)をJSON形式で指定する。
> POST /todo/api/v1/todos HTTP/1.1
> Content-Type: application/json
> Content-Length: 29
>
{"todoTitle": "Study Spring"}
[レスポンス]
作成したTodoリソースをJSON形式で返却する。
< HTTP/1.1 201 Created
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"todoId":"d6101d61-b22c-48ee-9110-e106af6a1404","todoTitle":"Study Spring","finished":false,"createdAt":"2014-02-25T04:05:58.752+0000"}
11.2.3.1.3. GET Todo¶
[リクエスト]
todoId」に、取得対象のTodoリソースのIDを指定する。todoId」に9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558を指定している。> GET /todo/api/v1/todos/9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558 HTTP/1.1
[レスポンス]
パス変数「todoId」に一致するTodoリソースをJSON形式で返却する。
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"todoId":"9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558","todoTitle":"Hello World!","finished":false,"createdAt":"2014-02-25T02:21:48.493+0000"}
11.2.3.1.4. PUT Todo¶
[リクエスト]
todoId」に、更新対象のTodoのIDを指定する。> PUT /todo/api/v1/todos/9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558 HTTP/1.1
[レスポンス]
パス変数「todoId」に一致するTodoリソースを完了状態(finishedフィールドをtrue)に更新し、JSON形式で返却する。
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"todoId":"9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558","todoTitle":"Hello World!","finished":true,"createdAt":"2014-02-25T02:21:48.493+0000"}
11.2.3.1.5. DELETE Todo¶
[リクエスト]
パス変数「todoId」に、削除対象のTodoリソースのIDを指定する。
> DELETE /todo/api/v1/todos/9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558 HTTP/1.1
[レスポンス]
DELETE Todoでは、Todoリソースの削除が完了した事で返却するリソースが存在しなくなった事を示すために、レスポンスBODYを返却しないインタフェース仕様にしている。
< HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
11.2.3.1.6. エラー応答¶
チュートリアル(Todoアプリケーション)では、エラーメッセージはプログラムの中でハードコーディングしていたが、本チュートリアルでは、エラーメッセージはエラーコードをキーにプロパティファイルから取得するように修正する。
[入力チェックエラー発生時のレスポンス仕様]
< HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"code":"E400","message":"[E400] The requested Todo contains invalid values.","details":[{"code":"NotNull","message":"todoTitle may not be null.",target:"todoTitle"}]}
[業務エラー発生時のレスポンス仕様]
< HTTP/1.1 409 Conflict
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"code":"E002","message":"[E002] The requested Todo is already finished. (id=353fb5db-151a-4696-9b4a-b958358a5ab3)"}
[リソース未検出時のレスポンス仕様]
< HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"code":"E404","message":"[E404] The requested Todo is not found. (id=353fb5db-151a-4696-9b4a-b958358a5ab2)"}
[システムエラー発生時のレスポンス仕様]
< HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server Error
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"code":"E500","message":"[E500] System error occurred."}
11.2.3.2. REST API用のDispatcherServletを用意¶
まず、REST API用のリクエストを処理するためのDispatcherServletの定義を追加する。
11.2.3.2.1. web.xmlの修正¶
src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
version="3.0">
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!-- Root ApplicationContext -->
<param-value>
classpath*:META-INF/spring/applicationContext.xml
classpath*:META-INF/spring/spring-security.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.terasoluna.gfw.web.logging.HttpSessionEventLoggingListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<filter>
<filter-name>MDCClearFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.terasoluna.gfw.web.logging.mdc.MDCClearFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>MDCClearFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter>
<filter-name>exceptionLoggingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>exceptionLoggingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter>
<filter-name>XTrackMDCPutFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.terasoluna.gfw.web.logging.mdc.XTrackMDCPutFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>XTrackMDCPutFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!-- (1) -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>restApiServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!-- ApplicationContext for Spring MVC (REST) -->
<param-value>classpath*:META-INF/spring/spring-mvc-rest.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<!-- (2) -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>restApiServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/api/v1/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!-- ApplicationContext for Spring MVC -->
<param-value>classpath*:META-INF/spring/spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<jsp-config>
<jsp-property-group>
<url-pattern>*.jsp</url-pattern>
<el-ignored>false</el-ignored>
<page-encoding>UTF-8</page-encoding>
<scripting-invalid>false</scripting-invalid>
<include-prelude>/WEB-INF/views/common/include.jsp</include-prelude>
</jsp-property-group>
</jsp-config>
<error-page>
<error-code>500</error-code>
<location>/WEB-INF/views/common/error/systemError.jsp</location>
</error-page>
<error-page>
<error-code>404</error-code>
<location>/WEB-INF/views/common/error/resourceNotFoundError.jsp</location>
</error-page>
<error-page>
<exception-type>java.lang.Exception</exception-type>
<location>/WEB-INF/views/common/error/unhandledSystemError.html</location>
</error-page>
<session-config>
<!-- 30min -->
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
<cookie-config>
<http-only>true</http-only>
<!-- <secure>true</secure> -->
</cookie-config>
<tracking-mode>COOKIE</tracking-mode>
</session-config>
</web-app>
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
初期化パラメータ「
contextConfigLocation」に、REST用のSpring MVC設定ファイルを指定する。本チュートリアルでは、クラスパス上にある「
META-INF/spring/spring-mvc-rest.xml」を指定している。 |
(2)
|
<url-pattern>要素に、REST API用のDispatcherServletにマッピングするURLのパターンを指定する。本チュートリアルでは、
/api/v1/から始まる場合はリクエストをREST APIへのリクエストとしてREST API用のDispatcherServletへマッピングしている。 |
11.2.3.2.2. spring-mvc-rest.xmlの作成¶

src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/spring-mvc-rest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util https://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
">
<!-- (1) -->
<context:property-placeholder
location="classpath*:/META-INF/spring/*.properties" />
<!-- (2) -->
<bean id="jsonMessageConverter"
class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter">
<property name="objectMapper" ref="objectMapper" />
</bean>
<bean id="objectMapper" class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.Jackson2ObjectMapperFactoryBean">
<!-- (3) -->
<property name="dateFormat">
<bean class="com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.util.StdDateFormat" />
</property>
</bean>
<!-- (4) -->
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:message-converters register-defaults="false">
<ref bean="jsonMessageConverter" />
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example.todo.api" /> <!-- (5) -->
<!-- (6) -->
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**" />
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/resources/**" />
<bean
class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.logging.TraceLoggingInterceptor" />
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
<!-- (7) -->
<!-- Setting AOP. -->
<bean id="handlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor"
class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor">
<property name="exceptionLogger" ref="exceptionLogger" />
</bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="handlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor"
pointcut="execution(* org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver.resolveException(..))" />
</aop:config>
</beans>
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
アプリケーション層のコンポーネントでプロパティファイルに定義されている値を参照する必要がある場合は、<context:property-placeholder>要素を使用してプロパティファイルを読み込む必要がある。 |
(2)
|
Controllerの引数と返り値で扱うJavaBeanをシリアライズ/デシリアライズするためのクラス(
|
(3)
|
本チュートリアルでは、 |
(4)
|
Spring MVCのデフォルト設定ではアプリケーションのクラスパスに応じて使用可能な |
(5)
|
REST API用のパッケージ配下のコンポーネントをスキャンする。 本チュートリアルでは、REST API用のパッケージを |
(6)
|
Controllerの処理開始、終了時の情報をログに出力するために、共通ライブラリから提供されているTraceLoggingInterceptorを定義する。 |
(7)
|
Spring MVCのフレームワークでハンドリングされた例外を、ログ出力するためのAOP定義を指定する。 |
11.2.3.3. REST API用のSpring Securityの定義追加¶
src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/spring-security.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security https://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
">
<sec:http pattern="/resources/**" security="none"/>
<!-- (1) -->
<sec:http pattern="/api/v1/**" security="none"/>
<sec:http>
<sec:form-login/>
<sec:logout/>
<sec:access-denied-handler ref="accessDeniedHandler"/>
<sec:custom-filter ref="userIdMDCPutFilter" after="ANONYMOUS_FILTER"/>
<sec:session-management />
</sec:http>
<sec:authentication-manager />
<!-- CSRF Protection -->
<bean id="accessDeniedHandler"
class="org.springframework.security.web.access.DelegatingAccessDeniedHandler">
<constructor-arg index="0">
<map>
<entry
key="org.springframework.security.web.csrf.InvalidCsrfTokenException">
<bean
class="org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandlerImpl">
<property name="errorPage"
value="/WEB-INF/views/common/error/invalidCsrfTokenError.jsp" />
</bean>
</entry>
<entry
key="org.springframework.security.web.csrf.MissingCsrfTokenException">
<bean
class="org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandlerImpl">
<property name="errorPage"
value="/WEB-INF/views/common/error/missingCsrfTokenError.jsp" />
</bean>
</entry>
</map>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1">
<bean
class="org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandlerImpl">
<property name="errorPage"
value="/WEB-INF/views/common/error/accessDeniedError.jsp" />
</bean>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- Put UserID into MDC -->
<bean id="userIdMDCPutFilter" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.security.web.logging.UserIdMDCPutFilter">
</bean>
</beans>
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
REST API用のSpring Securityのセキュリティ機能を無効にする定義を追加する。
<sec:http>要素のpattern属性に、REST API用のリクエストパスのURLパターンを指定している。本チュートリアルでは
/api/v1/で始まるリクエストパスをREST API用のリクエストパスとして扱う。 |
11.2.3.4. REST API用パッケージの作成¶
REST API用のクラスを格納するパッケージを作成する。
apiとして、配下にリソース毎のパッケージ(リソース名の小文字)を作成する事を推奨する。com.example.todo.api.todoパッケージを作成する。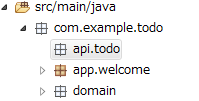
Note
作成したパッケージに格納するクラスは、通常以下の3種類となる。 作成するクラスのクラス名は、以下のネーミングルールとする事を推奨する。
[リソース名]Resource[リソース名]RestController[リソース名]Helper(必要に応じて)
本チュートリアルで扱うリソースのリソース名がTodoなので、
TodoResourceTodoRestController
を作成する。
本チュートリアルでは、TodoRestHelperは作成しない。
11.2.3.5. Resourceクラスの作成¶
TodoResourceクラスを作成する。src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/todo/TodoResource.java
package com.example.todo.api.todo;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
public class TodoResource implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String todoId;
@NotNull
@Size(min = 1, max = 30)
private String todoTitle;
private boolean finished;
private Date createdAt;
public String getTodoId() {
return todoId;
}
public void setTodoId(String todoId) {
this.todoId = todoId;
}
public String getTodoTitle() {
return todoTitle;
}
public void setTodoTitle(String todoTitle) {
this.todoTitle = todoTitle;
}
public boolean isFinished() {
return finished;
}
public void setFinished(boolean finished) {
this.finished = finished;
}
public Date getCreatedAt() {
return createdAt;
}
public void setCreatedAt(Date createdAt) {
this.createdAt = createdAt;
}
}
Note
DomainObjectクラス(本チュートリアルではTodoクラス)があるにも関わらず、Resourceクラスを作成する理由は、
クライアントとの入出力で使用するインタフェース上の情報と、業務処理で扱う情報は必ずしも一致しないためである。
これらを混同して使用すると、アプリケーション層の影響がドメイン層におよび、保守性を低下させる。 DomainObjectとResourceクラスは別々に作成し、Dozer等のBeanMapperを利用してデータ変換を行うことを推奨する。
ResourceクラスはFormクラスと役割が似ているが、FormクラスはHTMLの<form> タグをJavaBeanで表現したもの、
ResourceクラスはREST APIの入出力をJavaBeanで表現したものであり、本質的には異なるものである。
ただし、実体としてはBean Validationのアノテーションを付与したJavaBeanであり、Controllerクラスと同じパッケージに格納することから、 Formクラスとほぼ同じである。
11.2.3.6. Controllerクラスの作成¶
TodoResourceのREST APIを提供するTodoRestControllerクラスを作成する。
src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/todo/TodoRestController.java
package com.example.todo.api.todo;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController // (1)
@RequestMapping("todos") // (2)
public class TodoRestController {
}
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
@RestControllerを指定する。@RestControllerの詳細については、 RestControllerクラスの作成 を参照されたい。 |
(2)
|
リソースのパスを指定する。
/api/v1/の部分はweb.xmlに定義しているため、この設定を行うことで/<contextPath>/api/v1/todosというパスにマッピングされる。 |
11.2.3.6.1. GET Todosの実装¶
作成済みのTodoリソースを全件取得するAPI(GET Todos)の処理を、TodoRestControllerのgetTodosメソッドに実装する。
src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/todo/TodoRestController.java
package com.example.todo.api.todo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import com.github.dozermapper.core.Mapper;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.todo.domain.model.Todo;
import com.example.todo.domain.service.todo.TodoService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("todos")
public class TodoRestController {
@Inject
TodoService todoService;
@Inject
Mapper beanMapper;
@GetMapping // (1)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) // (2)
public List<TodoResource> getTodos() {
Collection<Todo> todos = todoService.findAll();
List<TodoResource> todoResources = new ArrayList<>();
for (Todo todo : todos) {
todoResources.add(beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class)); // (3)
}
return todoResources; // (4)
}
}
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
メソッドがGETのリクエストを処理するために、
@GetMappingアノテーションを設定する。 |
(2)
|
応答するHTTPステータスコードを
@ResponseStatusアノテーションに指定する。HTTPステータスとして、”200 OK”を設定するため、
value属性にはHttpStatus.OKを設定する。 |
(3)
|
TodoServiceのfindAllメソッドから返却されたTodoオブジェクトを、応答するJSONを表現するTodoResource型のオブジェクトに変換する。TodoとTodoResourceの変換処理は、Dozerのcom.github.dozermapper.core.Mapperインタフェースを使うと便利である。 |
(4)
|
List<TodoResource>オブジェクトを返却することで、spring-mvc-rest.xmlに定義したMappingJackson2HttpMessageConverterによってJSONにシリアライズされる。 |
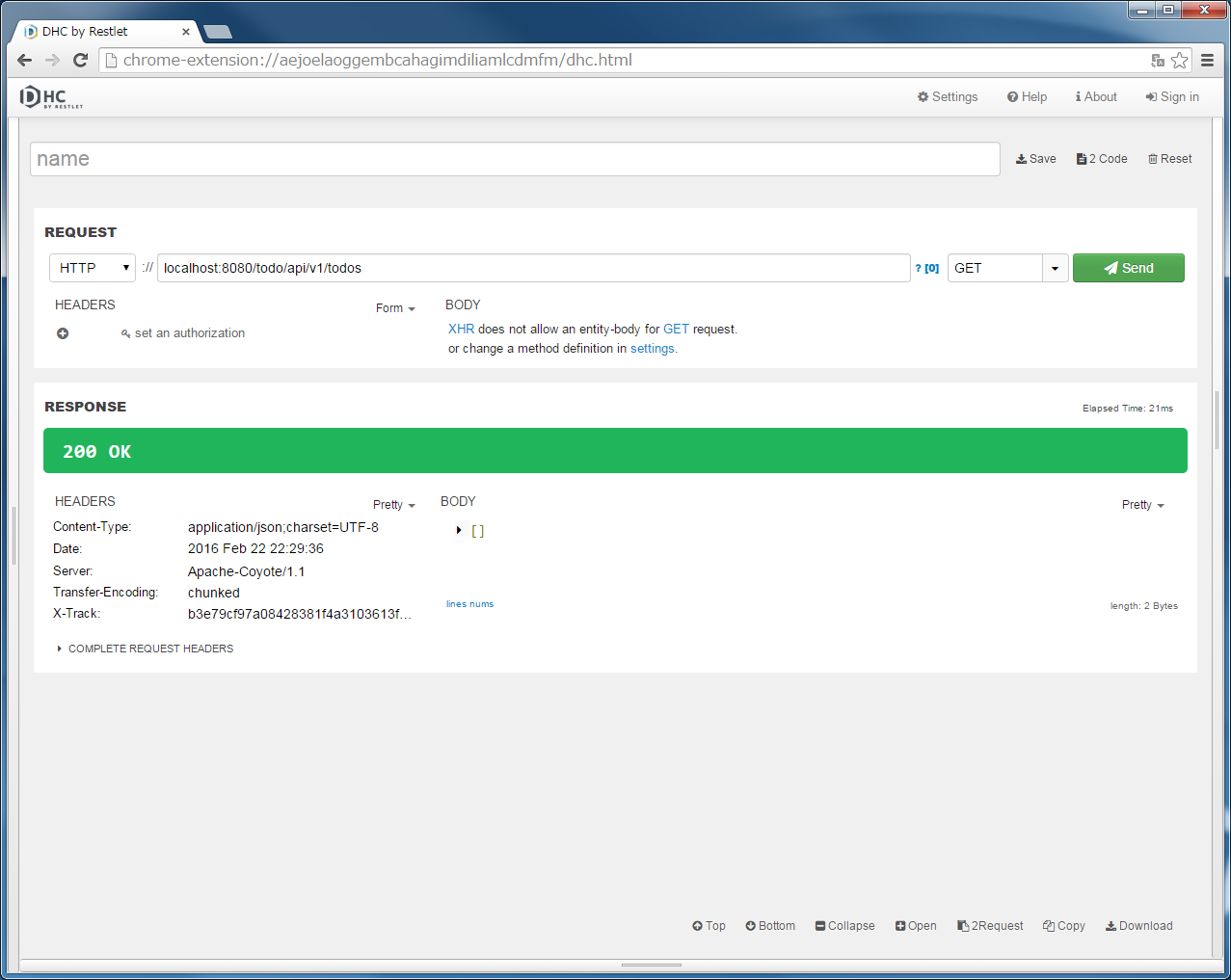
Application Serverを起動し、実装したAPIの動作確認を行う。
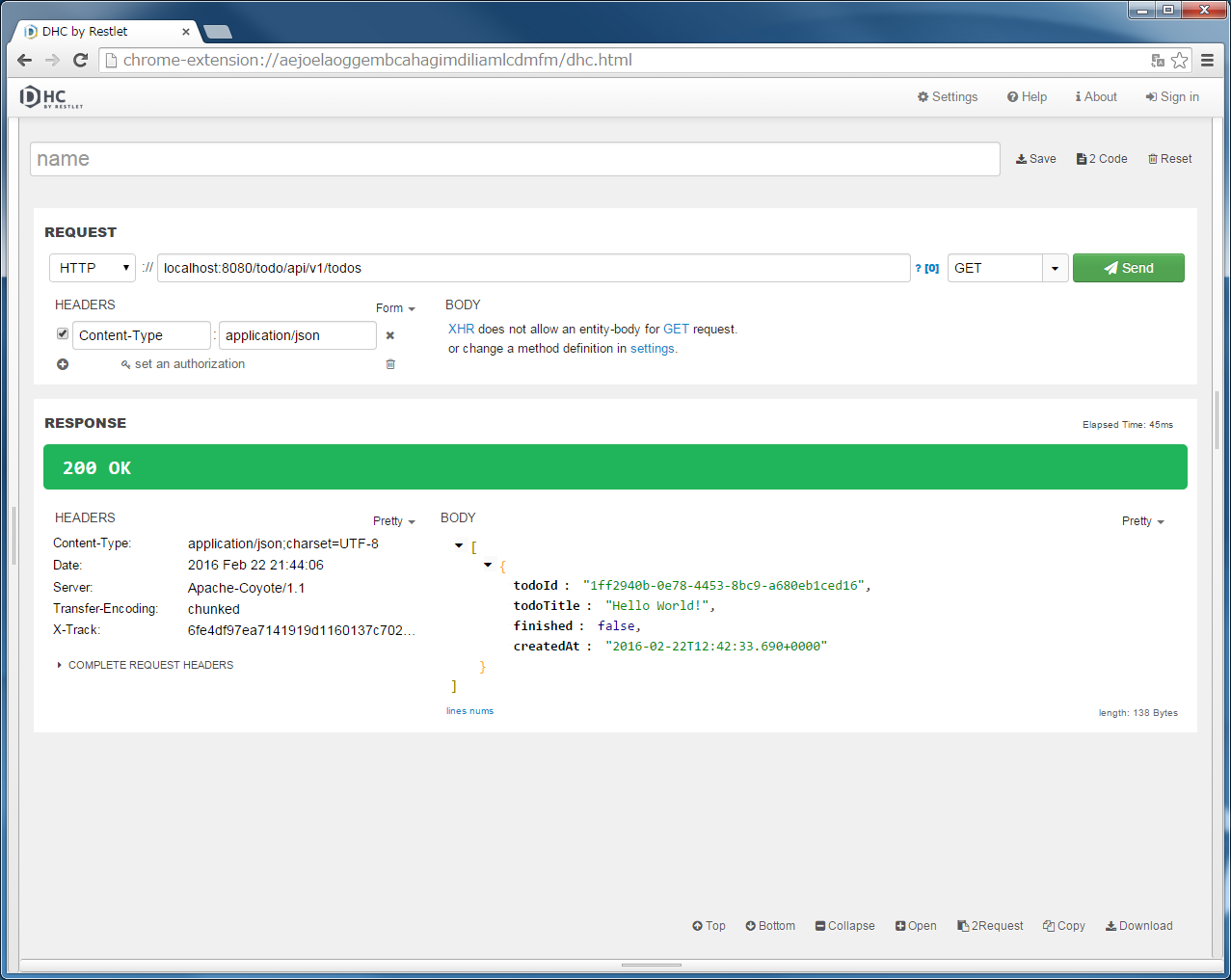
localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todosを入力し、メソッドにGETを指定して、”Send”ボタンをクリックする。[]が返却される。11.2.3.6.2. POST Todosの実装¶
Todoリソースを新規作成するAPI(POST Todos)の処理を、TodoRestControllerのpostTodosメソッドに実装する。
src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/todo/TodoRestController.java
package com.example.todo.api.todo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import com.github.dozermapper.core.Mapper;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.todo.domain.model.Todo;
import com.example.todo.domain.service.todo.TodoService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("todos")
public class TodoRestController {
@Inject
TodoService todoService;
@Inject
Mapper beanMapper;
@GetMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public List<TodoResource> getTodos() {
Collection<Todo> todos = todoService.findAll();
List<TodoResource> todoResources = new ArrayList<>();
for (Todo todo : todos) {
todoResources.add(beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class));
}
return todoResources;
}
@PostMapping // (1)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED) // (2)
public TodoResource postTodos(@RequestBody @Validated TodoResource todoResource) { // (3)
Todo createdTodo = todoService.create(beanMapper.map(todoResource, Todo.class)); // (4)
TodoResource createdTodoResponse = beanMapper.map(createdTodo, TodoResource.class); // (5)
return createdTodoResponse; // (6)
}
}
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
メソッドがPOSTのリクエストを処理するために、
@PostMappingアノテーションを設定する。 |
(2)
|
応答するHTTPステータスコードを
@ResponseStatusアノテーションに指定する。HTTPステータスとして、”201 Created”を設定するため、
value属性にはHttpStatus.CREATEDを設定する。 |
(3)
|
HTTPリクエストのBody(JSON)をJavaBeanにマッピングするために、
@RequestBodyアノテーションをマッピング対象のTodoResourceクラスに付与する。また、入力チェックするために
@Validatedも付与する。例外ハンドリングは別途行う必要がある。 |
(4)
|
TodoResourceをTodoクラスに変換後、TodoServiceのcreateメソッドを実行し、Todoリソースを新規作成する。 |
(5)
|
TodoServiceのcreateメソッドによって新規作成されたTodoオブジェクトを、応答するJSONを表現するTodoResource型に変換する。 |
(6)
|
TodoResourceオブジェクトを返却することで、spring-mvc-rest.xmlに定義したMappingJackson2HttpMessageConverterによってJSONにシリアライズされる。 |
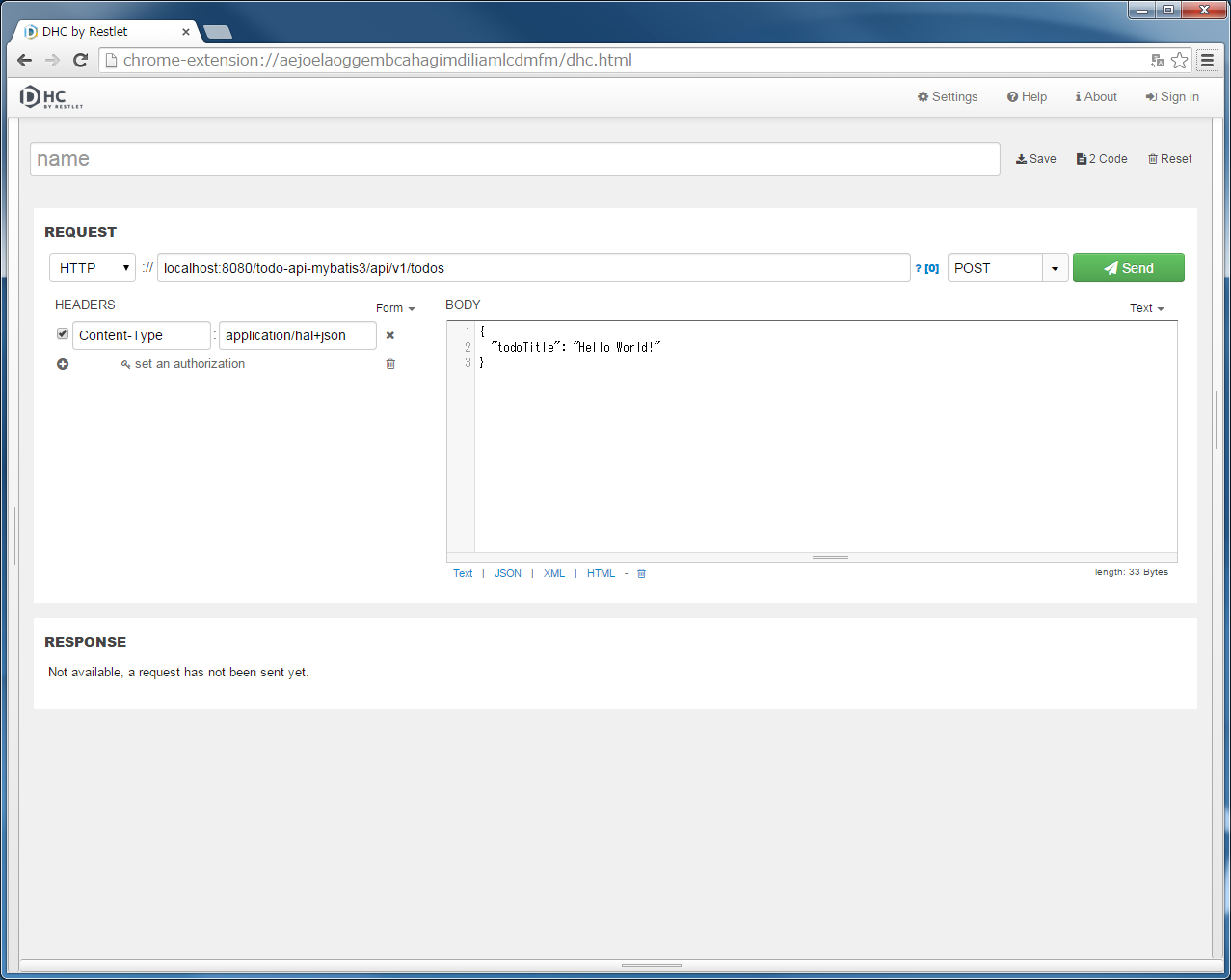
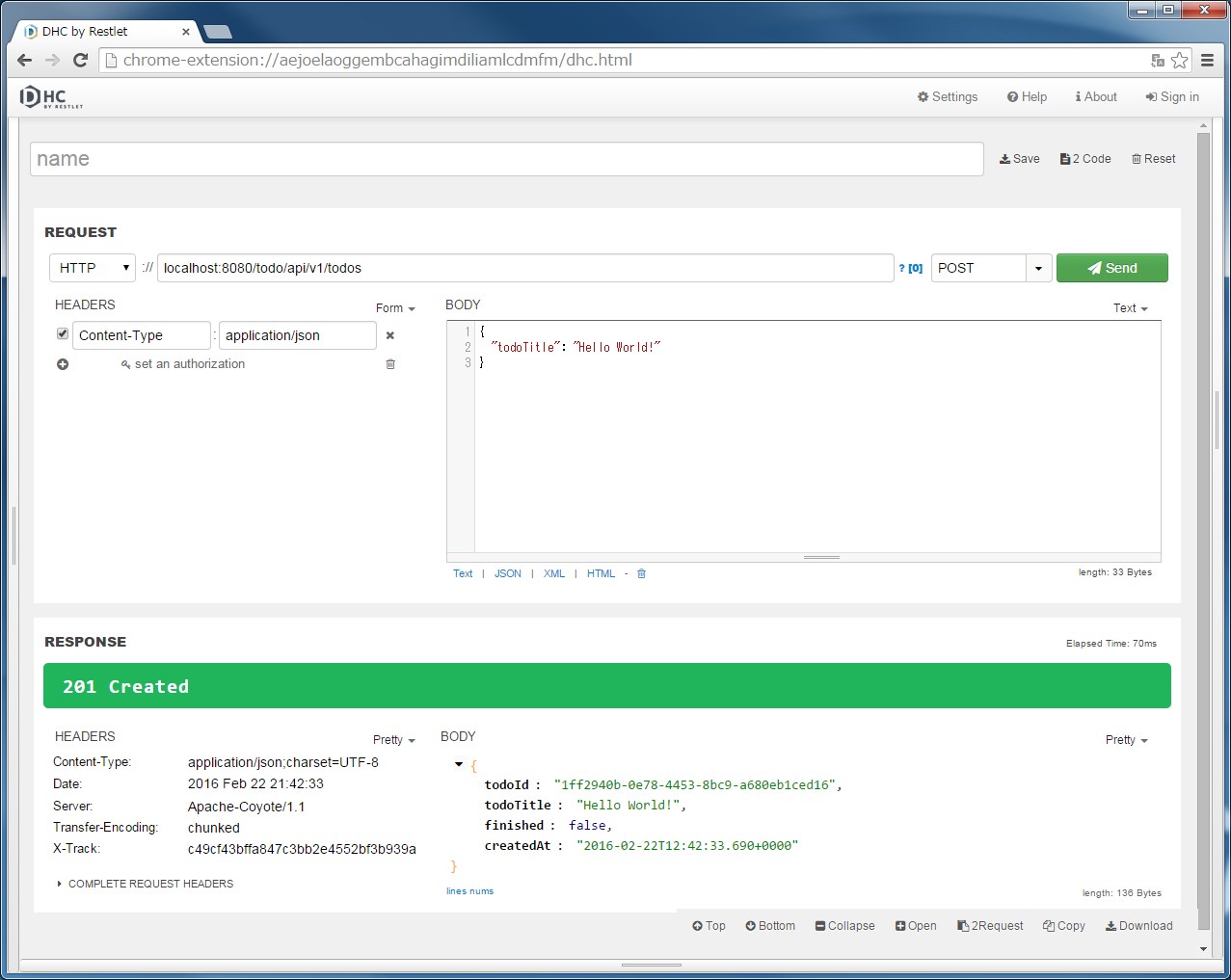
localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todosを入力し、メソッドにPOSTを指定する。{
"todoTitle": "Hello World!"
}
また、「REQUEST」の「HEADERS」の「+」ボタンでHTTPヘッダーを追加し、「Content-Type」に「application/json」を設定後、”Send”ボタンをクリックする。
“201 Created”のHTTPステータスが返却され、「RESPONSE」の「Body」に新規作成されたTodoリソースのJSONが表示される。
この状態で再びGET Todosを実行すると、作成したTodoリソースを含む配列が返却される。
11.2.3.6.3. GET Todoの実装¶
チュートリアル(Todoアプリケーション)では、TodoServiceに一件取得用のメソッド(findOne)を作成しなかったため、
TodoServiceとTodoServiceImplに以下のハイライト部を修正・追加する。
findOneメソッドの定義を追加する。src/main/java/com/example/todo/domain/service/todo/TodoService.javapackage com.example.todo.domain.service.todo;
import java.util.Collection;
import com.example.todo.domain.model.Todo;
public interface TodoService {
Todo findOne(String todoId);
Collection<Todo> findAll();
Todo create(Todo todo);
Todo finish(String todoId);
void delete(String todoId);
}
findOneメソッド呼び出し時に開始されるトランザクションを読み取り専用に設定し、アクセス修飾子をpublicに変更してfindAllメソッドの上に移動する。src/main/java/com/example/todo/domain/service/todo/TodoServiceImpl.javapackage com.example.todo.domain.service.todo;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.UUID;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessage;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessages;
import com.example.todo.domain.model.Todo;
import com.example.todo.domain.repository.todo.TodoRepository;
@Service
@Transactional
public class TodoServiceImpl implements TodoService {
private static final long MAX_UNFINISHED_COUNT = 5;
@Inject
TodoRepository todoRepository;
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public Todo findOne(String todoId) {
return todoRepository.findById(todoId).orElseThrow(() -> {
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error();
messages.add(ResultMessage
.fromText("[E404] The requested Todo is not found. (id="
+ todoId + ")"));
return new ResourceNotFoundException(messages);
});
}
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public Collection<Todo> findAll() {
return todoRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public Todo create(Todo todo) {
long unfinishedCount = todoRepository.countByFinished(false);
if (unfinishedCount >= MAX_UNFINISHED_COUNT) {
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error();
messages.add(ResultMessage
.fromText("[E001] The count of un-finished Todo must not be over "
+ MAX_UNFINISHED_COUNT + "."));
throw new BusinessException(messages);
}
String todoId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Date createdAt = new Date();
todo.setTodoId(todoId);
todo.setCreatedAt(createdAt);
todo.setFinished(false);
todoRepository.create(todo);
/* REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA
todoRepository.save(todo);
REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA */
return todo;
}
@Override
public Todo finish(String todoId) {
Todo todo = findOne(todoId);
if (todo.isFinished()) {
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error();
messages.add(ResultMessage
.fromText("[E002] The requested Todo is already finished. (id="
+ todoId + ")"));
throw new BusinessException(messages);
}
todo.setFinished(true);
todoRepository.update(todo);
/* REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA
todoRepository.save(todo);
REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA */
return todo;
}
@Override
public void delete(String todoId) {
Todo todo = findOne(todoId);
todoRepository.delete(todo);
}
}
TodoRestControllerのgetTodoメソッドに実装する。src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/todo/TodoRestController.javapackage com.example.todo.api.todo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import com.github.dozermapper.core.Mapper;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.todo.domain.model.Todo;
import com.example.todo.domain.service.todo.TodoService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("todos")
public class TodoRestController {
@Inject
TodoService todoService;
@Inject
Mapper beanMapper;
@GetMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public List<TodoResource> getTodos() {
Collection<Todo> todos = todoService.findAll();
List<TodoResource> todoResources = new ArrayList<>();
for (Todo todo : todos) {
todoResources.add(beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class));
}
return todoResources;
}
@PostMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public TodoResource postTodos(@RequestBody @Validated TodoResource todoResource) {
Todo createdTodo = todoService.create(beanMapper.map(todoResource, Todo.class));
TodoResource createdTodoResponse = beanMapper.map(createdTodo, TodoResource.class);
return createdTodoResponse;
}
@GetMapping("{todoId}") // (1)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public TodoResource getTodo(@PathVariable("todoId") String todoId) { // (2)
Todo todo = todoService.findOne(todoId); // (3)
TodoResource todoResource = beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class);
return todoResource;
}
}
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
メソッドがGETのリクエストを処理するために、
@GetMappingアノテーションを設定する。パスから
todoIdを取得するために、value属性にパス変数を指定する。 |
(2)
|
@PathVariableアノテーションのvalue属性に、todoIdを取得するためのパス変数名を指定する。 |
(3)
|
パス変数から取得した
todoIdを使用して、Todoリソースを一件取得する。 |
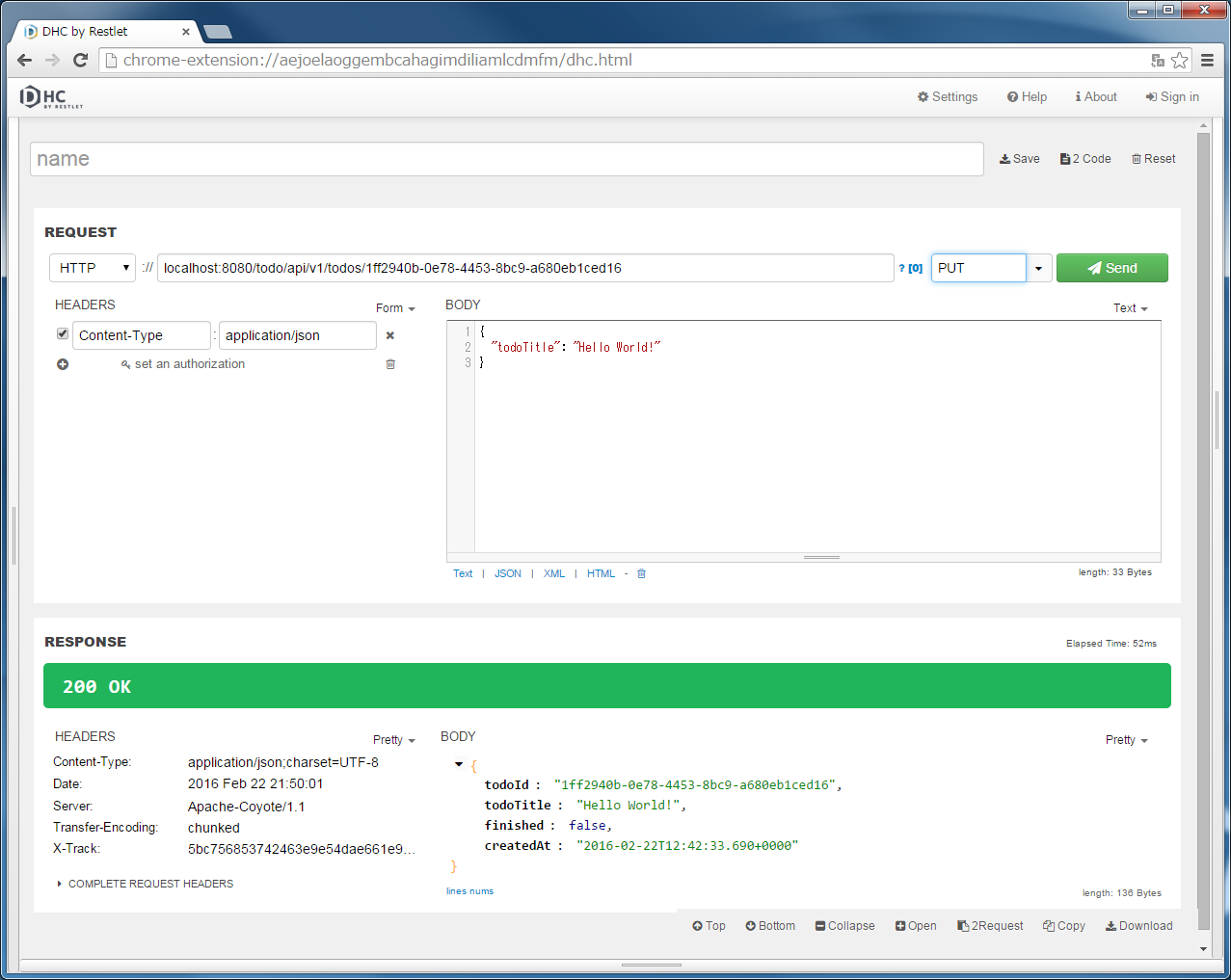
localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos/{todoId}を入力し、メソッドにGETを指定する。{todoId}の部分は実際のIDを入れる必要があるので、POST TodosまたはGET Todosを実行してResponse中のtodoIdをコピーして貼り付けてから、”Send”ボタンをクリックする。“200 OK”のHTTPステータスが返却され、「RESPONSE」の「Body」に指定したTodoリソースのJSONが表示される。
11.2.3.6.4. PUT Todoの実装¶
Todoリソースを一件更新(完了状態へ更新)するAPI(PUT Todo)の処理を、TodoRestControllerのputTodoメソッドに実装する。
src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/todo/TodoRestController.java
package com.example.todo.api.todo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import com.github.dozermapper.core.Mapper;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.todo.domain.model.Todo;
import com.example.todo.domain.service.todo.TodoService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("todos")
public class TodoRestController {
@Inject
TodoService todoService;
@Inject
Mapper beanMapper;
@GetMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public List<TodoResource> getTodos() {
Collection<Todo> todos = todoService.findAll();
List<TodoResource> todoResources = new ArrayList<>();
for (Todo todo : todos) {
todoResources.add(beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class));
}
return todoResources;
}
@PostMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public TodoResource postTodos(@RequestBody @Validated TodoResource todoResource) {
Todo createdTodo = todoService.create(beanMapper.map(todoResource, Todo.class));
TodoResource createdTodoResponse = beanMapper.map(createdTodo, TodoResource.class);
return createdTodoResponse;
}
@GetMapping("{todoId}")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public TodoResource getTodo(@PathVariable("todoId") String todoId) {
Todo todo = todoService.findOne(todoId);
TodoResource todoResource = beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class);
return todoResource;
}
@PutMapping("{todoId}") // (1)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public TodoResource putTodo(@PathVariable("todoId") String todoId) { // (2)
Todo finishedTodo = todoService.finish(todoId); // (3)
TodoResource finishedTodoResource = beanMapper.map(finishedTodo, TodoResource.class);
return finishedTodoResource;
}
}
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
メソッドがPUTのリクエストを処理するために、
@PutMappingアノテーションを設定する。パスから
todoIdを取得するために、value属性にパス変数を指定する。 |
(2)
|
@PathVariableアノテーションのvalue属性に、todoIdを取得するためのパス変数名を指定する。 |
(3)
|
パス変数から取得した
todoIdを使用して、Todoリソースを完了状態へ更新する。 |
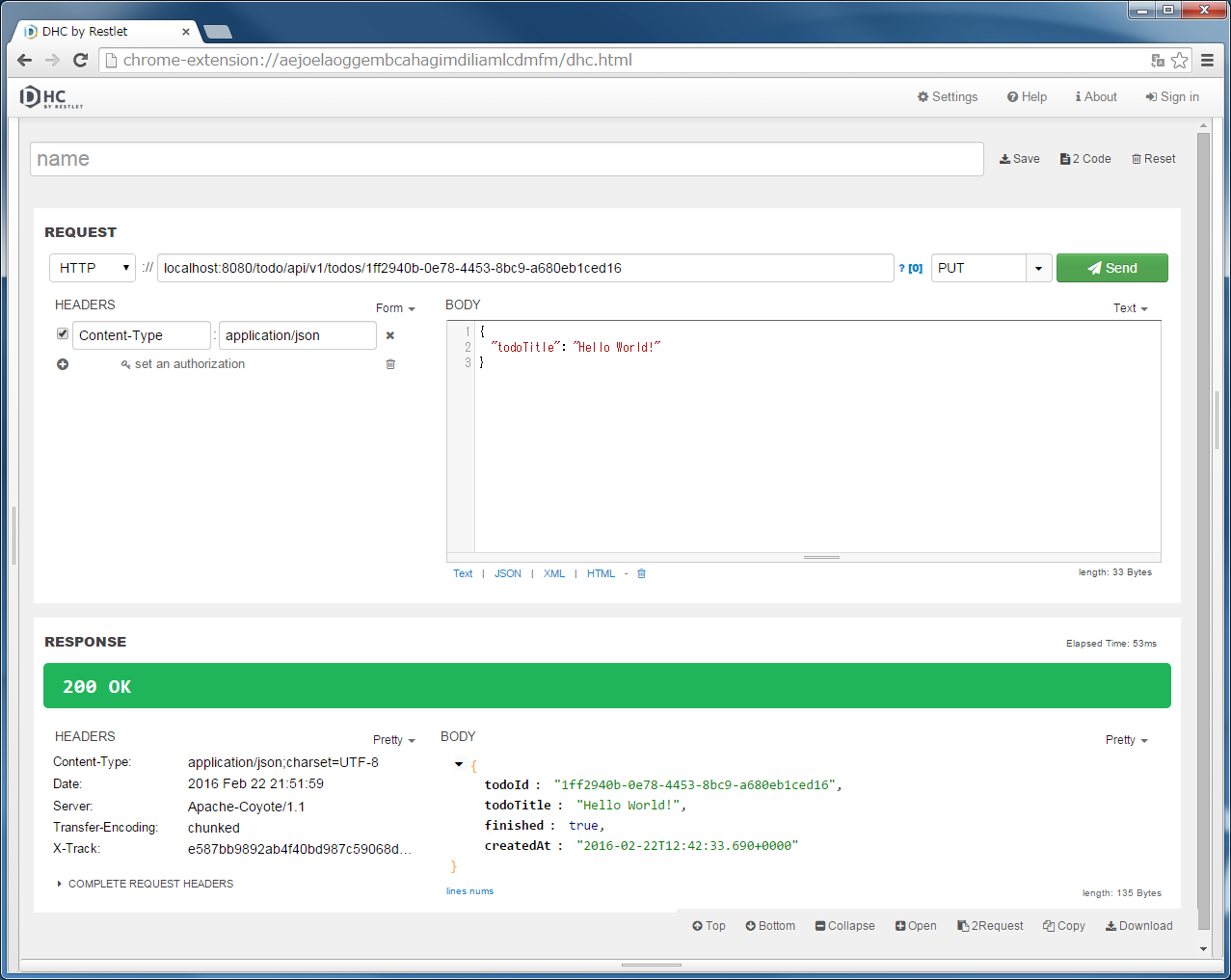
localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos/{todoId}を入力し、メソッドにPUTを指定する。{todoId}の部分は実際のIDを入れる必要があるので、POST TodosまたはGET Todosを実行してResponse中のtodoIdをコピーして貼り付けてから、”Send”ボタンをクリックする。finishedがtrueに更新されている。11.2.3.6.5. DELETE Todoの実装¶
最後に、Todoリソースを一件削除するAPI(DELETE Todo)の処理を、TodoRestControllerのdeleteTodoメソッドに実装する。
src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/todo/TodoRestController.java
package com.example.todo.api.todo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import com.github.dozermapper.core.Mapper;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.todo.domain.model.Todo;
import com.example.todo.domain.service.todo.TodoService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("todos")
public class TodoRestController {
@Inject
TodoService todoService;
@Inject
Mapper beanMapper;
@GetMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public List<TodoResource> getTodos() {
Collection<Todo> todos = todoService.findAll();
List<TodoResource> todoResources = new ArrayList<>();
for (Todo todo : todos) {
todoResources.add(beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class));
}
return todoResources;
}
@PostMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public TodoResource postTodos(@RequestBody @Validated TodoResource todoResource) {
Todo createdTodo = todoService.create(beanMapper.map(todoResource, Todo.class));
TodoResource createdTodoResponse = beanMapper.map(createdTodo, TodoResource.class);
return createdTodoResponse;
}
@GetMapping("{todoId}")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public TodoResource getTodo(@PathVariable("todoId") String todoId) {
Todo todo = todoService.findOne(todoId);
TodoResource todoResource = beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class);
return todoResource;
}
@PutMapping("{todoId}")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public TodoResource putTodo(@PathVariable("todoId") String todoId) {
Todo finishedTodo = todoService.finish(todoId);
TodoResource finishedTodoResource = beanMapper.map(finishedTodo, TodoResource.class);
return finishedTodoResource;
}
@DeleteMapping("{todoId}") // (1)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) // (2)
public void deleteTodo(@PathVariable("todoId") String todoId) { // (3)
todoService.delete(todoId); // (4)
}
}
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
メソッドがDELETEのリクエストを処理するために、
@DeleteMappingアノテーションを設定する。パスから
todoIdを取得するために、value属性にパス変数を指定する。 |
(2)
|
応答するHTTPステータスコードを
@ResponseStatusアノテーションに指定する。HTTPステータスとして、”204 No Content”を設定するため、
value属性にはHttpStatus.NO_CONTENTを設定する。 |
(3)
|
DELETEの場合は返却するコンテンツがないため、返り値の型を
voidとする。 |
(4)
|
パス変数から取得した
todoIdを使用して、Todoリソースを削除する。 |
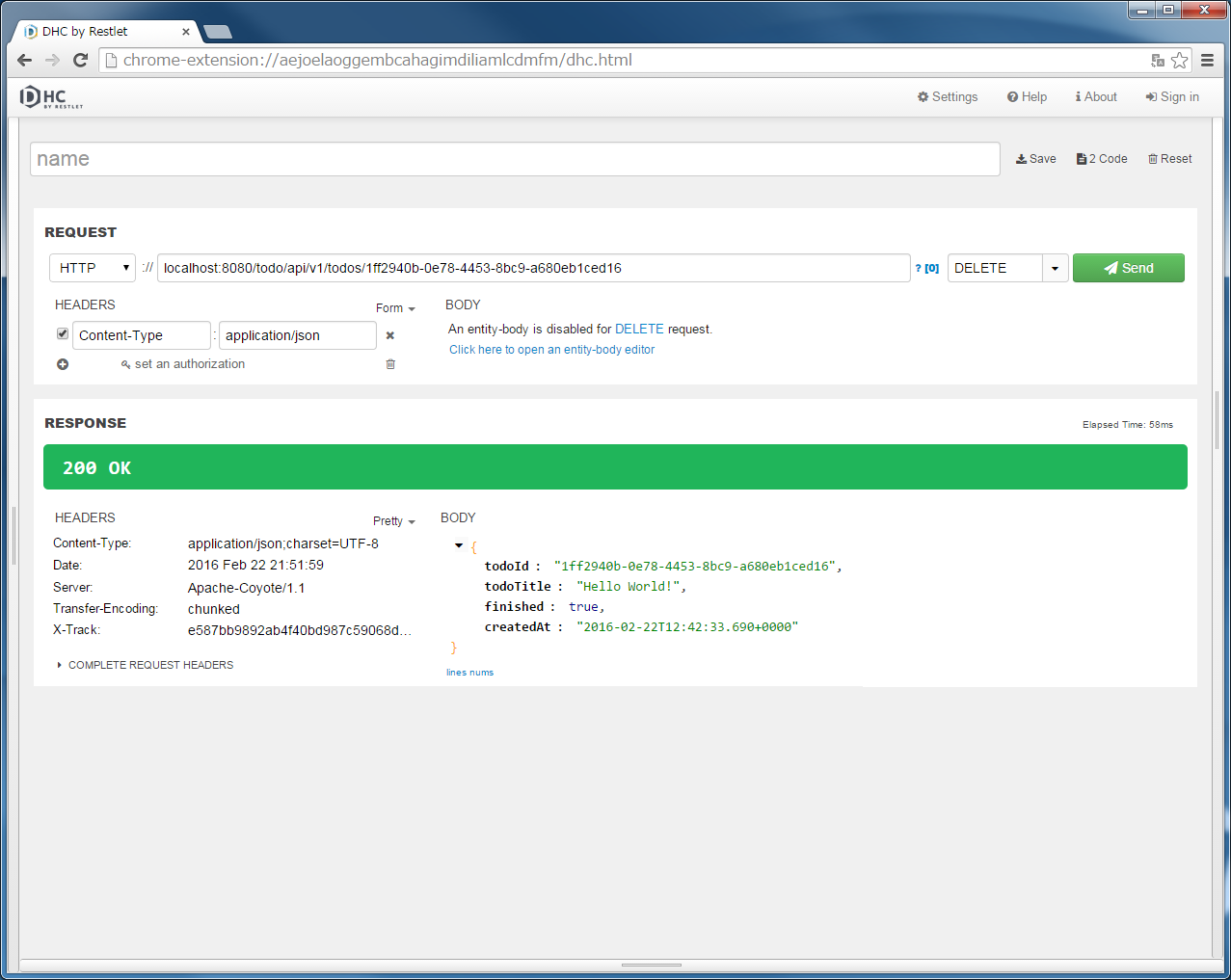
localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos/{todoId}を入力し、メソッドにDELETEを指定する。{todoId}の部分は実際のIDを入れる必要があるので、POST TodosまたはGET Todosを実行してResponse中のtodoIdをコピーして貼り付けてから、”Send”ボタンをクリックする。“204 No Content”のHTTPステータスが返却され、「RESPONSE」の「Body」は空である。
localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todosを入力し、メソッドにGETを指定してから”Send”ボタンをクリックする。11.2.3.7. 例外ハンドリングの実装¶
11.2.3.7.1. ドメイン層の実装を変更¶
src/main/java/com/example/todo/domain/service/todo/TodoServiceImpl.javapackage com.example.todo.domain.service.todo;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.UUID;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessages;
import com.example.todo.domain.model.Todo;
import com.example.todo.domain.repository.todo.TodoRepository;
@Service
@Transactional
public class TodoServiceImpl implements TodoService {
private static final long MAX_UNFINISHED_COUNT = 5;
@Inject
TodoRepository todoRepository;
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public Todo findOne(String todoId) {
return todoRepository.findById(todoId).orElseThrow(() -> {
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error();
messages.add("E404", todoId);
return new ResourceNotFoundException(messages);
});
}
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public Collection<Todo> findAll() {
return todoRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public Todo create(Todo todo) {
long unfinishedCount = todoRepository.countByFinished(false);
if (unfinishedCount >= MAX_UNFINISHED_COUNT) {
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error();
messages.add("E001", MAX_UNFINISHED_COUNT);
throw new BusinessException(messages);
}
String todoId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Date createdAt = new Date();
todo.setTodoId(todoId);
todo.setCreatedAt(createdAt);
todo.setFinished(false);
todoRepository.create(todo);
/* REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA
todoRepository.save(todo);
REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA */
return todo;
}
@Override
public Todo finish(String todoId) {
Todo todo = findOne(todoId);
if (todo.isFinished()) {
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error();
messages.add("E002", todoId);
throw new BusinessException(messages);
}
todo.setFinished(true);
todoRepository.update(todo);
/* REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA
todoRepository.save(todo);
REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA */
return todo;
}
@Override
public void delete(String todoId) {
Todo todo = findOne(todoId);
todoRepository.delete(todo);
}
}
11.2.3.7.2. エラーメッセージの定義¶
処理結果用のエラーコードに対応するエラーメッセージを、メッセージ用のプロパティファイルに定義する。

src/main/resources/i18n/application-messages.properties
e.xx.fw.5001 = Resource not found.
e.xx.fw.7001 = Illegal screen flow detected!
e.xx.fw.7002 = CSRF attack detected!
e.xx.fw.7003 = Access Denied detected!
e.xx.fw.7004 = Missing CSRF detected!
e.xx.fw.8001 = Business error occurred!
e.xx.fw.9001 = System error occurred!
e.xx.fw.9002 = Data Access error!
# typemismatch
typeMismatch="{0}" is invalid.
typeMismatch.int="{0}" must be an integer.
typeMismatch.double="{0}" must be a double.
typeMismatch.float="{0}" must be a float.
typeMismatch.long="{0}" must be a long.
typeMismatch.short="{0}" must be a short.
typeMismatch.boolean="{0}" must be a boolean.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Integer="{0}" must be an integer.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Double="{0}" must be a double.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Float="{0}" must be a float.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Long="{0}" must be a long.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Short="{0}" must be a short.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Boolean="{0}" is not a boolean.
typeMismatch.java.util.Date="{0}" is not a date.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Enum="{0}" is not a valid value.
# For this tutorial
E001 = [E001] The count of un-finished Todo must not be over {0}.
E002 = [E002] The requested Todo is already finished. (id={0})
E400 = [E400] The requested Todo contains invalid values.
E404 = [E404] The requested Todo is not found. (id={0})
E500 = [E500] System error occurred.
E999 = [E999] Error occurred. Caused by : {0}
TodoResourceクラスで使用しているルール(@NotNullと@Size)に対応するメッセージのみ定義する。
src/main/resources/ValidationMessages.properties
javax.validation.constraints.NotNull.message = {0} may not be null.
javax.validation.constraints.Size.message = {0} size must be between {min} and {max}.
11.2.3.7.3. エラーハンドリング用のクラスを格納するパッケージの作成¶
com.example.todo.api.common.errorをエラーハンドリング用のクラスを格納するためのパッケージとする。
11.2.3.7.4. REST APIのエラーハンドリングを行うクラスの作成¶
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandlerを継承したクラスを作成し、@ControllerAdviceアノテーションを付与する方法でハンドリングする。ResponseEntityExceptionHandlerを継承したcom.example.todo.api.common.error.RestGlobalExceptionHandlerクラスを作成する。
src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/common/error/RestGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package com.example.todo.api.common.error;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
}
11.2.3.7.5. REST APIのエラー情報を保持するJavaBeanの作成¶
ApiErrorクラスをcom.example.todo.api.common.errorパッケージに作成する。ApiErrorクラスがJSONに変換されて、クライアントに応答される。
src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/common/error/ApiError.java
package com.example.todo.api.common.error;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude;
public class ApiError implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final String code;
private final String message;
@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_EMPTY)
private final String target;
@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_EMPTY)
private final List<ApiError> details = new ArrayList<>();
public ApiError(String code, String message) {
this(code, message, null);
}
public ApiError(String code, String message, String target) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
this.target = target;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public String getTarget() {
return target;
}
public List<ApiError> getDetails() {
return details;
}
public void addDetail(ApiError detail) {
details.add(detail);
}
}
11.2.3.7.6. HTTPレスポンスBODYにエラー情報を出力するための実装¶
ResponseEntityExceptionHandlerはデフォルトではHTTPステータス(400や500など)の設定のみを行い、HTTPレスポンスのBODYは設定しない。
そのため、handleExceptionInternalメソッドを以下のようにオーバーライドして、BODYを出力するように実装する。
src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/common/error/RestGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package com.example.todo.api.common.error;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@Inject
MessageSource messageSource;
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(Exception ex,
Object body, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status,
WebRequest request) {
Object responseBody = body;
if (body == null) {
responseBody = createApiError(request, "E999", ex.getMessage());
}
return ResponseEntity.status(status).headers(headers).body(responseBody);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request, String errorCode,
Object... args) {
return new ApiError(errorCode, messageSource.getMessage(errorCode,
args, request.getLocale()));
}
}
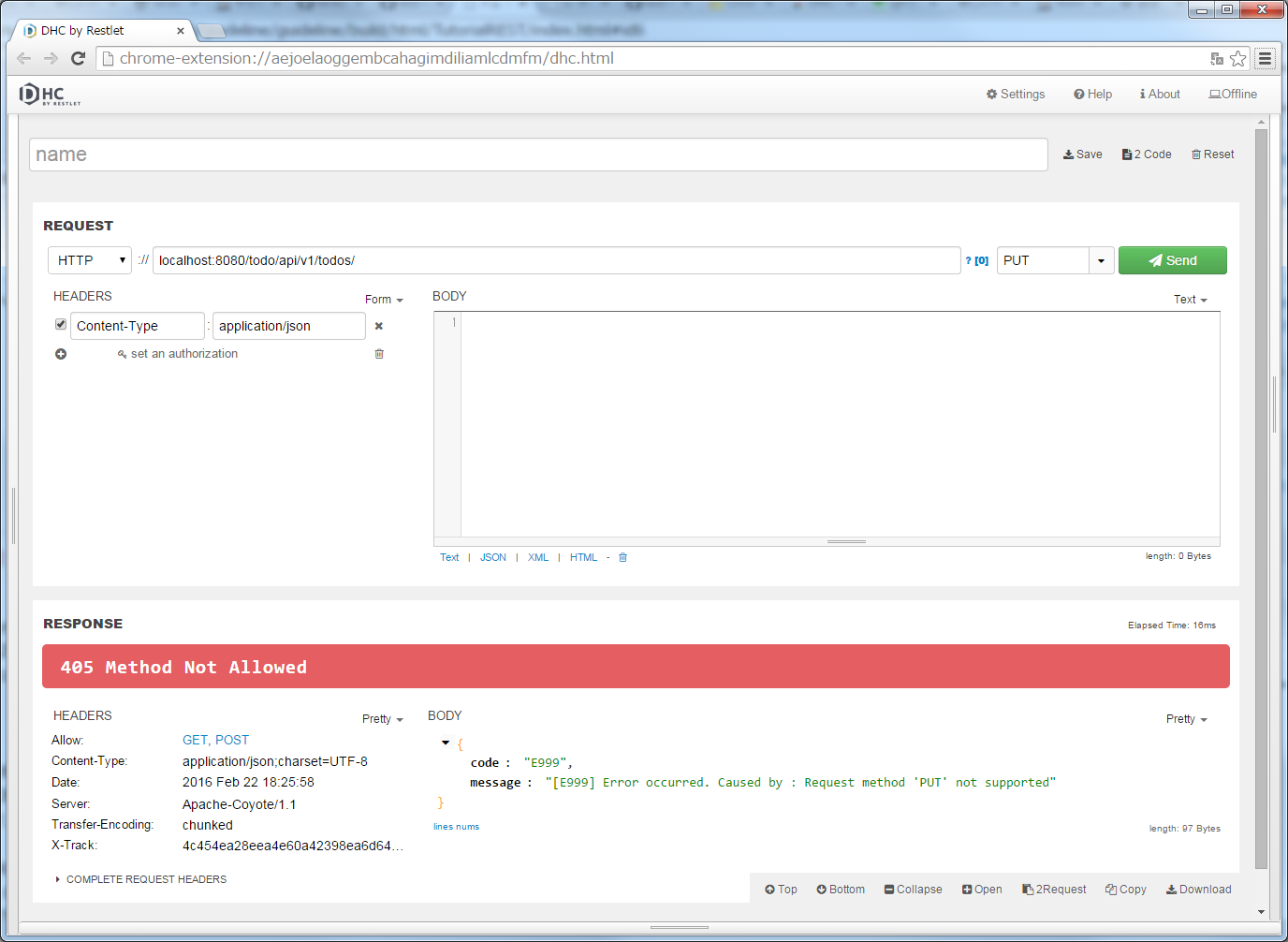
ResponseEntityExceptionHandlerでハンドリングされる例外については、HTTPレスポンスBODYにエラー情報が出力される。ResponseEntityExceptionHandlerでハンドリングされる例外については、DefaultHandlerExceptionResolverで設定されるHTTPレスポンスコードについてを参照されたい。localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todosを入力し、メソッドにPUTを指定してから、”Send”ボタンをクリックする。“405 Method Not Allowed”のHTTPステータスが返却され、「RESPONSE」の「Body」には、エラー情報のJSONが表示される。
11.2.3.7.7. 入力エラーのエラーハンドリングの実装¶
入力エラーの種類は、
org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidExceptionorg.springframework.validation.BindExceptionorg.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotReadableExceptionorg.springframework.beans.TypeMismatchException
となる。
MethodArgumentNotValidExceptionのエラーハンドリングの実装を行う。MethodArgumentNotValidExceptionは、HTTPリクエストBODYに格納されているデータに入力エラーがあった場合に発生する例外である。src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/common/error/RestGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package com.example.todo.api.common.error;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@Inject
MessageSource messageSource;
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(Exception ex,
Object body, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status,
WebRequest request) {
Object responseBody = body;
if (body == null) {
responseBody = createApiError(request, "E999", ex.getMessage());
}
return ResponseEntity.status(status).headers(headers).body(responseBody);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request, String errorCode,
Object... args) {
return new ApiError(errorCode, messageSource.getMessage(errorCode,
args, request.getLocale()));
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, "E400");
for (FieldError fieldError : ex.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, fieldError, fieldError
.getField()));
}
for (ObjectError objectError : ex.getBindingResult().getGlobalErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, objectError, objectError
.getObjectName()));
}
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request,
DefaultMessageSourceResolvable messageSourceResolvable,
String target) {
return new ApiError(messageSourceResolvable.getCode(), messageSource
.getMessage(messageSourceResolvable, request.getLocale()), target);
}
}
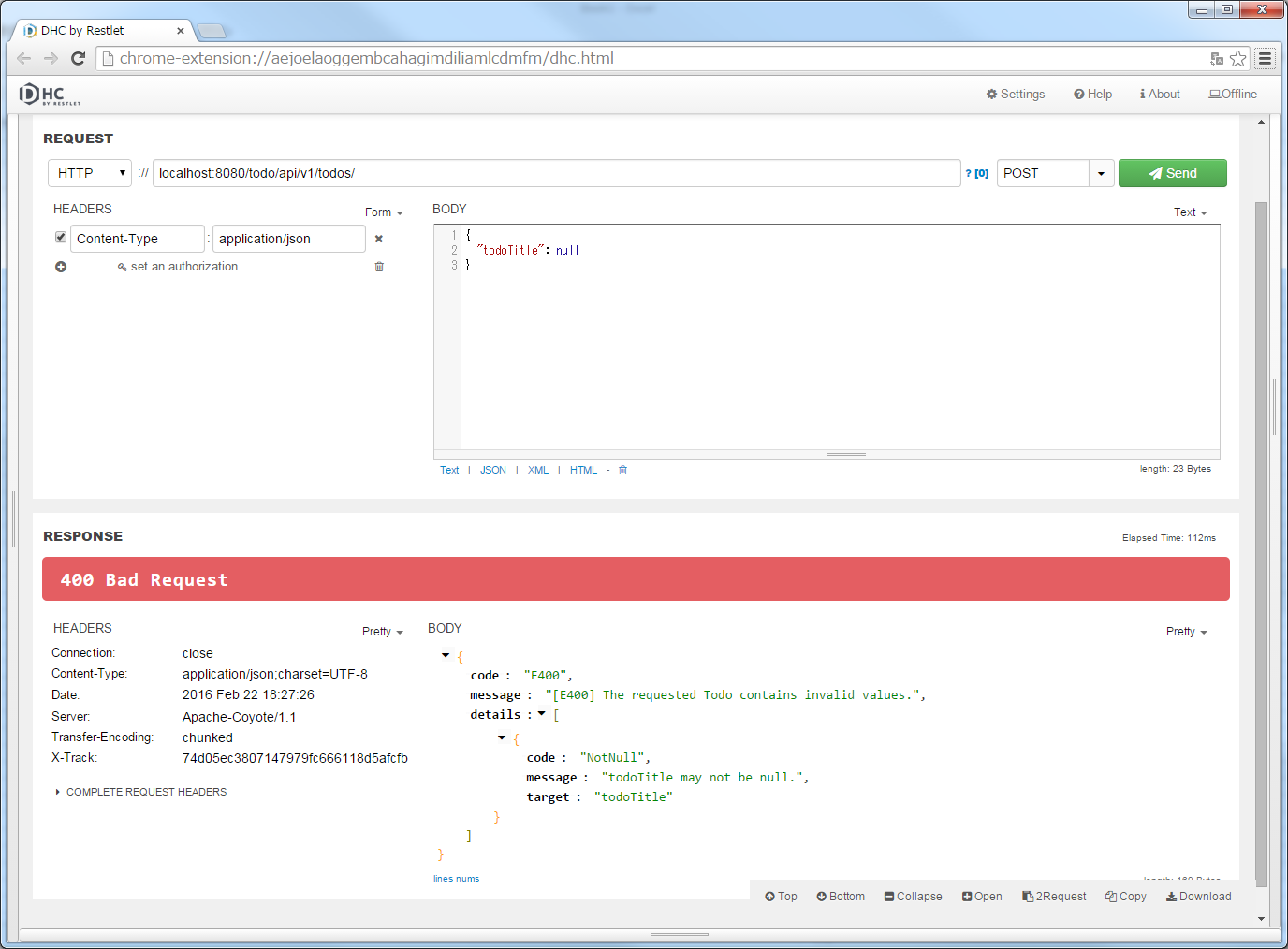
localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todosを入力し、メソッドにPOSTを指定する。{
"todoTitle": null
}
また、「REQUEST」の「HEADERS」の「+」ボタンでHTTPヘッダーを追加し、「Content-Type」に「application/json」を設定後、”Send”ボタンをクリックする。
todoTitleは必須項目なので、必須エラーが発生している。11.2.3.7.8. 業務例外のエラーハンドリングの実装¶
RestGlobalExceptionHandlerにorg.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessExceptionをハンドリングするメソッドを追加して、業務例外をハンドリングする。
業務例外が発生した場合は、”409 Conflict”のHTTPステータスを設定する。
src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/common/error/RestGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package com.example.todo.api.common.error;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResultMessagesNotificationException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessage;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@Inject
MessageSource messageSource;
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(Exception ex,
Object body, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status,
WebRequest request) {
Object responseBody = body;
if (body == null) {
responseBody = createApiError(request, "E999", ex.getMessage());
}
return ResponseEntity.status(status).headers(headers).body(responseBody);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request, String errorCode,
Object... args) {
return new ApiError(errorCode, messageSource.getMessage(errorCode,
args, request.getLocale()));
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, "E400");
for (FieldError fieldError : ex.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, fieldError, fieldError
.getField()));
}
for (ObjectError objectError : ex.getBindingResult().getGlobalErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, objectError, objectError
.getObjectName()));
}
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request,
DefaultMessageSourceResolvable messageSourceResolvable,
String target) {
return new ApiError(messageSourceResolvable.getCode(), messageSource
.getMessage(messageSourceResolvable, request.getLocale()), target);
}
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleBusinessException(BusinessException ex,
WebRequest request) {
return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.CONFLICT, request);
}
private ResponseEntity<Object> handleResultMessagesNotificationException(
ResultMessagesNotificationException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ResultMessage message = ex.getResultMessages().iterator().next();
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, message.getCode(), message
.getArgs());
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
}
localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos/{todoId}を入力し、メソッドにPUTを指定する。todoIdをコピーして貼り付けてから、”Send”ボタンを2回クリックする。todoIdを指定すること。2回目のリクエストに対するレスポンスとして、”409 Conflict”のHTTPステータスが返却され、「RESPONSE」の「Body」には、エラー情報のJSONが表示される。
11.2.3.7.9. リソース未検出例外のエラーハンドリングの実装¶
RestGlobalExceptionHandlerにorg.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundExceptionをハンドリングするメソッドを追加して、リソース未検出例外をハンドリングする。
リソース未検出例外が発生した場合、”404 NotFound”のHTTPステータスを設定する。
src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/common/error/RestGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package com.example.todo.api.common.error;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResultMessagesNotificationException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessage;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@Inject
MessageSource messageSource;
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(Exception ex,
Object body, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status,
WebRequest request) {
Object responseBody = body;
if (body == null) {
responseBody = createApiError(request, "E999", ex.getMessage());
}
return ResponseEntity.status(status).headers(headers).body(responseBody);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request, String errorCode,
Object... args) {
return new ApiError(errorCode, messageSource.getMessage(errorCode,
args, request.getLocale()));
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, "E400");
for (FieldError fieldError : ex.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, fieldError, fieldError
.getField()));
}
for (ObjectError objectError : ex.getBindingResult().getGlobalErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, objectError, objectError
.getObjectName()));
}
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request,
DefaultMessageSourceResolvable messageSourceResolvable,
String target) {
return new ApiError(messageSourceResolvable.getCode(), messageSource
.getMessage(messageSourceResolvable, request.getLocale()), target);
}
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleBusinessException(BusinessException ex,
WebRequest request) {
return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.CONFLICT, request);
}
private ResponseEntity<Object> handleResultMessagesNotificationException(
ResultMessagesNotificationException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ResultMessage message = ex.getResultMessages().iterator().next();
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, message.getCode(), message
.getArgs());
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleResourceNotFoundException(
ResourceNotFoundException ex, WebRequest request) {
return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, request);
}
}
localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos/{todoId}を入力し、メソッドにGETを指定する。“404 Not Found”のHTTPステータスが返却され、「RESPONSE」の「Body」には、エラー情報のJSONが表示される。
11.2.3.7.10. システム例外のエラーハンドリングの実装¶
最後に、RestGlobalExceptionHandlerにjava.lang.Exceptionをハンドリングするメソッドを追加して、システム例外をハンドリングする。
システム例外が発生した場合、”500 InternalServerError”のHTTPステータスを設定する。
src/main/java/com/example/todo/api/common/error/RestGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package com.example.todo.api.common.error;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResultMessagesNotificationException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessage;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@Inject
MessageSource messageSource;
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(Exception ex,
Object body, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status,
WebRequest request) {
Object responseBody = body;
if (body == null) {
responseBody = createApiError(request, "E999", ex.getMessage());
}
return ResponseEntity.status(status).headers(headers).body(responseBody);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request, String errorCode,
Object... args) {
return new ApiError(errorCode, messageSource.getMessage(errorCode,
args, request.getLocale()));
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, "E400");
for (FieldError fieldError : ex.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, fieldError, fieldError
.getField()));
}
for (ObjectError objectError : ex.getBindingResult().getGlobalErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, objectError, objectError
.getObjectName()));
}
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request,
DefaultMessageSourceResolvable messageSourceResolvable,
String target) {
return new ApiError(messageSourceResolvable.getCode(), messageSource
.getMessage(messageSourceResolvable, request.getLocale()), target);
}
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleBusinessException(BusinessException ex,
WebRequest request) {
return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.CONFLICT, request);
}
private ResponseEntity<Object> handleResultMessagesNotificationException(
ResultMessagesNotificationException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ResultMessage message = ex.getResultMessages().iterator().next();
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, message.getCode(), message
.getArgs());
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleResourceNotFoundException(
ResourceNotFoundException ex, WebRequest request) {
return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, request);
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleSystemError(Exception ex,
WebRequest request) {
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, "E500");
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, request);
}
}
src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/todo-infra.properties
database=H2
#database.url=jdbc:h2:mem:todo;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1;INIT=create table if not exists todo(todo_id varchar(36) primary key, todo_title varchar(30), finished boolean, created_at timestamp)
database.url=jdbc:h2:mem:todo;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1
database.username=sa
database.password=
database.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
# connection pool
cp.maxActive=96
cp.maxIdle=16
cp.minIdle=0
cp.maxWait=60000
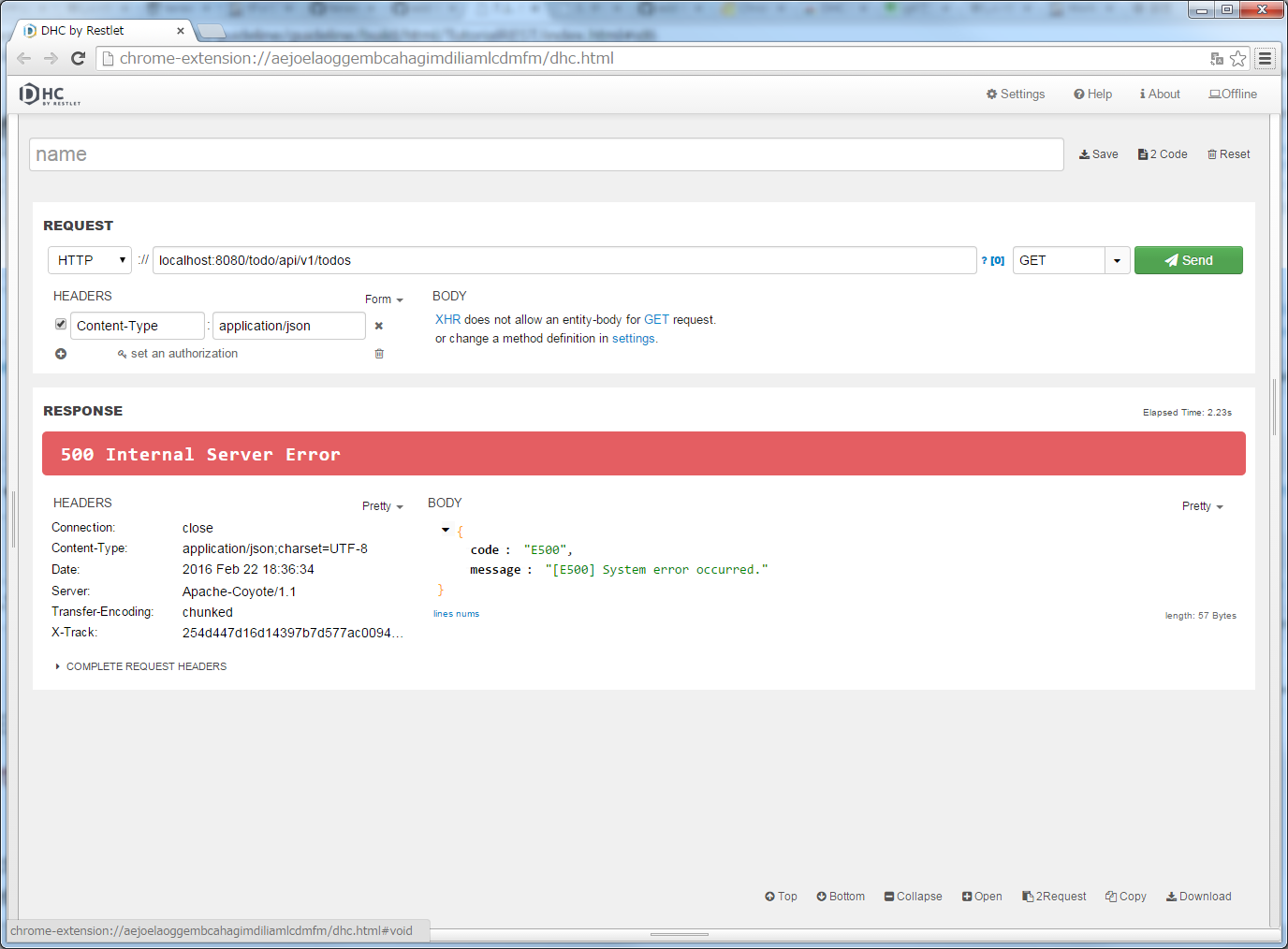
DHCを開いてURLにlocalhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todosを入力し、メソッドにGETを指定して、”Send”ボタンをクリックする。
“500 Internal Server Error”のHTTPステータスが返却され、「RESPONSE」の「Body」には、エラー情報のJSONが表示される。
Note
システムエラーが発生した場合、クライアントへ返却するメッセージは、エラー原因が特定されないシンプルなエラーメッセージを設定することを推奨する。 エラー原因が特定できるメッセージを設定してしまうと、システムの脆弱性をクライアントに公開する可能性があり、セキュリティー上問題がある。
エラー原因は、エラー解析用にログに出力すればよい。
Blankプロジェクトのデフォルトの設定では、共通ライブラリから提供しているExceptionLoggerによってログが出力されるようなっているため、ログを出力するための設定や実装は不要である。
ExceptionLoggerによって出力されるログは以下の通りである。
Todoテーブルが存在しない事が原因でシステムエラーが発生している事がわかる。
date:2015-01-19 02:08:47 thread:tomcat-http--4 X-Track:aadf5822205d423c95a6531f2f76036f level:ERROR logger:o.t.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionLogger message:[e.xx.fw.9002] ### Error querying database. Cause: org.h2.jdbc.JdbcSQLException: Table "TODO" not found; SQL statement: SELECT todo_id, todo_title, finished, created_at FROM todo [42102-182] ### The error may exist in com/example/todo/domain/repository/todo/TodoRepository.xml ### The error may involve com.example.todo.domain.repository.todo.TodoRepository.findAll ### The error occurred while executing a query ... (omitted)
11.2.4. おわりに¶
このチュートリアルでは、以下の内容を学習した。
- TERASOLUNA Server Framework for Java (5.x)による基本的なRESTful Webサービスの構築方法
- REST API(GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)を提供するControllerクラスの実装
- JavaBeanとJSONの相互変換方法
- エラーメッセージの定義方法
- Spring MVCを使用した各種例外のハンドリング方法
ここでは、基本的なRESTful Webサービスの実装法について示した。 考え方の元となるアーキテクチャ・設計指針等について理解を深める為には、「RESTful Web Service」 を参照されたい。