2.2. Overview of Spring MVC Architecture¶
Index
Official website of Spring MVC says the following
Spring’s web MVC framework is, like many other web MVC frameworks, request-driven, designed around a central Servlet that dispatches requests to controllers and offers other functionality that facilitates the development of web applications. Spring’s DispatcherServlet however, does more than just that. It is completely integrated with the Spring IoC container and as such allows you to use every other feature that Spring has.
2.2.1. Overview of Spring MVC Processing Sequence¶
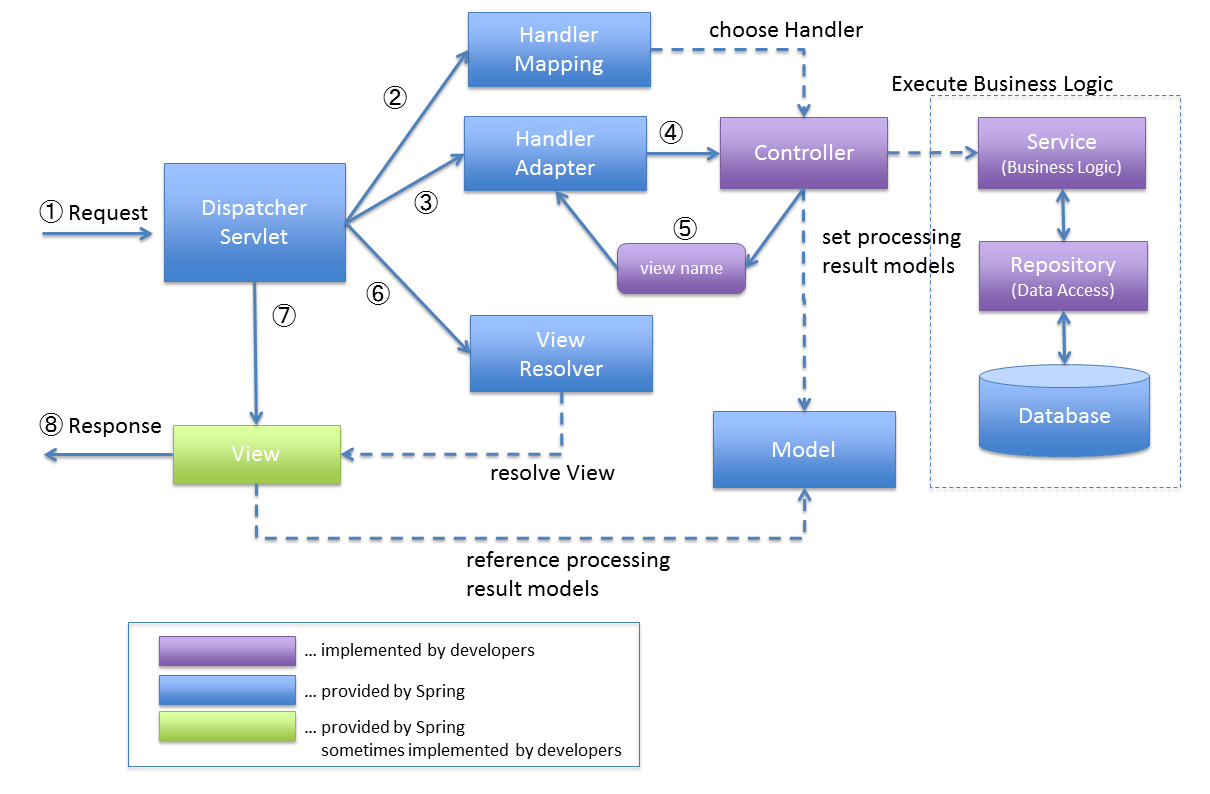
The processing flow of Spring MVC from receiving the request till the response is returned is shown in the following diagram.
DispatcherServletreceives the request.DispatcherServletdispatches the task of selecting an appropriatecontrollertoHandlerMapping.HandlerMappingselects the controller which is mapped to the incoming request URL and returns the(selected Handler)andControllertoDispatcherServlet.DispatcherServletdispatches the task of executing of business logic ofControllertoHandlerAdapter.HandlerAdaptercalls the business logic process ofController.Controllerexecutes the business logic, sets the processing result inModeland returns the logical name of view toHandlerAdapter.DispatcherServletdispatches the task of resolving theViewcorresponding to the View name toViewResolver.ViewResolverreturns theViewmapped to View name.DispatcherServletdispatches the rendering process to returnedView.ViewrendersModeldata and returns the response.
2.2.2. Implementation of each component¶
Among the components explained previously, the extendable components are implemented.
2.2.2.1. Implementation of HandlerMapping¶
Class hierarchy of HandlerMapping provided by Spring framework is shown below.
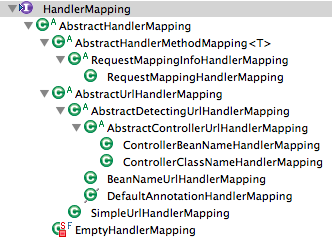
Usually org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping is used. This class reads @RequestMapping annotation from the Controller and uses the method of Controller that matches with URL as Handler class.
In Spring Framework 3.1, RequestMappingHandlerMapping is enabled by default when <mvc:annotation-driven> is set in Bean definition file read by DispatcherServlet.
(For the settings which get enabled with the use of <mvc:annotation-driven> annotation, refer
Web MVC framework.)
2.2.2.2. Implementation of HandlerAdapter¶
Class hierarchy of HandlerAdapter provided by Spring framework is shown below.
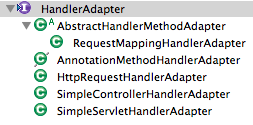
Usually org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter is used.
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter class calls the method of handler class (Controller) selected by HandlerMapping.
In Spring Framework 3.1, this class is also configured by default through <mvc:annotation-driven>.
2.2.2.3. Implementation of ViewResolver¶
Classes that implement ViewResolver provided by Spring framework and dependent libraries are shown below.

Normally (When JSP is used),
org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolveris used,
however, when template engine Tiles is to be used
org.springframework.web.servlet.view.tiles3.TilesViewResolver
and when stream is to be returned for file download
org.springframework.web.servlet.view.BeanNameViewResolver
Thereby, it is required to use different viewResolver based on the type of the View that needs to be returned.
View of multiple types is to be handled, multiple definitions of ViewResolver are required.ViewResolver is the screen application for which file download process exists.View is resolved using InternalResourceViewResolver and for File download View is resolved using BeanNameViewResolver.2.2.2.4. Implementation of View¶
Classes that implement View provided by Spring framework and its dependent libraries are shown below.

View changes with the type of response to be returned. When JSP is to be returned, org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView is used.
When View not provided by Spring framework and its dependent libraries are to be handled, it is necessary to extend the class in which View interface is implemented.
For details, refer File Download.