5.3. SOAP Web Service (Server/Client)¶
Index
5.3.1. Overview¶
This chapter explains fundamental concepts of SOAP Web Service and development of both SOAP server and client which use JAX-WS.
For basic idea of how to implement, refer
- It explains application configuration and how to implement API for SOAP Web Service which use JAX-WS.
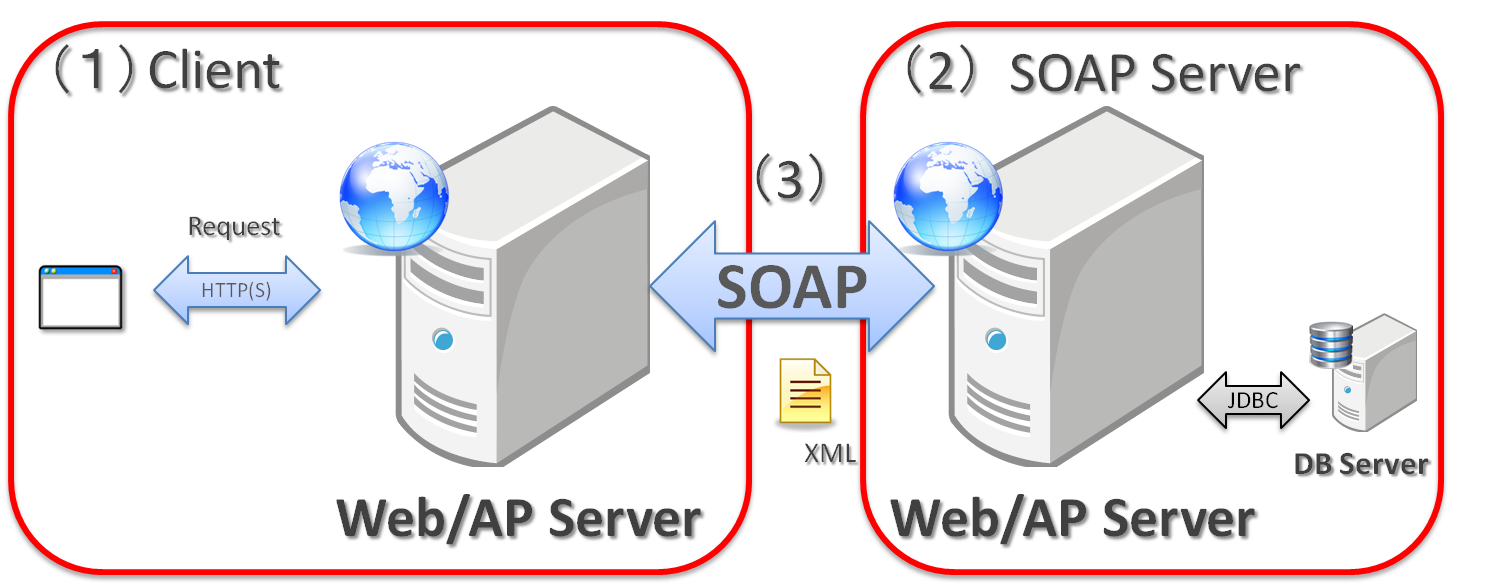
5.3.1.1. SOAP¶
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
A Web application which communicates with another SOAP server is assumed as a client.
Although it is referred as a client, precautions must be taken since it is envisaged as a Web application.
|
(2)
|
SOAP server publishes a Web service and performs a process by receiving XML through SOAP Web Service from client. Operations like accessing database etc and performing business process are assumed.
|
(3)
|
In SOAP Web Service, information is exchanged by using XML.
Here, both SOAP server and client are assumed to be in Java, however, communication is possible in other platforms as well without any issues.
|
5.3.1.2. Regarding development of Web service using JAX-WS¶
Note
Compliance to JAX-WS specifications and actual Web service operation are likely to differ depending on JAS-WX implementation of AP server, and implementation of this guide does not necessarily work with all the AP servers in the same way.
Always check manual of AP server to be used from Note of “Application configuration” before starting development.
5.3.1.3. JAX-WS¶
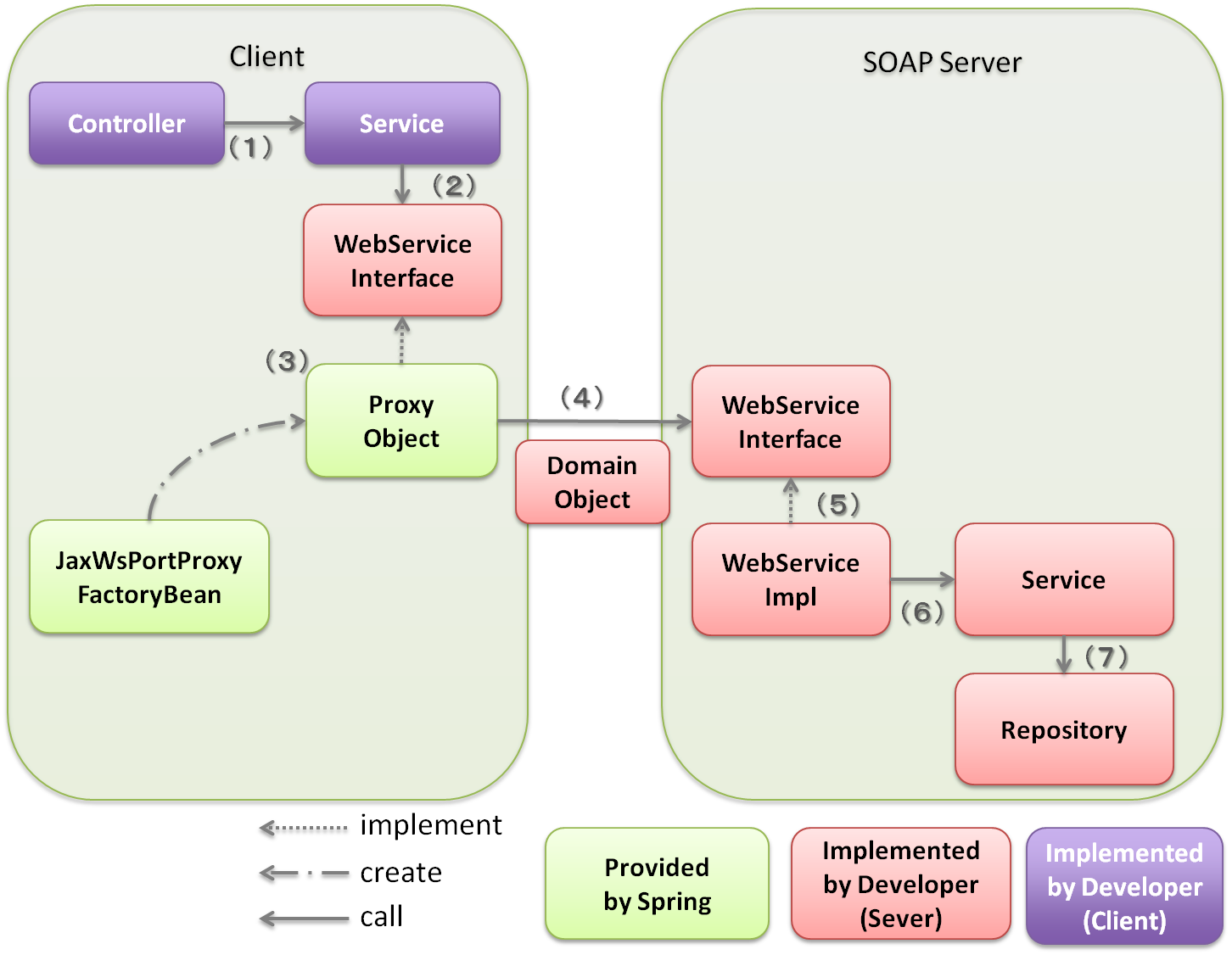
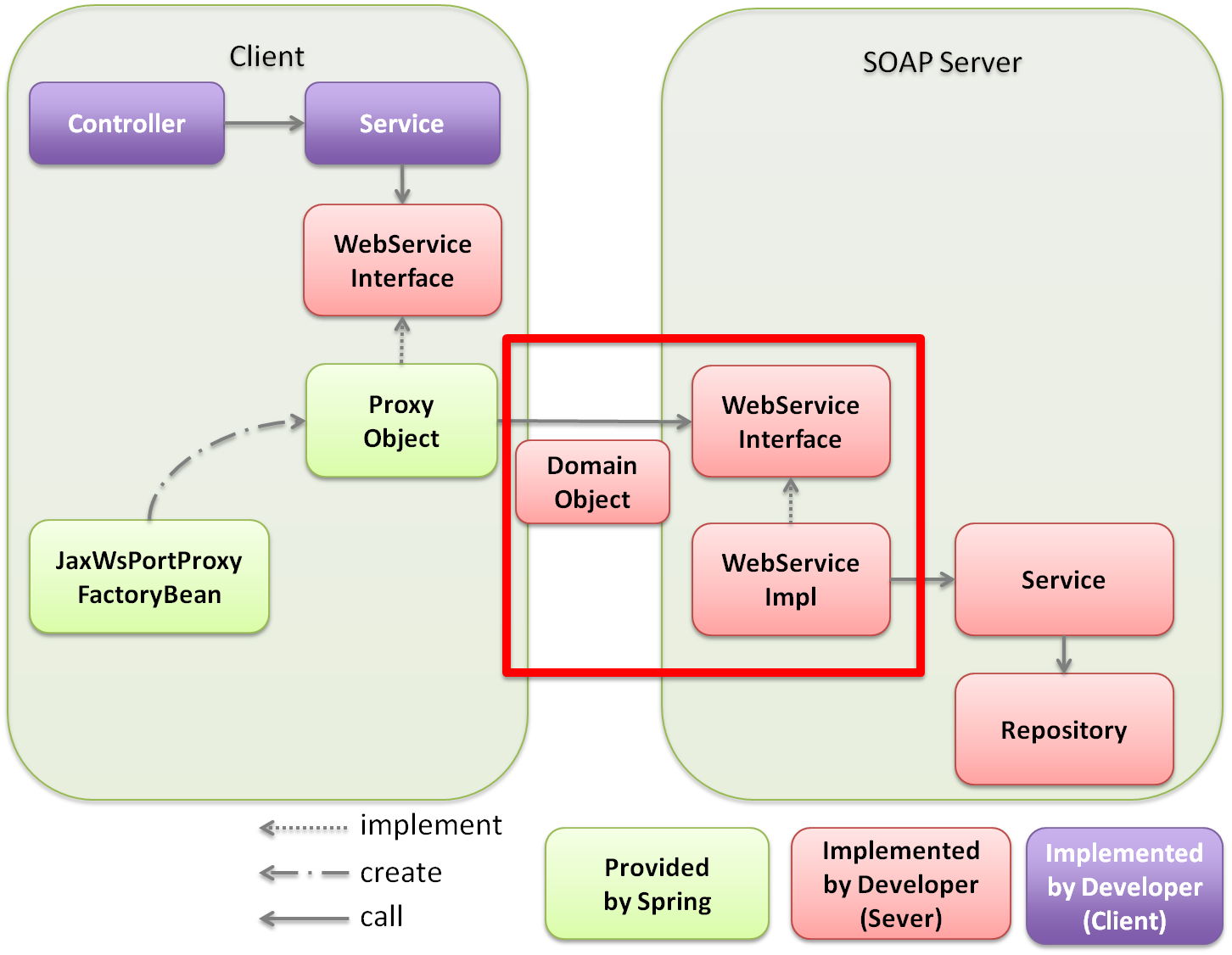
5.3.1.4. JAX-WS linkage function of Spring Framework¶
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
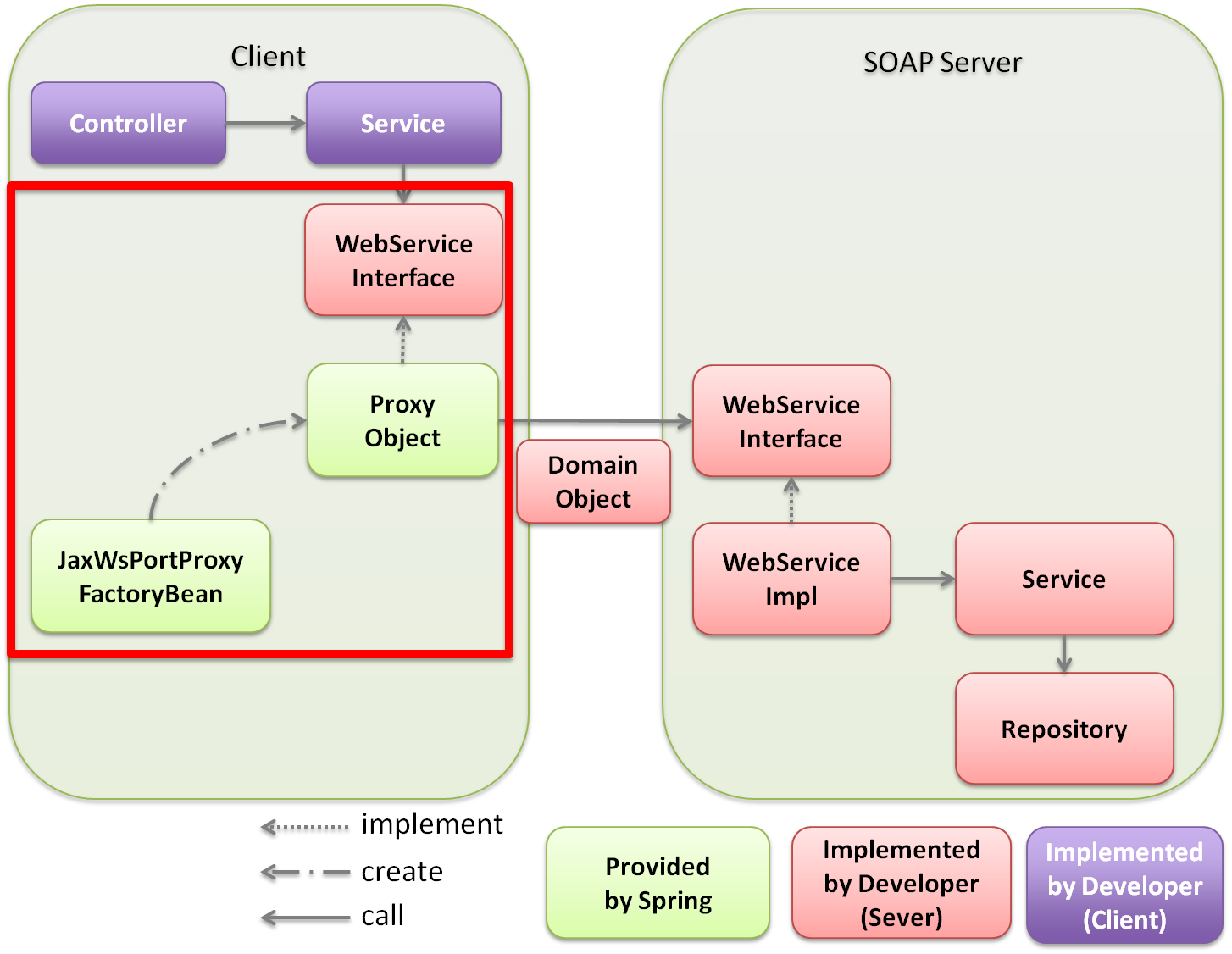
(1)
|
[Client] Controller calls the Service.
No specific changes are observed during normal calling.
|
(2)
|
[Client] Service calls WebService interface offered by SOAP server side.
In the Fig., Service calls the WebService interface, however, WebService interface can also be called directly from Controller if required.
|
(3)
|
[Client] If WebService interface is called, Proxy Object is called as an entity.
The Proxy Object is an implementation class of WebService interface generated in
org.springframework.remoting.jaxws.JaxWsPortProxyFactoryBean.The implementation class is injected in the Service, Service can carry out the process using SOAP Web Service only by calling WebService interface method.
|
(4)
|
ProxyObject calls WebService interface of SOAP server.
Values are exchanged between SOAP server and client by using Domain Object.
Note Strictly speaking, SOAP server and client communicate using XML. Although Domain Object and XML are mutually converted using JAXB during sending and receiving, SOAP Web Service creator can carry out development without being aware of XML. |
(5)
|
[Server] If WebService interface gets called, WebService implementation class is called as an entity.
A WebService implementation class is provided as an implementation class of WebService interface in SOAP server.
This WebService implementation class inherits
org.springframework.web.context.support.SpringBeanAutowiringSupport so that beans on the Spring’s DI container can be injected with @Autowired.Note WebService implementation class is not implemented on DispatcherServlet provided by Spring Framework but acts as a servlet implemented by JAX-WS engine of AP server. So it must be noted that following differences occur with that of implementation methods described in implementation of application layer of the guideline.
Also, it is recommended to inject SOAP server by In case of In contrast to the above, only Spring DI function is used in case of |
(6)
|
[Server] Call Service for carrying out business process in WebService implementation class.
|
(7)
|
[Server] Run business process by using Repository etc in Service.
No specific changes are observed during normal calling.
|
Note
Although a document driven Spring Web Service which develops a Web service is provided in the Spring, it is not addressed in this guideline. For details, refer Spring Web Services.
Note
For details of JAX-WS implementation in Spring, refer Spring Framework Reference Documentation -Remoting and web services using Spring(Web services)-.
5.3.1.4.1. Configuration of Web service module which uses JAX-WS¶
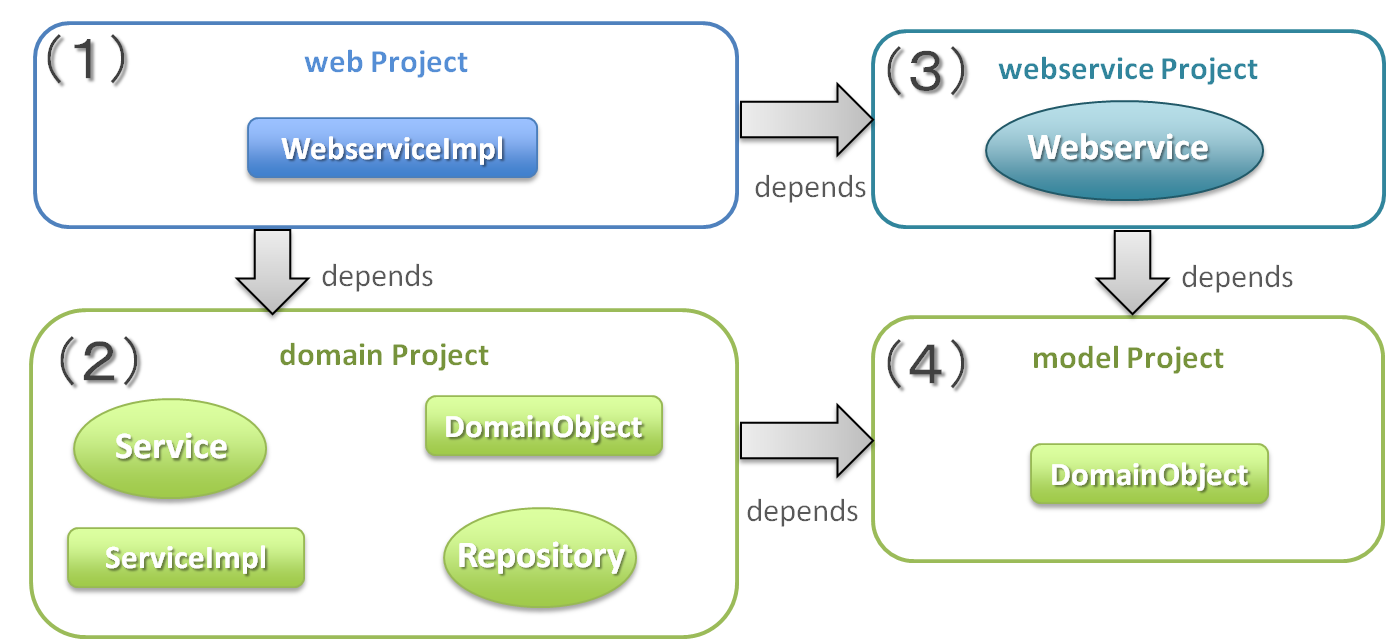
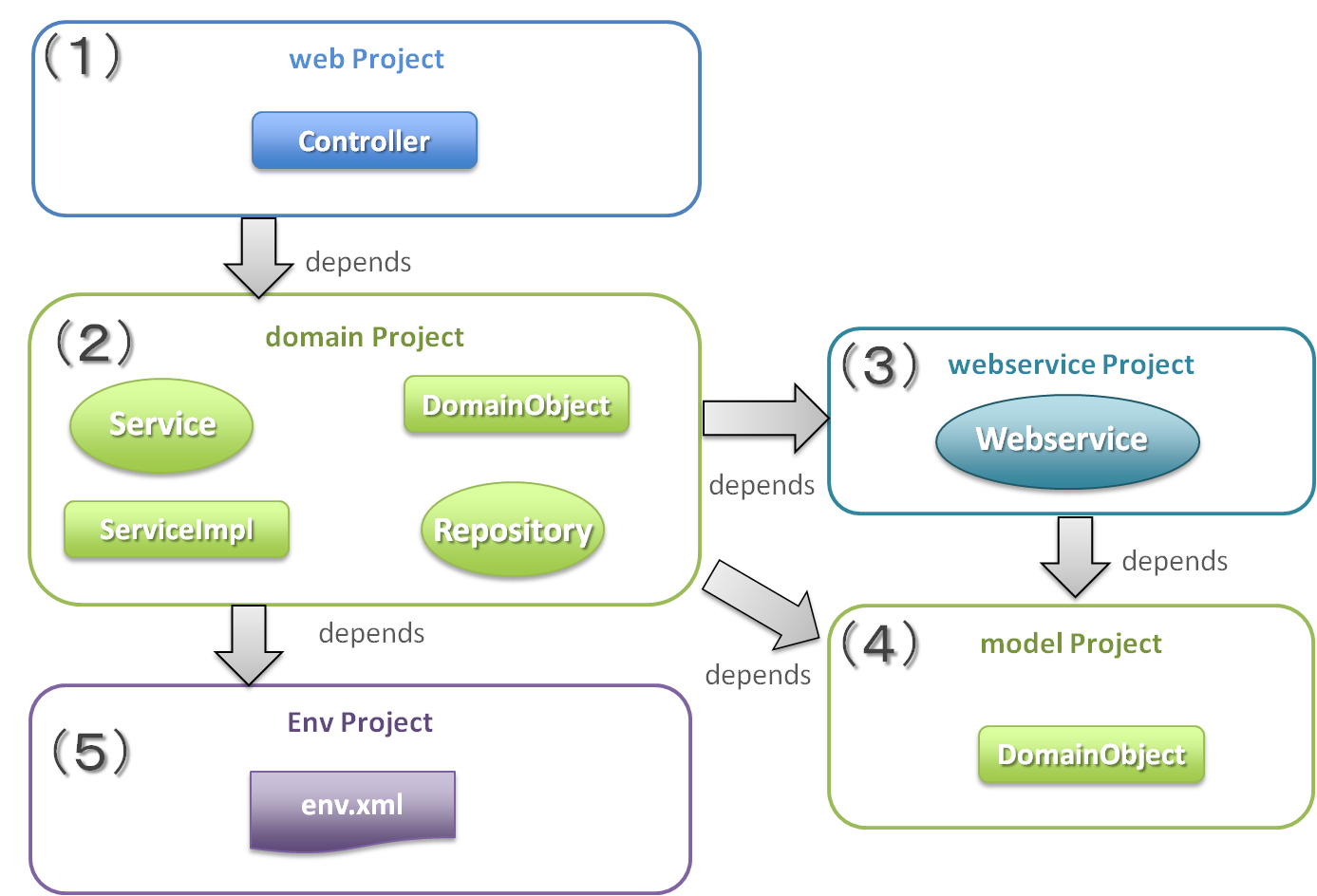
When Web service using JAX-WS is to be created, it is recommended to separately add two projects given below besides the existing blank project.
- model project
- webservice project
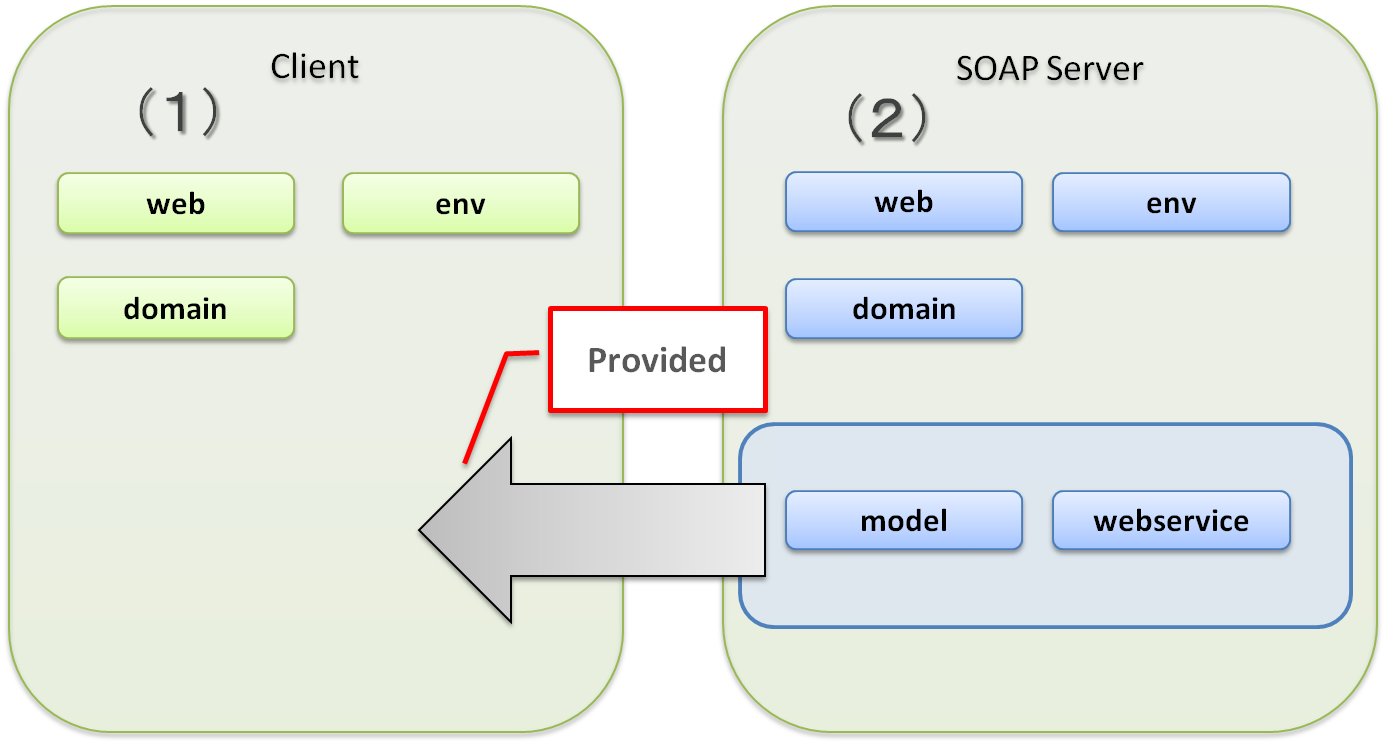
In this guideline, following configuration is used in the multi-projects.
Although client is again assumed to be a Web application, the basic idea for calling from desktop application or command line interface remains the same.
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
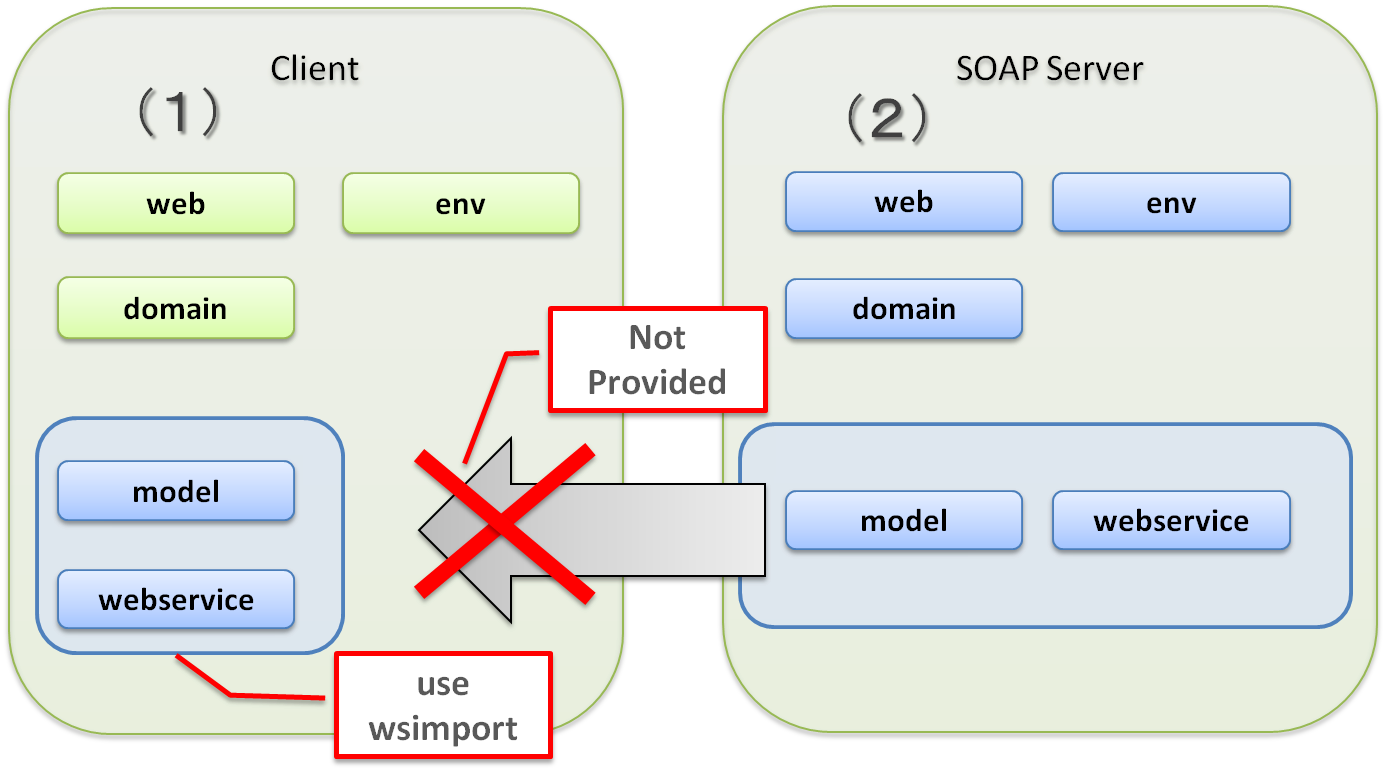
Add model project and webservice project offered by SOAP server to a conventional multi-project while creating a client.
Here, it is assumed that both the server and the client are developed together.
The project details are explained in “How to create SOAP server”.
Refer “Project configuration is changed for SOAP server.” for how to add.
When server and client are not developed separately, and model project and webservice project are not provided, or SOAP server is created in other than Java, Domain Object of model project and Web service interface in webservice project must be created on their own.
Domain Object and Web service interface can be easily created from WSDL by using wsimport.
For details, refer “wsimport”.
|
(2)
|
Add a model project and webservice project besides a conventional multi-project while creating a SOAP server.
Publish these two projects to the client.
It is assumed that the model and webservice projects of the client are added in the Maven dependencies.
|
Client project configuration is as given below.
5.3.1.5. URL to be published as Web service¶
- http://AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD:XXXX/ Context root/Web service name?wsdl
End point address defined in WSDL consists of following URL..
- http://AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD:XXXX/ Context root/Web service name
Note
In the guideline, it is assumed that a WAR file is used for deploying a web project of multi-project configuration in AP server. In this case, [server projectName]-web basically acts as a context root. However, it must be noted that root changes depending on AP server.
Note
In this guideline, since it is assumed that SOAP server and client are together published as a Web application, WSDL URL is specified in the client. The client can also be created by providing WSDL as a file instead of URL. For details, refer Implementation of Web service client.
Warning
In this guideline, AP server (library to be used in case of Tomcat) is configured to change mapping of context root and access by following URL.
- http://AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD:XXXX/[server projectName]-web/ws/TodoWebService?wsdl
How to map Web service in URL which is not under context root differs according to AP server. Refer following for details.
Sr. No. AP server name Description
5.3.2. How to use¶
This section specifically explains how to create SOAP Web Service.
5.3.2.1. How to create SOAP server¶
5.3.2.1.1. Project configuration¶
Dependency for each project
| Sr. No. | Project Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
(1)
|
web project
|
Deploy a Web service implementation class.
|
(2)
|
domain project
|
Deploy Service which is called from WebService implementation class.
Repository etc are same as used in the conventional project.
|
(3)
|
webservice project
|
Deploy interface of WebService to be published here.
Client runs Web service using this interface.
|
(4)
|
model project
|
Deploy only the class that is used in SOAP Web Service from the classes that belong to the domain layer.
Input value and return results from the client use the class in the project.
|
5.3.2.1.2. Application configuration¶
Default configuration while publishing Web service
Note
AP server manual is explained below as the reference material. It must be always checked that appropriate version of the manual is being referred.
Oracle WebLogic Server 12.2.1: Oracle(R) Fusion Middleware Understanding WebLogic Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server Features and Standards Supported by WebLogic Web Services
JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 7.0: DEVELOPING JAX-WS WEB SERVICES
JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 6.4: DEVELOPMENT GUIDE JAX-WS WEB SERVICES
WebSphere Application Server 9.0: IBM Knowledge Center - Web services
Configuration of component scan of package
[server projectName]-ws.xml is created for scanning the component to be used by Web service, component scan is defined and injection in the Web service is enabled.
[server projectName]-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/[server projectName]-ws.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- (1) -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example.ws" />
</beans>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify a package wherein the component to be used in Web service is stored.
|
[server projectName]-web/src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!-- Root ApplicationContext -->
<!-- (1) -->
<param-value>
classpath*:META-INF/spring/applicationContext.xml
classpath*:META-INF/spring/spring-security.xml
classpath*:META-INF/spring/[server projectName]-ws.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Add
[server projectName]-ws.xml to reading target while generating a root ApplicationContext. |
Definition for input check
[server projectName]-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/applicationContext.xml
<bean class="org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.MethodValidationPostProcessor">
<property name="validator" ref="validator" />
</bean>
<bean id="validator" class="org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.LocalValidatorFactoryBean" />
5.3.2.1.3. Web service implementation¶
Following are created.
- Creating Domain Object
- Creating WebService interface
- Creating WebService implementation class
Creating Domain Object
java.io.Serializable interface.[server projectName]-model/src/main/java/com/example/domain/model/Todo.java
package com.example.domain.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
public class Todo implements Serializable {
private String todoId;
private String title;
private String description;
private boolean finished;
private Date createdAt;
// omitted setter and getter
}
Creating WebService interface
An interface to call Web service is created in webservice project.
[server projectName]-webservice/src/main/java/com/example/ws/todo/TodoWebService.java
package com.example.ws.todo;
import java.util.List;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebParam;
import javax.jws.WebResult;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import com.example.domain.model.Todo;
import com.example.ws.webfault.WebFaultException;
@WebService(targetNamespace = "http://example.com/todo") // (1)
public interface TodoWebService {
@WebMethod // (2)
@WebResult(name = "todo") // (3)
Todo getTodo(@WebParam(name = "todoId") /* (4) */ String todoId) throws WebFaultException;
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
WebService interface is declared by applying
@WebService.Although namespace is defined in the
targetNamespace attribute, it is recommended to match it with the package name of the Web service used for creating it.Warning Value of Note Value of |
(2)
|
Apply
@WebMethod to the method which is published as a Web service method.Method can be published on WSDL and used externally by applying this annotation.
|
(3)
|
Apply
@WebResult to return value and specify name in name attribute. It is not required in the absence of a return value.It is published as a return value on WSDL by applying this annotation.
|
(4)
|
Apply
@WebParam in the argument and specify name in name attribute.Argument is published on WSDL and defined as a parameter required for external calling, by applying this annotation.
For details of
WebFaultException, refer “Implementing exception handling”. |
Note
How to apply package name and namespace
When the package name is in the following format
- [Domain].[Application name (System name)].ws.[Used case name]
In this guideline, it is recommended to use namespace as given below..
- http:// [Domain]/[Application name (System name)]
Note
Relation between namespace and package name
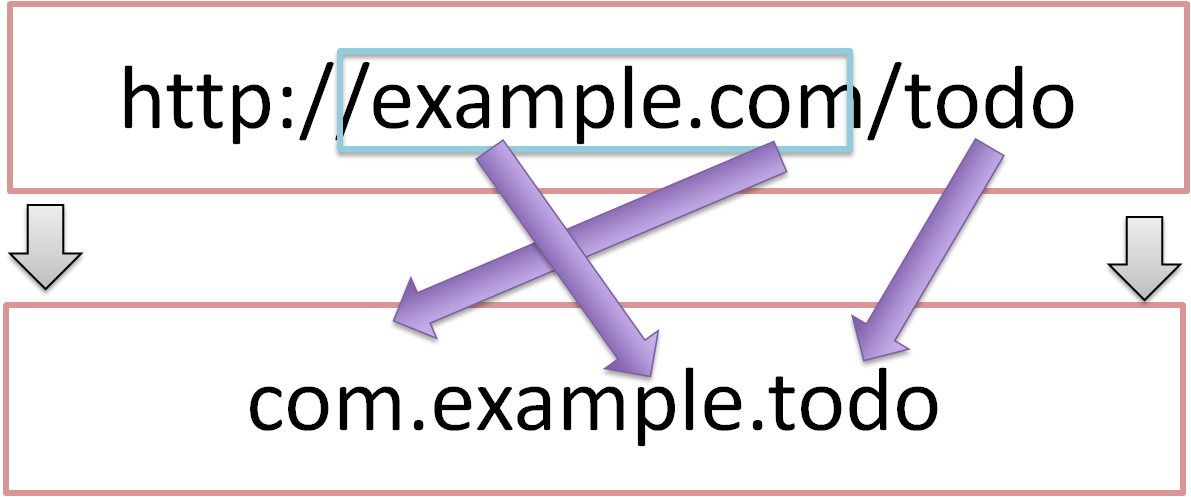
When com.example is used as a domain and todo is used as an application name, Namespace is linked with Java package as below.
Although it is not specified, naming of Namespace and package is summarised in XML Namespace Mapping(Red Hat JBoss Fuse).
Creating WebService implementation class
Create an implementation class of WebService interface in web project.
[server projectName]-web/src/main/java/com/example/ws/todo/TodoWebServiceImpl.java
package com.example.ws.todo;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import javax.jws.HandlerChain;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.xml.ws.BindingType;
import javax.xml.ws.soap.SOAPBinding;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.SpringBeanAutowiringSupport;
import com.example.domain.model.Todo;
import com.example.domain.service.TodoService;
import com.example.ws.webfault.WebFaultException;
import com.example.ws.exception.WsExceptionHandler;
import com.example.ws.todo.TodoWebService;
@WebService(
portName = "TodoWebPort",
serviceName = "TodoWebService",
targetNamespace = "http://example.com/todo",
endpointInterface = "com.example.ws.todo.TodoWebService") // (1)
@BindingType(SOAPBinding.SOAP12HTTP_BINDING) // (2)
public class TodoWebServiceImpl extends SpringBeanAutowiringSupport implements TodoWebService { // (3)
@Autowired // (4)
TodoService todoService;
@Override // (5)
public Todo getTodo(String todoId) throws WebFaultException {
return todoService.getTodo(todoId);
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
WebService implementation class is declared by applying
@WebService.portName attribute is published as a port name on WSDL.serviceName attribute is published as a service name on WSDL.targetNamespace attribute is a namespace used on WSDL.endpointInterface attribute defines an interface name of Web service implemented by this class.Note
|
(2)
|
Specify binding method by applying
@BindingType.When
SOAPBinding.SOAP12HTTP_BINDING is defined, it acts as a binding in SOAP1.2.If annotation is not applied, binding in SOAP1.1 is used.
Note It must be noted that behaviour may differ according to binding method, depending on JAX-WS implementation of AP server to be used. For example, WSDL is not auto-generated for binding with SOAP 1.2, in certain versions of WebSphere Application Server. For details, refer IBM Knowledge Center - Using annotations to create web services. |
(3)
|
Implement
TodoWebService interface created earlier.Enable DI for Spring Bean by inheriting
org.springframework.web.context.support.SpringBeanAutowiringSupport. |
(4)
|
Inject Service.
Same as while calling the service in normal Controller.
|
(5)
|
Run business process by calling Service.
Same as while calling the service in normal Controller.
|
Note
It is recommended to summarise Web service related class under ws package. This is to differentiate it from application layer class which is placed under app package.
5.3.2.1.4. Input check implementation¶
[server projectName]-domain/src/main/java/com/example/domain/service/todo/TodoService.java
package com.example.domain.service.todo;
import java.util.List;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import javax.validation.groups.Default;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import com.example.domain.model.Todo;
@Validated // (1)
public interface TodoService {
Todo getTodo(@NotNull String todoId); // (2)
Todo createTodo(@Valid Todo todo); // (3)
@Validated({ Default.class, Todo.Update.class }) // (4)
Todo updateTodo(@Valid Todo todo);
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Implementation class of this interface is declared as a target for input check by applying
@Validated. |
(2)
|
Apply annotation to argument itself while checking the argument.
|
(3)
|
Apply
@Valid in the argument while carrying out input check of JavaBean. |
(4)
|
Input check can also be carried out by specifying
@Validated in the group and narrowing down the specific conditions.Group details are explained in the JavaBean described next.
|
[server projectName]-model/src/main/java/com/example/domain/model/Todo.java
package com.example.domain.model;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import javax.validation.constraints.Null;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
// (1)
public class Todo implements Serializable {
// (2)
public interface Create {
}
public interface Update {
}
@Null(groups = Create.class)
@NotNull(groups = Update.class)
private String todoId;
@NotNull
private String title;
private String description;
private boolean finished;
@Null(groups = Create.class)
private Date createdAt;
// omitted setter and getter
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Define JavaBean input check in the Bean Validation.
For details, refer “Input Validation”.
|
(2)
|
Define an interface used for grouping of validation.
|
5.3.2.1.5. Security measures¶
Authentication process
A configuration example of Spring Security carrying out Basic authentication for SOAP Web Service is shown below.
[server projectName]-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/spring-security.xml
<sec:http pattern="/ws/**"
create-session="stateless">
<sec:csrf disabled="true" />
<sec:http-basic /> <!-- (1) -->
</sec:http>
<!-- (2) -->
<sec:authentication-manager>
<sec:authentication-provider
user-service-ref="sampleUserDetailsService">
<sec:password-encoder ref="passwordEncoder" />
</sec:authentication-provider>
</sec:authentication-manager>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Basic authentication can be carried out if
sec:http-basic tag is described.Authentication is carried out only for the Web service execution by using
pattern attribute. |
(2)
|
Define authentication method by using
authentication-provider.Actual authentication and fetching user information must be implemented by creating
UserDetailsService.For details, refer “Authentication”.
|
Authorization process
[server projectName]-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/spring-security.xml
<sec:global-method-security pre-post-annotations="enabled" /> <!-- (1) -->
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify
pre-post-annotations attribute of <sec:global-method-security> element in enabled. |
[server projectName]-domain/src/main/java/com/example/domain/service/todo/TodoServiceImpl.java
public class TodoServiceImpl implements TodoService {
// omitted
// (1)
@PreAuthorize("isAuthenticated()")
public List<Todo> getTodos() {
// omitted
}
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')")
public Todo createTodo(Todo todo) {
// omitted
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify
org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize annotation in the method which carries out authorization. |
CSRF measures
[server projectName]-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/spring-security.xml
<!-- (1) -->
<sec:http pattern="/ws/**"
create-session="stateless">
<sec:http-basic />
<sec:csrf disabled="true" />
</sec:http>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Add definition of Spring Security for SOAP Web Service.
Specify URL pattern of request path for SOAP Web Service in
pattern attribute of <sec:http> element.In this code example, request path starting at
/ws/ acts as a request path for SOAP Web Service.Further, the session can no longer be used in Spring Security process by making
create-session attribute stateless.Set
disabled attribute of <sec:csrf> element to true for disabling CSRF measures. |
5.3.2.1.6. Implementation of exception handling¶
Exception occurred in SOAP server
Exception occurred at SOAP server can determine the notification message to the client by using class (SOAPFault) which implements exception described henceforth.
Basically the class given below is created.
| Sr. No. | Class Name | Overview |
|---|---|---|
(1)
|
ErrorBean |
A class which retains code and message of occurred exception.
|
(2)
|
WebFaultType |
Enum type used to determine the type of exception.
|
(3)
|
WebFaultBean |
A class which retains
ErrorBean and WebFaultType. Multiple exception information can be retained by retaining ErrorBean in List. |
(4)
|
WebFaultException |
Exception class which retains
WebFaultBean. |
These exceptions are placed on [server projectName]-webservice since these are shared by SOAP server and client.
[server projectName]-webservice/src/main/java/com/example/ws/webfault/ErrorBean.java
package com.example.ws.webfault;
public class ErrorBean { // (1)
private String code;
private String message;
private String path;
// omitted setter and getter
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Create a class which retains exception messages etc.
|
[server projectName]-webservice/src/main/java/com/example/ws/webfault/WebFaultType.java
package com.example.ws.webfault;
public enum WebFaultType { // (2)
AccessDeniedFault,
BusinessFault,
ResourceNotFoundFault,
ValidationFault,
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Define an enum type used to identify type of exception.
|
[server projectName]-webservice/src/main/java/com/example/ws/webfault/WebFaultBean.java
package com.example.ws.webfault;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class WebFaultBean { // (3)
private WebFaultType type;
private List<ErrorBean> errors = new ArrayList<ErrorBean>();
public WebFaultBean(WebFaultType type) {
this.type = type;
}
public void addError(String code, String message) {
addError(code, message, null);
}
public void addError(String code, String message, String path) {
errors.add(new ErrorBean(code, message, path));
}
// omitted setter and getter
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Create a class which retains
ErrorBean and WebFaultType. |
[server projectName]-webservice/src/main/java/com/example/ws/webfault/WebFaultException.java
package com.example.ws.webfault;
import java.util.List;
import javax.xml.ws.WebFault;
@WebFault(name = "WebFault", targetNamespace = "http://example.com/todo") // (1)
public class WebFaultException extends Exception {
private WebFaultBean faultInfo; // (2)
public WebFaultException() {
}
public WebFaultException(String message, WebFaultBean faultInfo) {
super(message);
this.faultInfo = faultInfo;
}
public WebFaultException(String message, WebFaultBean faultInfo, Throwable e) {
super(message, e);
this.faultInfo = faultInfo;
}
public List<ErrorBean> getErrors() {
return this.faultInfo.getErrors();
}
public WebFaultType getType() {
return this.faultInfo.getType();
}
// omitted setter and getter
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Declare SOAPFault by applying
@WebFault to Exception inheritance class.Specify
name attribute of SOAPFault sent to client in name attribute.Specify namespace to be used in
targetNamespace attribute. It must be same as in Web service. |
(2)
|
It consists of constructor and method below, as shown in code example besides retaining the faultInfo in the field.
|
Note
Reason of inheriting Exception in WebFaultException instead of RuntimeException
If parent class of WebFaultException is set to RuntimeException, exception process can be further simplified. However, parent class should not be set to RuntimeException. it is also declared that it cannot be defined in JSR 224: JavaTM API for XML-Based Web Services as well. Although, it depends on JAS-WS implementation of AP server during an actual attempt, exception class (WebFaultException) wherein @WebFault is applied in the client cannot be fetched resulting in inability to fetch error types and message. Inheriting Exceptionalso results in non-implementation of exception process using AOP.
Warning
Constructor and field of WebFaultException
A setter corresponding to each field and default constructor is mandatory in WebFaultException. This is an internal process of client and is used while creating WebFaultException. Therefore, it is also not possible to consider each field as final.
WebFaultException is inherited, and types to be communicated to the client and child class are created.- Business error exception
- Input error exception
- Resource not detected exception
- Exclusive error exception
- Authorization exception
- System error exception
Following is an example of business error exception.
[server projectName]-webservice/src/main/java/com/example/ws/webfault/BusinessFaultException.java
package com.example.ws.webfault;
import javax.xml.ws.WebFault;
@WebFault(name = "BusinessFault", targetNamespace = "http://example.com/todo") // (1)
public class BusinessFaultException extends WebFaultException {
public BusinessFaultException(String message, WebFaultBean faultInfo) {
super(message, faultInfo);
}
public BusinessFaultException(String message, WebFaultBean faultInfo, Throwable e) {
super(message, faultInfo, e);
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Inherit
WebFaultException and create only constructor.Field and other methods are not required to be described since parent class method is used.
|
Exception handler which wraps exceptions that have occurred by SOAPFault
Exception handler class is created for wrapping the run-time exceptions which occur in Service by SOAPFault. This guideline adopts a policy wherein WebService implementation class converts and throws exceptions using this handler.
Exception thrown from Service assumes the following. It should be added when required.
| Exception name | Details |
|---|---|
org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException |
Exception at the time of authorization error
|
javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException |
Exception at the time of input check error
|
org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException |
Exception when resource is not detected
|
org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException |
Business exception
|
[server projectName]-web/src/main/java/com/example/ws/exception/WsExceptionHandler.java
package com.example.ws.exception;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolation;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException;
import javax.validation.Path;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionCodeResolver;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionLogger;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.SystemException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessage;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessages;
import com.example.ws.webfault.WebFaultBean;
import com.example.ws.webfault.WebFaultException;
import com.example.ws.webfault.WebFaultType;
@Component // (1)
public class WsExceptionHandler {
@Autowired
MessageSource messageSource; // (2)
@Autowired
ExceptionCodeResolver exceptionCodeResolver; // (3)
@Autowired
ExceptionLogger exceptionLogger; // (4)
// (5)
public void translateException(Exception e) throws WebFaultException {
loggingException(e);
WebFaultBean faultInfo = null;
if (e instanceof AccessDeniedException) {
faultInfo = new WebFaultBean(WebFaultType.AccessDeniedFault);
faultInfo.addError(e.getClass().getName(), e.getMessage());
} else if (e instanceof ConstraintViolationException) {
faultInfo = new WebFaultBean(WebFaultType.ValidationFault);
this.addErrors(faultInfo, ((ConstraintViolationException) e).getConstraintViolations());
} else if (e instanceof ResourceNotFoundException) {
faultInfo = new WebFaultBean(WebFaultType.ResourceNotFoundFault);
this.addErrors(faultInfo, ((ResourceNotFoundException) e).getResultMessages());
} else if (e instanceof BusinessException) {
faultInfo = new WebFaultBean(WebFaultType.BusinessFault);
this.addErrors(faultInfo, ((BusinessException) e).getResultMessages());
} else {
// not translate.
throw new SystemException("e.ex.fw.9001", e);
}
throw new WebFaultException(e.getMessage(), faultInfo, e.getCause());
}
private void loggingException(Exception e) {
exceptionLogger.log(e);
}
private void addErrors(WebFaultBean faultInfo, Set<ConstraintViolation<?>> constraintViolations) {
for (ConstraintViolation<?> v : constraintViolations) {
Iterator<Path.Node> pathIt = v.getPropertyPath().iterator();
pathIt.next(); // method name node (skip)
Path.Node methodArgumentNameNode = pathIt.next();
faultInfo.addError(
v.getConstraintDescriptor().getAnnotation().annotationType().getSimpleName(),
v.getMessage(),
pathIt.hasNext() ? pathIt.next().toString() : methodArgumentNameNode.toString());
}
}
private void addErrors(WebFaultBean faultInfo, ResultMessages resultMessages) {
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
for (ResultMessage message : resultMessages) {
faultInfo.addError(
message.getCode(),
messageSource.getMessage(message.getCode(), message.getArgs(), message.getText(), locale));
}
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Apply
@Component for managing the class in DI container. |
(2)
|
Use
MessageSource to fetch the message to be output. |
(3)
|
Use
ExceptionCodeResolverMessageSource provided by common library and map exception types and exception codes.For details, refer “Exception Handling”.
|
(4)
|
Use
ExceptionLogger provided by common library and output exception information in the exception.For details, refer “Exception Handling”.
|
(5)
|
Each exception occurring in Service is wrapped in
SOAPFault.Refer table at the beginning for exception mapping.
|
Note
Other exception handling
In case of other exceptions (else part of translateException method described above), detailed exception details are not notified to the client and only com.sun.xml.internal.ws.fault.ServerSOAPFaultException is thrown.Exception can also be wrapped like other exceptions and notified to the client side.
Exception occurred in the Service is wrapped in Web service by calling exception handler
Exception handler is called in Web service class. Example is given below.
[server projectName]-web/src/main/java/com/example/ws/todo/TodoWebServiceImpl.java
@WebService(
portName = "TodoWebPort",
serviceName = "TodoWebService",
targetNamespace = "http://example.com/todo",
endpointInterface = "com.example.ws.todo.TodoWebService")
@BindingType(SOAPBinding.SOAP12HTTP_BINDING)
public class TodoWebServiceImpl extends SpringBeanAutowiringSupport implements TodoWebService {
@Autowired
TodoService todoService;
@Autowired
WsExceptionHandler handler; // (1)
@Override
public Todo getTodo(String todoId) throws WebFaultException /* (2) */ {
try {
return todoService.getTodo(todoId);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
handler.translateException(e); // (3)
}
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Inject exception handler.
|
(2)
|
Apply throws clause since the exception is thrown after wrapping in
WebFaultException. |
(3)
|
In case of run-time exception, delegate the process to exception handler class.
|
5.3.2.1.7. How to handle large binary data using MTOM¶
[server projectName]-webservice/src/main/java/com/example/ws/todo/TodoWebService.java
package com.example.ws.todo;
import java.util.List;
import javax.activation.DataHandler;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebParam;
import javax.jws.WebResult;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlMimeType;
import com.example.domain.model.Todo;
import com.example.ws.webfault.WebFaultException;
@WebService(targetNamespace = "http://example.com/todo")
public interface TodoWebService {
// omitted
@WebMethod
void uploadFile(@XmlMimeType("application/octet-stream") /* (1) */ DataHandler dataHandler) throws WebFaultException;
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Apply
@XmlMimeType for javax.activation.DataHandler which processes binary data. |
[server projectName]-web/src/main/java/com/example/ws/todo/TodoWebServiceImpl.java
package com.example.ws.todo;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import javax.activation.DataHandler;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import javax.jws.HandlerChain;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.xml.ws.BindingType;
import javax.xml.ws.soap.MTOM;
import javax.xml.ws.soap.SOAPBinding;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.SpringBeanAutowiringSupport;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.SystemException;
import com.example.domain.model.Todo;
import com.example.domain.service.TodoService;
import com.example.ws.webfault.WebFaultException;
import com.example.ws.exception.WsExceptionHandler;
// (1)
@MTOM
@WebService(
portName = "TodoWebPort",
serviceName = "TodoWebService",
targetNamespace = "http://example.com/todo",
endpointInterface = "com.example.ws.todo.TodoWebService")
@BindingType(SOAPBinding.SOAP12HTTP_BINDING)
public class TodoWebServiceImpl extends SpringBeanAutowiringSupport implements TodoWebService {
@Autowired
TodoService todoService;
// omitted
@Override
public void uploadFile(DataHandler dataHandler) throws WebFaultException {
try (InputStream inputStream = dataHandler.getInputStream()){ // (2)
todoService.uploadFile(inputStream);
} catch (Exception e) {
handler.translateException(e);
}
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Apply
@MTOM and declare the use of implementation in compliance with MTOM. |
(2)
|
Fetch
java.io.InputStream from javax.activation.DataHandler and handle the file. |
5.3.2.2. Creation of client¶
5.3.2.2.1. Project configuration¶
As described in “Regarding development of Web service using JAX-WS”, model project and webservice project are assumed to be received by SOAP server.
| Sr. No. | Project name | Description |
|---|---|---|
(1)
|
web project
|
Create Controller.
No specific change in the Controller during normal screen transition.
|
(2)
|
domain project
|
Call Web service by using WebService interface which is provided in webservice project from Service class.
|
(3)
|
webservice project
|
Configure data same as SOAP server.
Client uses this interface to implement Web service.
|
(4)
|
model project
Configure data same as SOAP server.
|
Use class in the project for input value and return results passed to SOAP server.
|
(5)
|
env project
|
Define a proxy class which implements WebService interface used while communicating with SOAP server.
Since proxy class definition is often environment dependent, it is defined in env project.
|
5.3.2.2.2. Implementation of Web service client¶
Implement class as below.
- Define a proxy class which implements WebService interface
- Call Web service from Service class through WebService interface.
Creating proxy class which implements WebService interface
Define org.springframework.remoting.jaxws.JaxWsPortProxyFactoryBean generating a proxy class which implements a WebService interface.
[client projectName]-env/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/[client projectName]-env.xml
<bean id="todoWebService"
class="org.springframework.remoting.jaxws.JaxWsPortProxyFactoryBean"><!-- (1) -->
<property name="serviceInterface" value="com.example.ws.todo.TodoWebService" /><!-- (2) -->
<!-- (3) -->
<property name="serviceName" value="TodoWebService" />
<property name="portName" value="TodoWebPort" />
<property name="namespaceUri" value="http://example.com/todo" />
<property name="wsdlDocumentResource" value="${webservice.todoWebService.wsdlDocumentResource}" /><!-- (4) -->
</bean>
[client projectName]-env/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/[client projectName]-infra.properties
# (5)
webservice.todoWebService.wsdlDocumentResource=http://AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD:XXXX/[server projectName]-web/ws/TodoWebService?wsdl
| Sr. No.. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Define
org.springframework.remoting.jaxws.JaxWsPortProxyFactoryBean.SOAP server can be accessed through proxy class generated by this class. |
(2)
|
Define an interface that should be implemented by Web service in
serviceInterface property. |
(3)
|
Details same as defined on the server side must be defined in
serviceName ,portName and namespaceUri property respectively. |
(4)
|
Specify URL of WDSL published in
wsdlDocumentResource property.Property key is specified since URL is described in the property file described later.
|
(5)
|
Specify value of property key defined in
[client projectName]-env.xml.Describe URL of WSDL.Note Specify other than URL of WSDL file to wsdlDocumentResource In the example above, it is assumed that SOAP server publishes WSDL file. A static file can be specified as well by using |
Note
Overwriting end point address
Access URL configuration is not required in the client since access URL at the time of executing Web service (end point address) is described in WSDL file.
However, when a URL not described in WSDL file is to be accessed, end point address can be overwritten by configuring endpointAddress property of org.springframework.remoting.jaxws.JaxWsPortProxyFactoryBean.
It should preferably be used while changing the environment in tests etc.
Configuration example is as below.
[client projectName]-env/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/[client projectName]-env.xml
<bean id="todoWebService" class="org.springframework.remoting.jaxws.JaxWsPortProxyFactoryBean"> <property name="serviceInterface" value="com.example.ws.todo.TodoWebService" /> <property name="serviceName" value="TodoWebService" /> <property name="portName" value="TodoWebPort" /> <property name="namespaceUri" value="http://example.com/todo" /> <property name="wsdlDocumentResource" value="${webservice.todoWebService.wsdlDocumentResource}" /> <property name="endpointAddress" value="${webservice.todoWebService.endpointAddress}" /><!-- (1) --> </bean>
[client projectName]-env/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/[client projectName]-infra.properties
# (2) webservice.todoWebService.endpointAddress=http://AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD:XXXX/[server projectName]-web/ws/TodoWebService
Sr. No. Description [client projectName]-env.xml. Describe end point address.
Call Web service from Service
Inject Web service created above by Service and run Web service.
[client projectName]-domain/src/main/java/com/example/domain/service/todo/TodoServiceImpl.java
package com.example.soap.domain.service.todo;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.example.domain.model.Todo;
import com.example.ws.webfault.WebFaultException;
import com.example.ws.todo.TodoWebService;
@Service
public class TodoServiceImpl implements TodoService {
@Autowired
TodoWebService todoWebService;
@Override
public void createTodo(Todo todo) {
// (1)
try {
todoWebService.createTodo(todo);
} catch (WebFaultException e) {
// (2)
// handle exception…
}
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Inject
TodoWebService and call Service to be run. |
(2)
|
When an exception occurs at the server side, it is wrapped in
WebFaultException and sent.Carry out process depending on the details.
For details of exception process, refer “Implementing exception handling”.
|
Note
Defining proxy class
It is recommended to define proxy class in env project. This is to enable changing implementation class of Web service by changing maven profile. When sending destination of SOAP server for testing is to be changed or when the SOAP server is not ready, the testing can be carried out without changing another source by creating a stub class.
Note
Fetch response information
When the response information is to be fetched by the client for example retry, it can be fetched by casting in javax.xml.ws.BindingProviderclass as given below.
BindingProvider provider = (BindingProvider) todoWebService; int status = (int) provider.getResponseContext().get(MessageContext.HTTP_RESPONSE_CODE);
For details of BindingProvider, refer The Java API for XML-Based Web Services(JAX-WS) 2.2 -4.2 javax.xml.ws.BindingProvider-.
However, when Apatch CXF library is included in the dependency relation of the client, it is not possible to fetch response information by the method given above at the time of communication error. This is because Apatch CXF proxy is automatically used when Apatch CXF library is included in the dependency relation and Apache CXF proxy does not retain response information in response context at the time of communication error. For error handling of Apache CXF, refer Apache CXF Software Architecture Guide -Fault Handling-.
According to Web service and relay service which includes client of another Web service, if dependency relation of Apache CXF library is necessarily included in the client, it must be considered as a restricted item and adequate care must be taken.
5.3.2.2.3. Security measures¶
Authentication process
When the communication is to be established with SOAP server which uses Basic authentication while using org.springframework.remoting.jaxws.JaxWsPortProxyFactoryBean, authentication can be done only if user name and password are added to bean definition.
[client projectName]-env/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/[client projectName]-env.xml
<bean id="todoWebService"
class="org.springframework.remoting.jaxws.JaxWsPortProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="serviceInterface" value="com.example.ws.todo.TodoWebService" />
<property name="serviceName" value="TodoWebService" />
<property name="portName" value="TodoWebPort" />
<property name="namespaceUri" value="http://example.com/todo" />
<property name="wsdlDocumentResource" value="${webservice.todoWebService.wsdlDocumentResource}" />
<!-- (1) -->
<property name="username" value="${webservice.todoWebService.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${webservice.todoWebService.password}" />
</bean>
[client projectName]-env/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/[client projectName]-infra.properties
# (2)
webservice.todoWebService.username=testuser
webservice.todoWebService.password=password
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Authentication information for Basic authentication can be sent by adding user name and password in bean definition of
org.springframework.remoting.jaxws.JaxWsPortProxyFactoryBean.It is a sample wherein user name and password are transferred to the property file.
|
(2)
|
Specify value of property key defined in
[client projectName]-env.xml. Describe user name and password used for authentication. |
5.3.2.2.4. Implementing exception handling¶
WebFaultExceptionand throw the same.WebFaultException, determines the cause for exception and carry out respective processing.@Override
public void createTodo(Todo todo) {
try {
// (1)
todoWebService.createTodo(todo);
} catch (WebFaultException e) {
// (2)
switch (e.getFaultInfo().getType()) {
case ValidationFault:
// handle exception…
break;
case BusinessFault:
// handle exception…
break;
default:
// handle exception…
break;
}
}
}
| Sr.No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Call Web service.
WebFaultException must be caught since throws clause is applied. |
(2)
|
Determine exception by
faultInfotype and describe respective process (sending a message to the screen, throwing an exception etc) |
5.3.2.2.5. Timeout configuration¶
Timeout that can be specified by client is broadly classified into following two types.
- Connection timeout for each SOAP server
- Request timeout for each SOAP server
org.springframework.remoting.jaxws.JaxWsPortProxyFactoryBean.[client projectName]-env/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/[client projectName]-env.xml
<bean id="todoWebService"
class="org.springframework.remoting.jaxws.JaxWsPortProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="serviceInterface" value="com.example.ws.todo.TodoWebService" />
<property name="serviceName" value="TodoWebService" />
<property name="portName" value="TodoWebPort" />
<property name="namespaceUri" value="http://example.com/todo" />
<property name="wsdlDocumentResource" value="${webservice.todoWebService.wsdlDocumentResource}" />
<!-- (1) -->
<property name="customProperties">
<map>
<!-- (2) -->
<entry key="com.sun.xml.internal.ws.connect.timeout" value="${webservice.connect.timeout}"/>
<entry key="com.sun.xml.internal.ws.request.timeout" value="${webservice.request.timeout}"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
[client projectName]-env/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/[client projectName]-infra.properties
# (3)
webservice.request.timeout=3000
webservice.connect.timeout=3000
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Define a custom property by specifying Map in
customProperties property. |
(2)
|
Define connection timeout and request timeout.
It is a sample wherein the respective values are transferred to a property file.
Warning Key used for defining timeout It is necessary to specify a different value based on JAX-WS implementation as a key to define respective timeout. For details, refer JAX_WS-1166 Standardize timeout settings. Note When corresponding key is specified in WebLogic, If it is not specified, JAX-WS implementation library of WebLogic while attempting to cast
from Setting method is shown below.
|
(3)
|
Specify value of property key defined in
[client projectName]-env.xml. Connection timeout and request timeout are described. |
5.3.3. Appendix¶
5.3.3.1. Project configuration is changed for SOAP server.¶
artifactId
├── pom.xml
├── artifactId-domain
├── artifactId-env
├── artifactId-initdb
├── artifactId-selenium
└── artifactId-web
Project configuration is as below.
artifactId
├── pom.xml
├── artifactId-domain
├── artifactId-env
├── artifactId-initdb
├── artifactId-selenium
├── artifactId-web
├── artifactId-model
└── artifactId-webservice
5.3.3.1.1. Changing existing project¶
5.3.3.1.2. Creating model project¶
model project configuration is explained.
artifactId-model
├── pom.xml ... (1)
Sr. No.
|
Description
|
|---|---|
(1)
|
A POM (Project Object Model) file which defines model module configuration. Following are defined in this file.
|
pom.xml is as shown in the image below. It must be edited when required.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>artifactId-model</artifactId>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<parent>
<groupId>groupId</groupId>
<artifactId>artifactId</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<relativePath>../pom.xml</relativePath>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!-- == Begin TERASOLUNA == -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.terasoluna.gfw</groupId>
<artifactId>terasoluna-gfw-common-dependencies</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.terasoluna.gfw</groupId>
<artifactId>terasoluna-gfw-jodatime-dependencies</artifactId>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.terasoluna.gfw</groupId>
<artifactId>terasoluna-gfw-security-core-dependencies</artifactId>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.terasoluna.gfw</groupId>
<artifactId>terasoluna-gfw-recommended-dependencies</artifactId>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
<!-- == End TERASOLUNA == -->
</dependencies>
</project>
5.3.3.1.3. Creating webservice project¶
webservice project configuration is explained.
artifactId-webservice
├── pom.xml ... (1)
Sr. No.
|
Description
|
|---|---|
(1)
|
A POM (Project Object Model) file which defines webservice module configuration. Following are defined in this file.
|
pom.xml is as shown in the image below. It must be edited when required.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>artifactId-webservice</artifactId>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<parent>
<groupId>groupId</groupId>
<artifactId>artifactId</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<relativePath>../pom.xml</relativePath>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId>
<artifactId>artifactId-model</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- == Begin TERASOLUNA == -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.terasoluna.gfw</groupId>
<artifactId>terasoluna-gfw-common-dependencies</artifactId>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.terasoluna.gfw</groupId>
<artifactId>terasoluna-gfw-jodatime-dependencies</artifactId>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.terasoluna.gfw</groupId>
<artifactId>terasoluna-gfw-security-core-dependencies</artifactId>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.terasoluna.gfw</groupId>
<artifactId>terasoluna-gfw-recommended-dependencies</artifactId>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
<!-- == End TERASOLUNA == -->
</dependencies>
</project>
5.3.3.2. Package configuration of SOAP server¶
| Project name | Description |
|---|---|
[server projectName]-domain
|
Project which stores class and configuration file related to domain layer of SOAP server
|
[server projectName]-web
|
Project which stores class and configuration file related to application layer of SOAP server
|
[server projectName]-env
|
Project which stores files dependent on the environment of SOAP server
|
[server projectName]-model
|
Project which stores the class to be shared with the client and used while executing Web service, from the classes related to domain layer of SOAP server
|
[server projectName]-webservice
|
Project which stores interface of Web service offered by SOAP server
|
5.3.3.2.1. [server projectName]-domain¶
Following is added to pom.xml for adding dependency of [server projectName]-model.
<dependency>
<groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId>
<artifactId>artifactId-model</artifactId>
</dependency>
Refer “Project structure of Application Layering ” since package configuration besides these is not different from the usual domain project.
5.3.3.2.2. [server projectName]-web¶
Following is added to pom.xml for adding dependency of [server projectName]-webservice.
<dependency>
<groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId>
<artifactId>artifactId-webservice</artifactId>
</dependency>
Note
How to resolve a dependency
It is not necessary to define dependency of [server projectName]-model because a transitive dependency is added since dependency to [server projectName]-model is defined from [server projectName]-webservice.
Recommended configuration for [server projectName]-web project is shown below.
[server projectName]-web
└src
└main
├java
│ └com
│ └example
│ ├app...(1)
│ └ws...(2)
│ ├exception...(3)
│ │ └WsExceptionHandler.java
│ ├abc
│ │ └AbcWebServiceImpl.java
│ └def
│ └DefWebServiceImpl.java
├resources
│ ├META-INF
│ │ └spring
│ │ ├applicationContext.xml...(4)
│ │ ├application.properties...(5)
│ │ ├spring-mvc.xml ...(6)
│ │ ├spring-security.xml...(7)
│ │ └[server projectName]-ws.xml...(8)
│ └i18n
│ └application-messages.properties...(9)
└webapp
├resources...(10)
└WEB-INF
├views ...(11)
└web.xml...(12)
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Package which stores configuration elements of application layer.
It may be deleted if only Web service is required to be created.
|
(2)
|
Package which stores related class of Web service.
|
(3)
|
Package which stores exception handler etc of Web service.
|
(4)
|
Defines a bean related to overall application.
|
(5)
|
Define a property to be used in the application.
|
(6)
|
Define a Bean for configuring Spring MVC.
It may be deleted if only Web service is required to be created.
|
(7)
|
Define a Bean for configuring Spring Security.
|
(8)
|
Define a Bean for Web service.
|
(9)
|
Define a message (internationalization) for screen display.
|
(10)
|
Stores static resources (css, js, image etc).
It may be deleted if only Web service is required to be created.
|
(11)
|
Stores View (jsp).
It may be deleted if only Web service is required to be created.
|
(12)
|
Define Servlet deployment.
|
Note
Files not required for SOAP server
When only Web service is to be created in SOAP server, Spring MVC configuration file existing in the blank project is not required, hence can be deleted.
5.3.3.2.3. [server projectName]-env¶
Since [server projectName]-env does not differ from normal env project, refer “Project structure of Application Layering”.
5.3.3.2.4. [server projectName]-model¶
Recommended project configuration of [server projectName]-model is shown below.
[server projectName]-model
└src
└main
└java
└com
└example
└domain ...(1)
└model ...(2)
├Xxx.java
├Yyy.java
└Zzz.java
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Package which stores configuration elements of domain layer.
|
(2)
|
Package which stores the class to be used while implementing Web service in the Domain Object.
|
5.3.3.2.5. [server projectName]-webservice¶
Recommended project configuration of [server projectName]-webservice is shown below.
[server projectName]-webservice
└src
└main
└java
└com
└example
└ws...(1)
├webfault...(2)
├abc
│ └AbcWebService.java
└def
└DefWebService.java
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Package which stores Web service interface.
|
(2)
|
Package which stores webfault of Web service.
|
5.3.3.3. Package configuration of client¶
| Project name | Description |
|---|---|
[client projectName]-domain
|
Project which stores class and configuration file related to domain layer of client
|
[client projectName]-web
|
Project which stores class and configuration file related to application layer of client
|
[client projectName]-env
|
Project which stores files dependent on the client environment
|
Note
For [server projectName]-model and [server projectName]-webservice, refer ” Package configuration of SOAP server” described earlier.
5.3.3.3.1. [client projectName]-domain¶
Following is added to pom.xml for adding dependency of [server projectName]-webservice offered from SOAP server.
<dependency>
<groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId>
<artifactId>artifactId-webservice</artifactId>
</dependency>
Note
how to resolve dependency
Similar to [server projectName]-web, it is not necessary to define dependency of [server projectName]-model in pom.xml because a transitive dependency is added since dependency relation to [server projectName]-model is defined from [server projectName]-webservice.
Since package configuration other than this is not different from the usual domain project, refer “Project structure of Application Layering “.
5.3.3.3.2. [client projectName]-web¶
Since [client projectName]-web is not different from the usual web project, refer “Project structure of Application Layering”.
5.3.3.3.3. [client projectName]-env¶
Recommended project configuration of [client projectName]-env project is shown below.
[projectName]-env
├configs ...(1)
│ └[envName] ...(2)
│ └resources ...(3)
└src
└main
└resources ...(4)
├META-INF
│ └spring
│ ├[projectName]-env.xml ...(5)
│ └[projectName]-infra.properties ...(6)
├dozer.properties
├log4jdbc.properties
└logback.xml ...(7)
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Directory for managing environment dependent files of overall environment.
|
(2)
|
Directory for managing environment dependent files for each environment.
Specify a name which identifies the environment, as a directory name.
|
(3)
|
Directory for managing configuration files for each environment.
Subdirectory configuration and configuration files to be managed are same as (4).
|
(4)
|
Directory for managing configuration files for local development environment.
|
(5)
|
Define a Bean for local development environment.
Specify a proxy class of Web service in this file.
|
(6)
|
Define a property for local development environment.
Specify the value that can be changed for each environment like URL of WSDL.
|
(7)
|
Define log output for local development environment.
|
5.3.3.4. wsimport¶
5.3.3.4.1. Using wsimport¶
5.3.3.4.2. How to use wsimport¶
# (1)
wsimport -keep -p [Package name of the source to be output] -s [Location which stores source to be output] [URL of wsdl]
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify URL of WSDL as an argument of wsimport.
Following are used as an option.
For other options, refer Java Platform, Standard Edition Tools Reference -Web Services(wsimport)-.
|
Note
wsimport outputs only class file as the default behaviour. No action is required only for the moving operation, however when a debug operation is to be carried out, it is recommended to apply ‘keep’ option and store source as well.
For example, the commands are as below.
wsimport -keep -p com.example.ws.todo -s c:/tmp http://AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD:XXXX/soap-web/ws/TodoWebService?wsdl
Although the source created is dependent on Web service to be published, Java class used in the guideline is output.
- Web service interface (
TodoWebService.javain the source example) - Domain Object (
Todo.javain the source example)
Note
Java class to be output is also output in the cases other than above. A client can be created only by using source that has been output. However, as a policy in this guideline, since the client uses org.springframework.remoting.jaxws.JaxWsPortProxyFactoryBean, it is recommended to not to use another Java class.
5.3.3.5. Web service development on Tomcat¶
CXFServlet by changing the configuration.- A method wherein Web service implementation class is described in POJO
- A method wherein Web service implementation class is created by inheriting
SpringBeanAutowiringSupport. (method that has been described so far)
5.3.3.5.1. Configuration while using CXFServlet¶
Library configuration is described in pom.xml to use CXFServlet.
<!-- (1) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-frontend-jaxws</artifactId>
<version>3.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-transports-http</artifactId>
<version>3.1.4</version>
</dependency>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Add dependency to Apache CXF library for using
CXFServlet. |
Next, CXFServletwhich receives SOAP Web Service in web.xml is defined.
<!-- (1) -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>cxfServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.cxf.transport.servlet.CXFServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>config-location</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:/META-INF/spring/cxf-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<!-- (2) -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>cxfServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/ws/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Define servlet for
org.apache.cxf.transport.servlet.CXFServlet.Specify path of
cxf-servlet.xmlto be described later, in config-location. |
(2)
|
Define mapping for the servlet that has been defined. In this case, Web service is created under Context name/ws.
|
5.3.3.5.2. Configuration required in POJO method¶
Specify Web service implementation class as an endpoint.
[server projectName]-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/cxf-servlet.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws" xmlns:soap="http://cxf.apache.org/bindings/soap"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws
http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/bindings/soap
http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/configuration/soap.xsd">
<!-- (1) -->
<jaxws:endpoint id="todoWebEndpoint" implementor="#todoWebServiceImpl"
address="/TodoWebService" />
</beans>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Define the endpoint to be published.
Specify bean name (“bean name” format) of Web service class which is registered in DI container, in the
implementor attribute.Specify address which publishes Web service, in
address attribute.Address describes only the path of end point to be published.
For attribute details, refer Apache CXF JAX-WS Configuration.
|
Create TodoWebServiceImpl as POJO.
[server projectName]-web/src/main/java/com/example/ws/todo/TodoWebServiceImpl.java
package com.example.ws.todo;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import javax.jws.HandlerChain;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.xml.ws.BindingType;
import javax.xml.ws.soap.SOAPBinding;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.SpringBeanAutowiringSupport;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.example.domain.model.Todo;
import com.example.domain.service.TodoService;
import com.example.ws.webfault.WebFaultException;
import com.example.ws.exception.WsExceptionHandler;
import com.example.ws.todo.TodoWebService;
// (1)
@Component
@WebService(
portName = "TodoWebPort",
serviceName = "TodoWebService",
targetNamespace = "http://example.com/todo",
endpointInterface = "com.example.ws.todo.TodoWebService")
@BindingType(SOAPBinding.SOAP12HTTP_BINDING)
// (2)
public class TodoWebServiceImpl implements TodoWebService {
// omitted
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Apply
@Component and register to DI container. |
(2)
|
Create as POJO since registration to DI container is possible by component scan. Basically, inheriting
org.springframework.web.context.support.SpringBeanAutowiringSupport is not necessary. |
5.3.3.5.3. Configuration required for the method that inherits SpringBeanAutowiringSupport¶
Class name and address acting as SOAP end points are defined in the Bean definition file for CXFServlet.
[server projectName]-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/cxf-servlet.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws" xmlns:soap="http://cxf.apache.org/bindings/soap"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws
http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/bindings/soap
http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/configuration/soap.xsd">
<!-- (1) -->
<jaxws:endpoint id="todoWebEndpoint" implementor="com.example.ws.todo.TodoWebServiceImpl"
address="/TodoWebService" />
</beans>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Define endpoint to be published.
Specify implementation class of Web service to be published in
implementor attribute.Specify address which publishes Web service in
address attribute.Address describes only the path of end point to be published.
For attribute details, refer Apache CXF JAX-WS Configuration.
|