4.2. Exception Handling¶
Table of Contents
- Overview
- Detail
- Types of exceptions
- Exception Handling Patterns
- When notifying partial redo of a use case (from middle)
- When notifying redo of a use case (from beginning)
- When notifying that the system or application is not in a normal state
- When notifying that the request contents are invalid
- When a fatal error has been detected
- When notifying that an exception has occurred in the presentation layer (JSP etc.)
- Basic Flow of Exception Handling
- Basic flow when the Controller class handles the exception at request level
- Basic flow when the Controller class handles the exception at use case level
- Basic flow when the framework handles the exception at servlet level
- Basic flow when the servlet container handles the exception at web application level
- How to use
- How to use (Ajax)
- Appendix
This chapter describes exception handling mechanism for web applications created using this guideline.
4.2.1. Overview¶
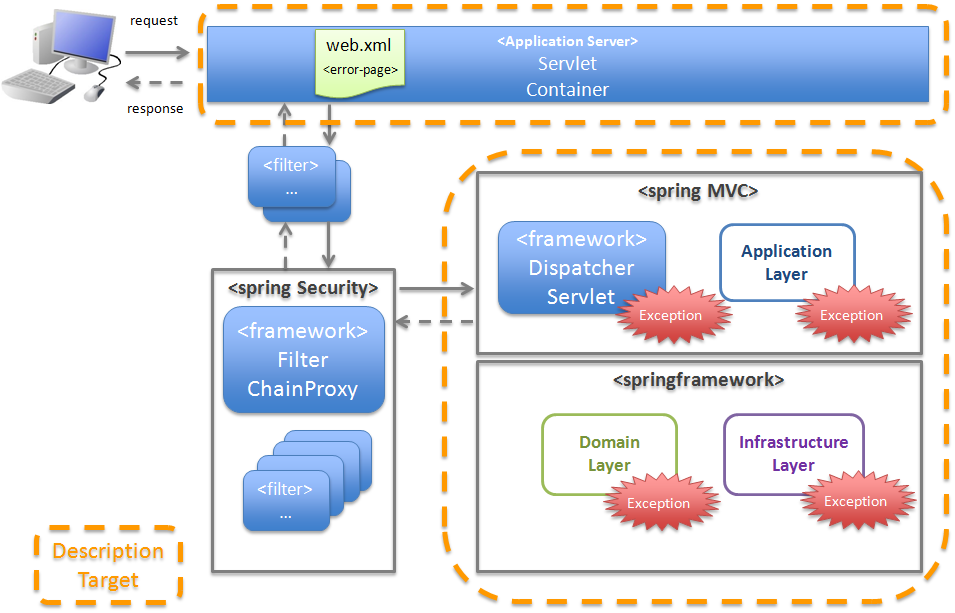
This section illustrates handling of exceptions occurring within the boundary of Spring MVC. The scope of description is as follows:
4.2.1.1. Classification of exceptions¶
The exceptions that occur when an application is running, can be broadly classified into following 3 categories.
| Sr. No. | Classification | Description | Types of exceptions |
|---|---|---|---|
(1)
|
Exceptions wherein cause can be resolved if the user re-executes the operation (by changing input values etc.)
|
The exceptions wherein cause can be resolved if the user re-executes the operation, are handled in application code.
|
|
(2)
|
Exceptions wherein cause cannot be resolved even if the user re-executes the operation
|
The exceptions wherein cause cannot be resolved even if the user re-executes the operation, are handled using the framework.
|
|
(3)
|
Exceptions due to invalid requests from the client
|
The exceptions which occur due to invalid requests from the client, are handled using the framework.
|
Note
Who is a target audience for exceptions?
- Application Developer should be aware of exception (1).
- Application Architect should be aware of exceptions (2) and (3).
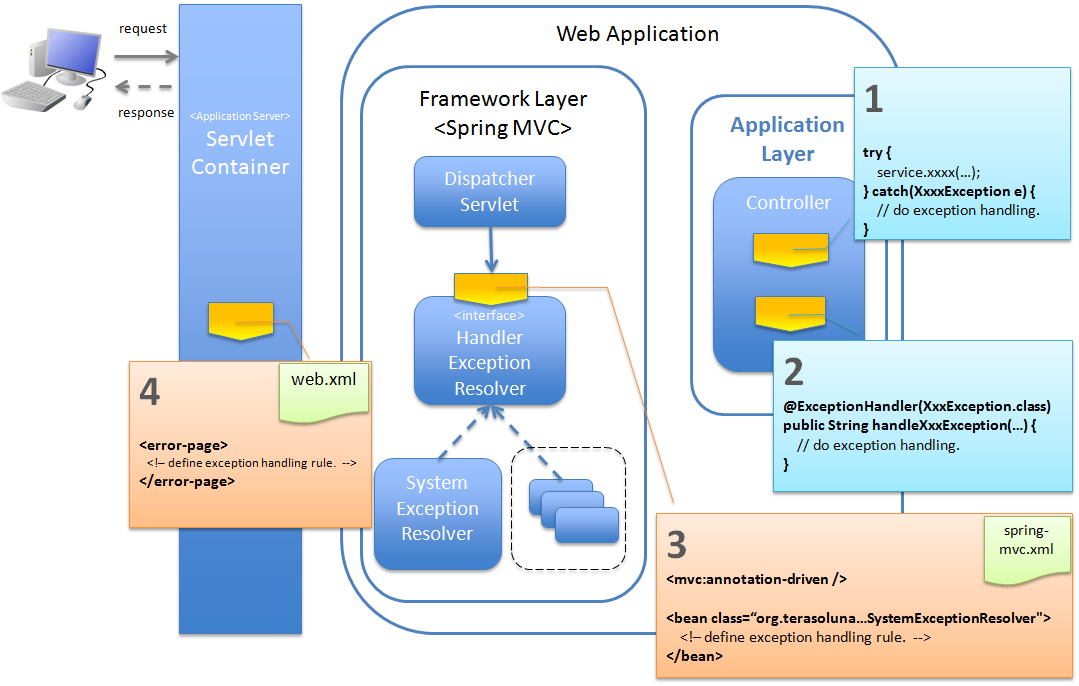
4.2.1.2. Exception handling methods¶
| Sr. No. | Handling Method | Description | Exception Handling Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|
(1)
|
Use
try-catch in the application code to carry out exception handling. |
Use this in order to handle exceptions at request (Controller method) level.
For details, refer to Basic flow when the Controller class handles the exception at request level.
|
|
(2)
|
Use
@ExceptionHandler annotation to carry out exception handling in application code. |
Use this when exceptions are to be handled at use case (Controller) level.
For details, refer to Basic flow when the Controller class handles the exception at use case level.
|
|
(3)
|
Use HandlerExceptionResolver mechanism provided by the framework to carry out exception handling.
|
Use this in order to handle exceptions at servlet level.
When
<mvc:annotation-driven> is specified, HandlerExceptionResolver uses automatically registered class, and SystemExceptionResolver provided by common library.For details, refer to Basic flow when the framework handles the exception at servlet level.
|
|
(4)
|
Use the error-page function of the servlet container to carry out exception handling.
|
Use this in order to handle fatal errors and exceptions which are out of the boundary of Spring MVC.
For details, refer to Basic flow when the servlet container handles the exception at web application level.
|
Note
Who will carry out exception handling?
- Application Developer should design and implement (1) and (2).
- Application Architect should design and configure (3) and (4).
Note
About automatically registered HandlerExceptionResolver
When <mvc:annotation-driven> is specified, the roles of HandlerExceptionResolver, which is registered automatically, are as follows:
The priority order will be as given below.
Sr. No. Class (Priority order) Role @ExceptionHandlerannotation.This class is necessary for implementing the handling method No. 2.@ResponseStatusis applied as class level annotation.HttpServletResponse#sendError(int sc, String msg)is called with the value specified in@ResponseStatus.HttpServletResponse#sendError(int sc)is called using the value of HTTP response code corresponding to framework exception.For details on HTTP response code to be set, refer to HTTP response code set by DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver.
Note
What is a role of SystemExceptionResolver provided by common library?
This is a class for handling exceptions which are not handled by HandlerExceptionResolver which is registered automatically when <mvc:annotation-driven> is specified. Therefore, the order of priority of this class should be set after DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver.
Note
About @ControllerAdvice annotation added from Spring Framework 3.2
@ControllerAdvicemade exception handling possible using@ExceptionHandlerat servlet level. If methods with@ExceptionHandlerannotation are defined in a class with@ControllerAdviceannotation, then exception handling carried out in the methods with@ExceptionHandlerannotation can be applied to all the Controllers in Servlet. When implementing the above in earlier versions, it was necessary to define methods with@ExceptionHandlerannotation in Controller base class and inherit each Controller from the base class.
About attribute of @ControllerAdvice annotation added from Spring Framework 4.0
By specifying attribute of@ControllerAdviceannotation, it has been improved in such a way that Controller that applies a method implemented in class with@ControllerAdvice, can be specified flexibly. For details on attribute, refer to attribute of @ControllerAdvice.
Note
Where to use @ControllerAdvice annotation?
- When logic other than determining the View name and HTTP response code is necessary for exception handling to be carried out at servlet level,
(If only determining View name and HTTP response code is sufficient, it can be implemented using
SystemExceptionResolver) - In case of exception handling carried out at servlet level, when response data is to be created by serializing the error model (JavaBeans) in JSON or XML formats without using template engines such as JSP. (Used for error handling at the time of creating Controller for AJAX or REST).
4.2.2. Detail¶
4.2.2.1. Types of exceptions¶
There are 6 types of exceptions that occur in a running application.
| Sr. No. | Types of Exceptions | Description |
|---|---|---|
(1)
|
Exception to notify a violation of a business rule
|
|
(2)
|
Amongst the exceptions that occur in framework and libraries, the exception which is likely to occur when the system is operating normally.
|
|
(3)
|
Exception to notify detection of a state which should not occur when the system is operating normally
|
|
(4)
|
Unchecked exception that does not occur when the system is operating normally
|
|
(5)
|
Error to notify an occurrence of a fatal error impacting the entire system (application)
|
|
(6)
|
Exception to notify that the framework has detected invalid request contents
|
4.2.2.1.1. Business exception¶
- If the reservation date is past the deadline when making travel reservations
- If a product is out of stock when it is ordered
- etc …
Note
Corresponding Exception Class
org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException(Class provided by common library).- When handling is to be carried out at detailed level, exception class that inherits BusinessException should be created.
- If the requirements cannot be met by the exception class provided by common library, a business exception class should be created for each project.
4.2.2.1.2. Library exceptions that occurs during normal operation¶
- Optimistic locking exception and pessimistic locking exception that occur if multiple users attempt to update same data simultaneously.
- Unique constraint violation exception that occurs if multiple users attempt to register same data simultaneously.
- etc …
Note
Examples of corresponding Exception Classes
org.springframework.dao.OptimisticLockingFailureException(Exception that occurs if there is an error due to optimistic locking).org.springframework.dao.PessimisticLockingFailureException(Exception that occurs if there is an error due to pessimistic locking).org.springframework.dao.DuplicateKeyException(Exception that occurs if there is a unique constraint violation).- etc …
Todo
Currently it has been found that unexpected errors occur if JPA(Hibernate) is used.
- In case of unique constraint violation,
org.springframework.dao.DataIntegrityViolationExceptionoccurs and notDuplicateKeyException.
4.2.2.1.3. System Exception¶
- If the master data, directories, files, etc. those should have pre-existed, do not exist
- Amongst the checked exceptions that occur in the framework, libraries, if exceptions classified as system errors are caught (IOException during file operations etc.).
- etc …
Note
Corresponding Exception Class
org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.SystemException(Class provided by common library).- When the error screen of View and HTTP response code need to be switched on the basis of the cause of each error, SystemException should be inherited for each error cause and the mapping between the inherited exception class and the error screen should be defined in the bean definition of SystemExceptionResolver.
- If the requirements are not met by the system exception class provided in the common library, a system exception class should be created in each respective project.
4.2.2.1.4. Unexpected System Exception¶
- When bugs are hidden in the application, framework or libraries
- When DB Server etc. is down
- etc …
Note
Example of Corresponding Exception Class
java.lang.NullPointerException(Exception caused due to bugs).org.springframework.dao.DataAccessResourceFailureException(Exception that occurs when DB server is down).- etc …
4.2.2.1.5. Fatal Errors¶
- If the memory available in Java virtual machine is inadequate
- etc …
Note
Example of corresponding Error Class
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError(Error due to inadequate memory).- etc …
4.2.2.1.6. Framework exception in case of invalid requests¶
- Exception that occurs when a request path for which only POST method is permitted, is accessed using GET method.
- Exception that occurs when type-conversion fails for the values extracted from URI using @PathVariable annotation.
- etc …
Note
Example of corresponding Exception Class
org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(Exception that occurs when the access is made through a HTTP method which is not supported).org.springframework.beans.TypeMismatchException(Exception that occurs if the specified value cannot be converted to URI).- etc …
Class for which HTTP status code is “4XX” in the list given at HTTP response code set by DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver.
4.2.2.2. Exception Handling Patterns¶
| Sr. No. | Purpose of handling | Types of exceptions | Handling method | Handling location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
(1)
|
Application code
(try-catch)
|
Request
|
||
(2)
|
Application code
(@ExceptionHandler)
|
Use case
|
||
(3)
|
Framework
(Handling rules are specified in
spring-mvc.xml) |
Servlet
|
||
(4)
|
Framework
|
Servlet
|
||
(5)
|
1. Fatal Errors
|
Servlet container
(Handling rules are specified in
web.xml) |
Web application
|
|
(6)
|
1. All the exceptions and errors that occur in the presentation layer
|
Servlet container
(Handling rules are specified in
web.xml) |
Web application
|
4.2.2.2.1. When notifying partial redo of a use case (from middle)¶
When partial redo (from middle) of a use case is to be notified, catch (try-catch) the exception in the application code of Controller class and carry out exception handling at request level.
Note
Example of notifying partial redo of a use case
- When an order is placed through a shopping site, if business exception notifying stock shortage occurs.In such a case, order can be placed if the no. of items to be ordered is reduced; hence display a screen on which no. of items can be changed and prompt a message asking to change the same.
4.2.2.2.2. When notifying redo of a use case (from beginning)¶
When redo of a use case (from beginning) is to be notified, catch the exception using @ExceptionHandler, and carry out exception handling at use case level.
Note
Example when notifying redo of a use case (from beginning)
- At the time of changing the product master on shopping site (site for administrator), it has been changed by other operator (in case of optimistic locking exception).In such a case, the operation needs to be carried out after verifying the changes made by the other user; hence display the front screen of the use case (for example: search screen of product master) and prompt a message asking the user to perform the operation again.
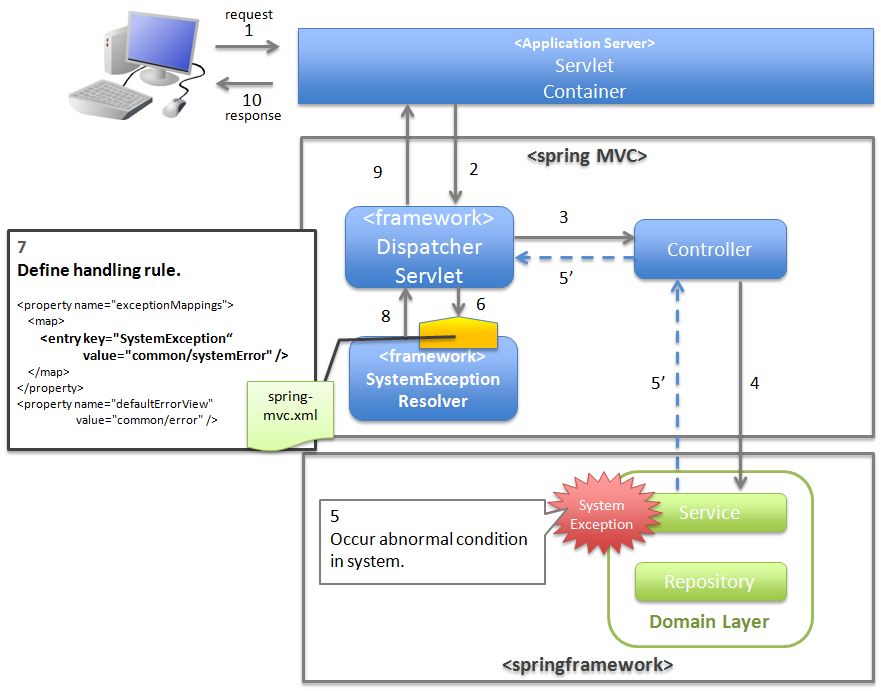
4.2.2.2.3. When notifying that the system or application is not in a normal state¶
When an exception to notify that system or application is not in a normal state is detected, catch the exception using SystemExceptionResolver and carry out exception handling at servlet level.
Note
Examples for notifying that the system or application is not in a normal state
- In case of a use case for connecting to an external system, if an exception occurs notifying that the external system is blocked.In such a case, since use case cannot be executed until external system resumes service, display the error screen, and notify that the use case cannot be executed till the external system resumes service.
- When searching master information with the value specified in the application, if the corresponding master information does not exist.In such a case, there is a possibility of bug in master maintenance function or of error (release error) in data input by the system administrator; hence display the system error screen and notify that a system error has occurred.
- When IOException occurs from the API during file operations.This could be a case of disk failure etc.; hence display the system error screen and notify that system error has occurred.
etc …
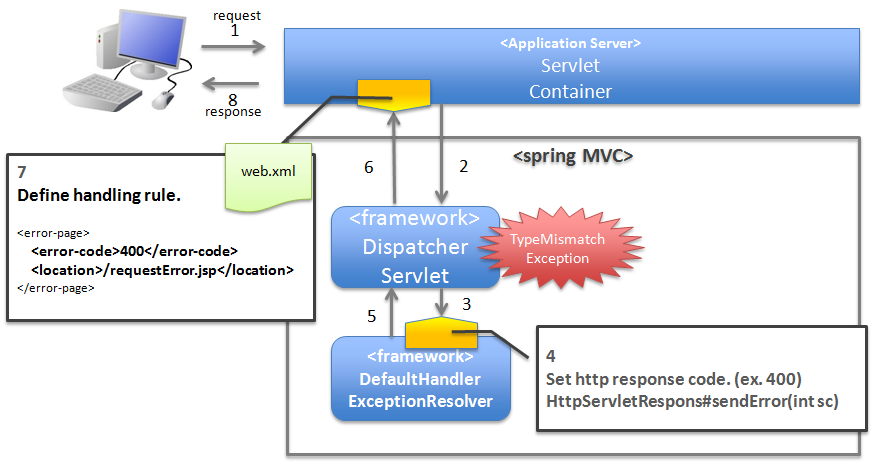
4.2.2.2.4. When notifying that the request contents are invalid¶
When notifying that an invalid request is detected by the framework, catch the exception using DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver, and carry out exception handling at servlet level.
Note
Example when notifying that the request contents are invalid
- When a URI is accessed using GET method, while only POST method is permitted.In such a case, it is likely that the access has been made directly using the Favorites feature etc. of the browser; hence display the error screen and notify that the request contents are invalid.
- When value cannot be extracted from URI using
@PathVariableannotationIn such a case, it is likely that the access has been made directly by replacing the value of the address bar on the browser; hence display the error screen and notify that the request contents are invalid. etc …
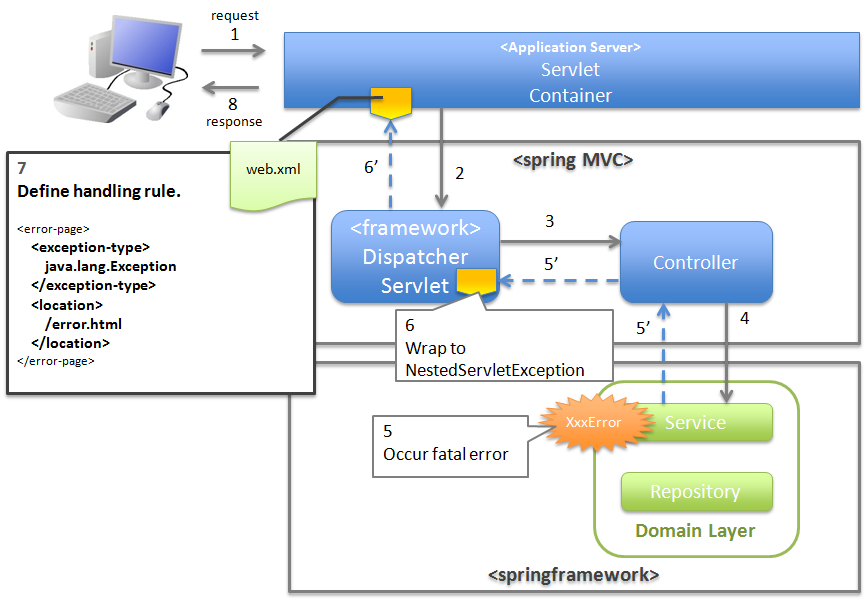
4.2.2.2.5. When a fatal error has been detected¶
When a fatal error has been detected, catch the exception using servlet container and carry out exception handling at web application level.
Warning
Regarding handling fatal errors using @ExceptionHandler and SystemExceptionResolver
Fatal error (java.lang.Error and its subclass) and the org.springframework.web.util.NestedServletException wrapped by java.lang.Throwable can be captured from Spring Framework 4.3
by using exception handler (HandlerExceptionResolver) of Spring MVC.
As a result of this change, the fatal error and Throwable are likely to get accidentally captured by SystemExceptionResolver offered by common library (inherit HandlerExceptionResolver) and the method which assigns @ExceptionHandler(run on HandlerExceptionResolversystem).
In order to capture the fatal errors by servlet containers, it is necessary to notify servlet container without using the methods which assign SystemExceptionResolver and @ExceptionHandler for handling NestedServletException.
“How to use” explains the method for not handling NestedServletException.
- For
SystemExceptionResolver, refer to Application Layer Settings. - For
@ExceptionHandler, refer to Method to handle exception at use case level.
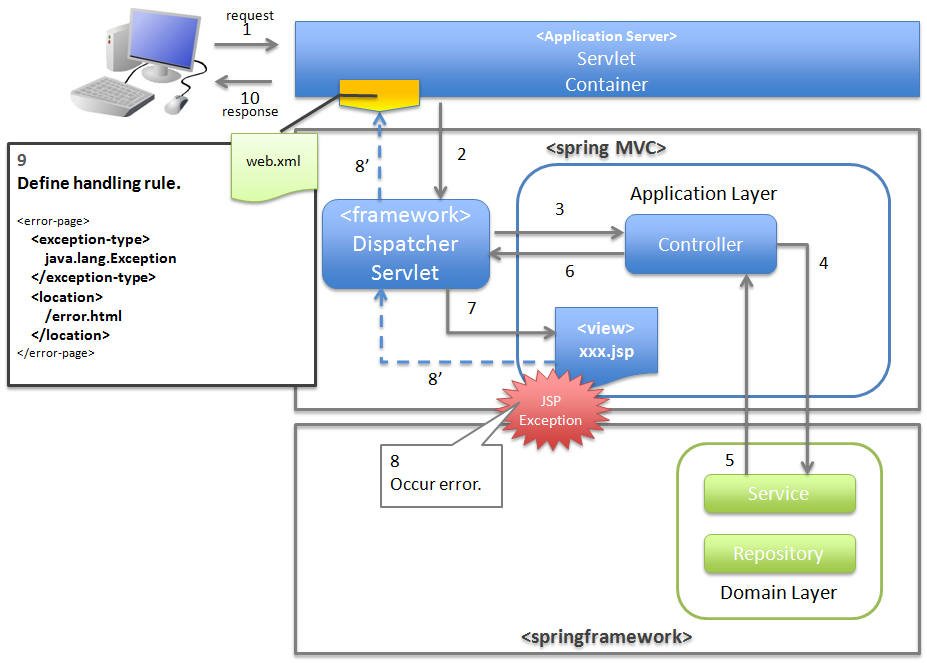
4.2.2.2.6. When notifying that an exception has occurred in the presentation layer (JSP etc.)¶
When notifying that an exception has occurred in the presentation layer (JSP etc.), catch the exception using servlet container and carry out exception handling at web application level.
4.2.2.3. Basic Flow of Exception Handling¶
- Basic flow when the Controller class handles the exception at request level
- Basic flow when the Controller class handles the exception at use case level
- Basic flow when the framework handles the exception at servlet level
- Basic flow when the servlet container handles the exception at web application level
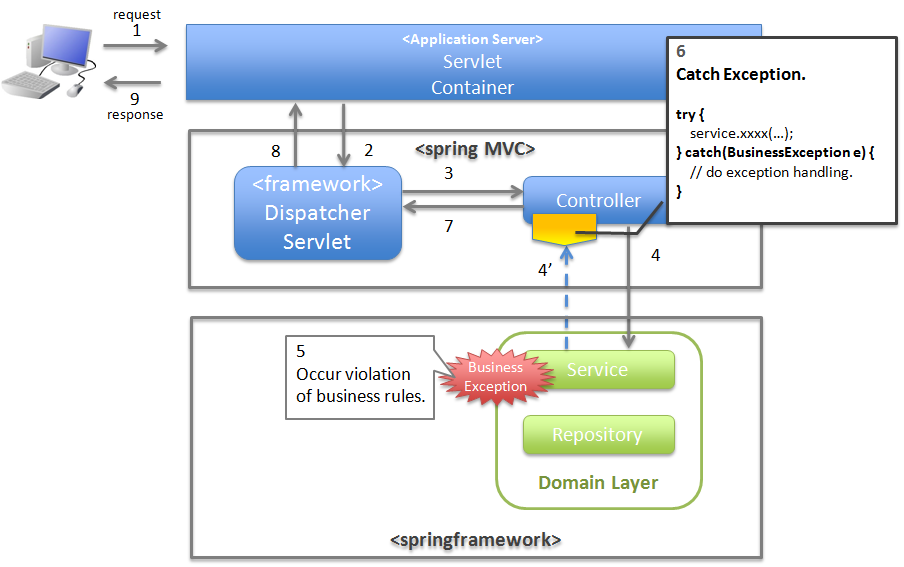
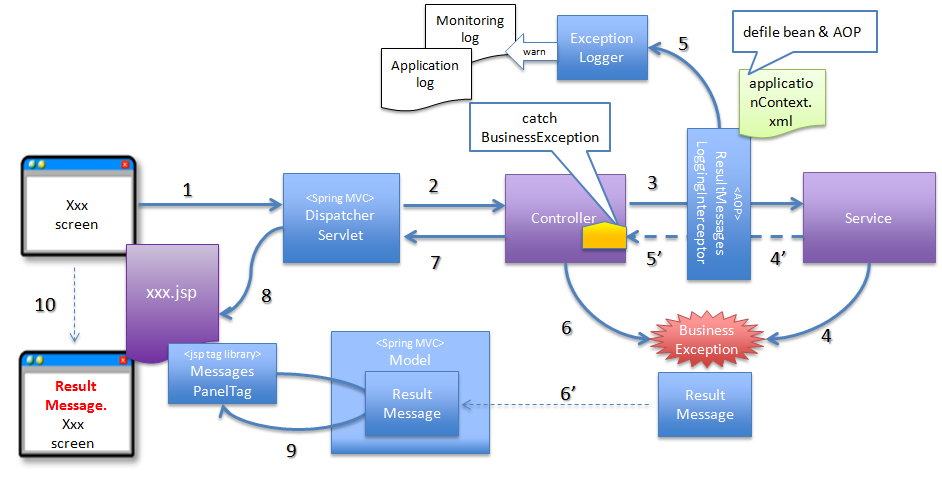
4.2.2.3.1. Basic flow when the Controller class handles the exception at request level¶
org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException) provided by common library.org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResultMessagesLoggingInterceptor) which records that an exception holding the result message has occurred.- In Service class, BusinessException is generated and thrown.
- ResultMessagesLoggingInterceptor calls ExceptionLogger, and outputs log of warn level (monitoring log and application log). ResultMessagesLoggingInterceptor class outputs logs only when sub exception (BusinessException/ResourceNotFoundException) of ResultMessagesNotificationException occurs.
- Controller class catches BusinessException, extracts the message information (ResultMessage) from BusinessException and sets it to Model for screen display(6’).
- Controller class returns the View name.
- DispatcherServlet calls JSP corresponding to the returned View name.
- JSP acquires message information (ResultMessage) using MessagesPanelTag and generates HTML code for message display.
- The response generated by JSP is displayed.
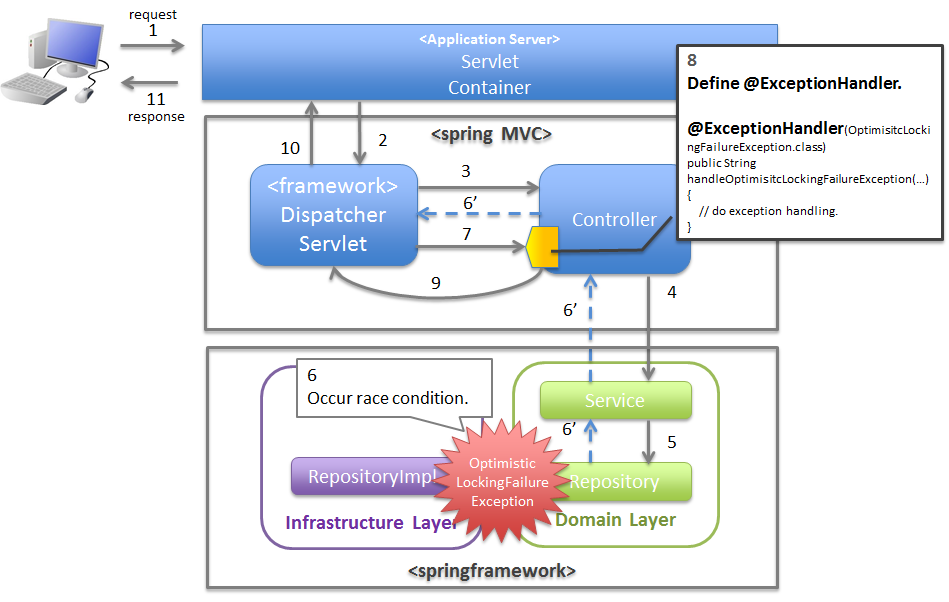
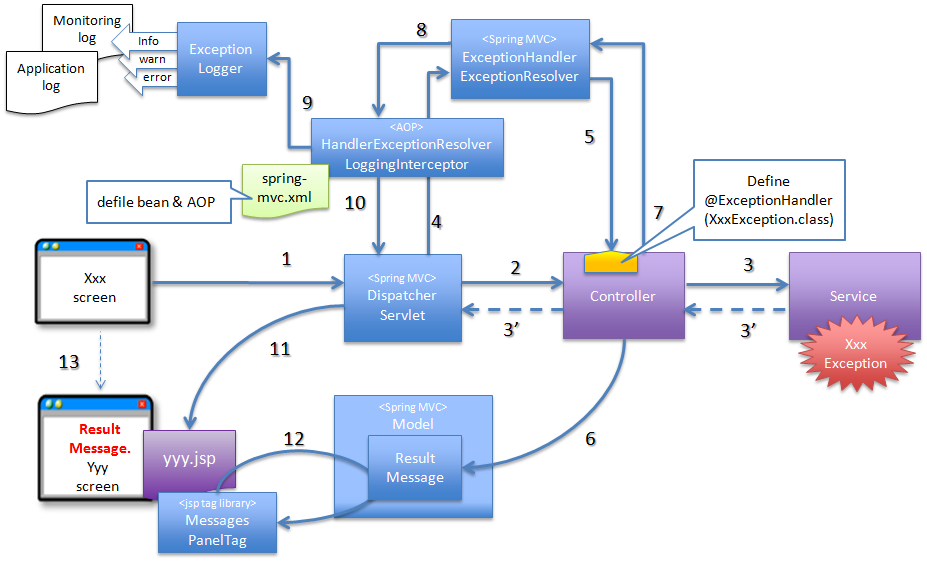
4.2.2.3.2. Basic flow when the Controller class handles the exception at use case level¶
@ExceptionHandler of Controller class.XxxException).org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor). This interceptor records that the exception is handled using HandlerExceptionResolver.- Exception (XxxException) is generated in the Service class called from Controller class.
- DispatcherServlet catches XxxException and calls ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver.
- ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver calls exception handling method provided in Controller class.
- Controller class generates message information (ResultMessage) and sets it to the Model for screen display.
- Controller class returns the View name.
- ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver returns the View name returned by the Controller.
- HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor calls ExceptionLogger and outputs logs (monitoring log and application log) (at info, warn, error levels) corresponding to the exception code.
- HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor returns View name returned by ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver.
- DispatcherServlet calls JSP that corresponds to the returned View name.
- JSP acquires the message information (ResultMessage) using MessagesPanelTag and generates HTML code for message display.
- The response generated by JSP is displayed.
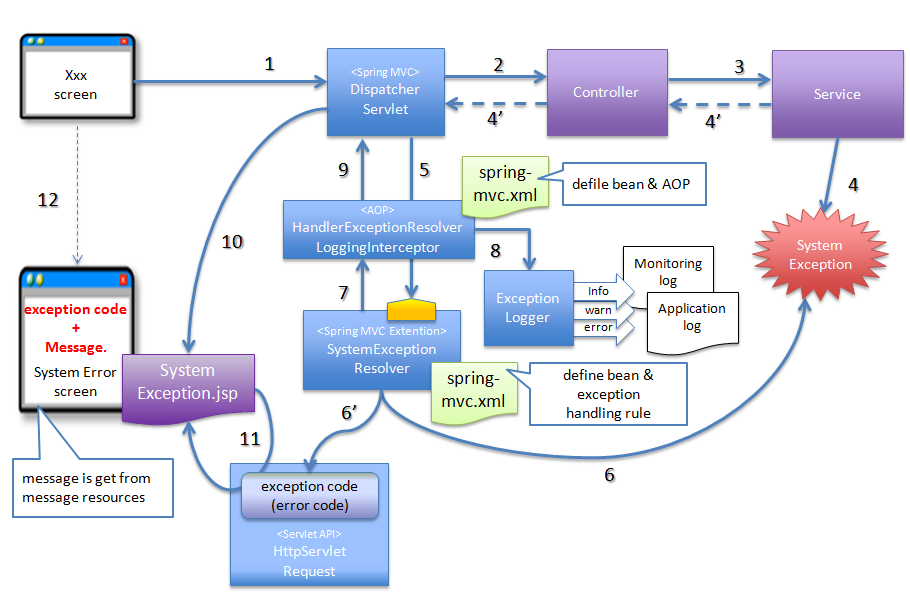
4.2.2.3.3. Basic flow when the framework handles the exception at servlet level¶
org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.SystemException) provided by common library using org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver .org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor) which records the exception specified in the argument of exception handling method.- A state equivalent to the system exception is detected in Service class; hence throw a SystemException.
- DispatcherServlet catches SystemException, and calls SystemExceptionResolver.
- SystemExceptionResolver acquires exception code from SystemException and sets it to HttpServletRequest for screen display (6’).
- SystemExceptionResolver returns the View name corresponding to SystemException.
- HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor calls ExceptionLogger and outputs logs (monitoring log and application log) (at info, warn, error levels) corresponding to the exception code.
- HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor returns the View name returned by SystemExceptionResolver.
- DispatcherServlet calls the JSP corresponding to the returned View name.
- JSP acquires the exception code from HttpServletRequest and inserts it in HTML code for message display.
- The response generated by JSP is displayed.
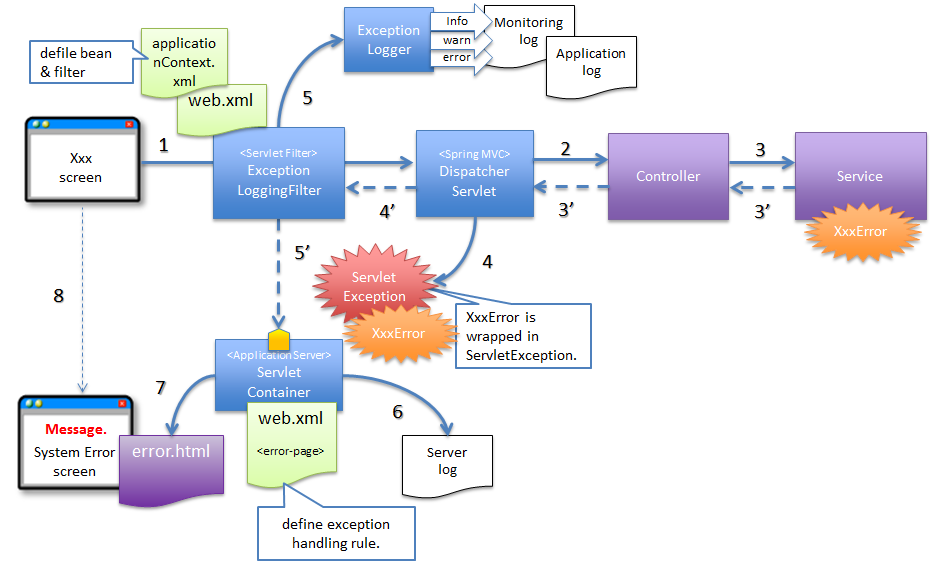
4.2.2.3.4. Basic flow when the servlet container handles the exception at web application level¶
org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.ExceptionLoggingFilter) which records that an unhandled exception has occurred.- DispatcherServlet catches XxxError, wraps it in ServletException and then throws it.
- ExceptionLoggingFilter catches ServletException and calls ExceptionLogger. ExceptionLogger outputs logs (monitoring log and application log) (at info, warn, error levels) corresponding to the exception code. ExceptionLoggingFilter re-throws ServletException.
- ServletContainer catches ServletException and outputs logs to server log. Log level varies depending on the application server.
- ServletContainer calls the View (HTML etc.) defined in
web.xml. - The response generated by the View which is called by the ServletContainer, is displayed.
4.2.3. How to use¶
The usage of exception handling functionality is described below.
For exception handling classes provided by common library, refer to Exception handling classes provided by the common library.
4.2.3.1. Application Settings¶
4.2.3.1.1. Common Settings¶
- Add bean definition of logger class (
ExceptionLogger) which will output exception log.
- applicationContext.xml
<!-- Exception Code Resolver. --> <bean id="exceptionCodeResolver" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.SimpleMappingExceptionCodeResolver"> <!-- (1) --> <!-- Setting and Customization by project. --> <property name="exceptionMappings"> <!-- (2) --> <map> <entry key="ResourceNotFoundException" value="e.xx.fw.5001" /> <entry key="BusinessException" value="e.xx.fw.8001" /> </map> </property> <property name="defaultExceptionCode" value="e.xx.fw.9001" /> <!-- (3) --> </bean> <!-- Exception Logger. --> <bean id="exceptionLogger" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionLogger"> <!-- (4) --> <property name="exceptionCodeResolver" ref="exceptionCodeResolver" /> <!-- (5) --> </bean>
Sr. No. Description ExceptionCodeResolverto bean definition.Note
About the Exception Code (Message ID)
The exception code is defined here for taking into account the case wherein message ID is not specified in generated “BusinessException”, however, it is recommended that you specify the “Exception Code (Message ID)” at the implementation side which generates the “BusinessException” (this point is explained later). Specification of “Exception Code (Message ID)” for “BusinessException” is an alternative measure in case it is not specified when “BusinessException” occurs.
[Location to be customized for each project]Note
Exception Code (Message ID)
Exception code is only to be output to log (It can also be fetched on screen). It is also possible to create an ID which need not be in the format usually used to define IDs in Properties file, but can be identified in the application. For example, MA7001 etc.
ExceptionLoggerto bean definition.ExceptionCodeResolverinto the bean definition ofExceptionLogger.
- Add log definition.
- logback.xml
Add log definition for monitoring log.
<appender name="MONITORING_LOG_FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender"> <!-- (1) --> <file>${app.log.dir:-log}/projectName-monitoring.log</file> <rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy"> <fileNamePattern>${app.log.dir:-log}/projectName-monitoring-%d{yyyyMMdd}.log</fileNamePattern> <maxHistory>7</maxHistory> </rollingPolicy> <encoder> <charset>UTF-8</charset> <pattern><![CDATA[date:%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}\tX-Track:%X{X-Track}\tlevel:%-5level\tmessage:%msg%n]]></pattern> </encoder> </appender> <logger name="org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionLogger.Monitoring" additivity="false"> <!-- (2) --> <level value="error" /> <!-- (3) --> <appender-ref ref="MONITORING_LOG_FILE" /> <!-- (4) --> </logger>
Sr. No. Description Warning
About additivity setting value
Specify
false. Iftrueis specified, the same log will be output by upper level logger (for example, root).Add log definition for application log.
<appender name="APPLICATION_LOG_FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender"> <!-- (1) --> <file>${app.log.dir:-log}/projectName-application.log</file> <rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy"> <fileNamePattern>${app.log.dir:-log}/projectName-application-%d{yyyyMMdd}.log</fileNamePattern> <maxHistory>7</maxHistory> </rollingPolicy> <encoder> <charset>UTF-8</charset> <pattern><![CDATA[date:%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}\tthread:%thread\tX-Track:%X{X-Track}\tlevel:%-5level\tlogger:%-48logger{48}\tmessage:%msg%n]]></pattern> </encoder> </appender> <logger name="org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionLogger"> <!-- (2) --> <level value="info" /> <!-- (3) --> </logger> <root level="warn"> <appender-ref ref="STDOUT" /> <appender-ref ref="APPLICATION_LOG_FILE" /> <!-- (4) --> </root>
Sr. No. Description Note
Appender definition for outputting application log
Rather than defining a separate appender for logging exceptions, it is recommended to use the same appender which is used for logging in application code or framework. By using same output destination, it becomes easier to track the process until an exception occurs.
4.2.3.1.2. Domain Layer Settings¶
When exceptions (BusinessException,ResourceNotFoundException) holding ResultMessages occur, add AOP settings and bean definition of interceptor class (ResultMessagesLoggingInterceptor) for log output.
- xxx-domain.xml
<!-- interceptor bean. --> <bean id="resultMessagesLoggingInterceptor" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResultMessagesLoggingInterceptor"> <!-- (1) --> <property name="exceptionLogger" ref="exceptionLogger" /> <!-- (2) --> </bean> <!-- setting AOP. --> <aop:config> <aop:advisor advice-ref="resultMessagesLoggingInterceptor" pointcut="@within(org.springframework.stereotype.Service)" /> <!-- (3) --> </aop:config>
Sr. No. Description ResultMessagesLoggingInterceptor.applicationContext.xml.@Serviceannotation).
4.2.3.1.3. Application Layer Settings¶
Add to bean definition, the class (SystemExceptionResolver) used for handling the exceptions which are not handled by HandlerExceptionResolver registered automatically when <mvc:annotation-driven> is specified. .
- spring-mvc.xml
<!-- Setting Exception Handling. --> <!-- Exception Resolver. --> <bean class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver"> <!-- (1) --> <property name="exceptionCodeResolver" ref="exceptionCodeResolver" /> <!-- (2) --> <!-- Setting and Customization by project. --> <property name="order" value="3" /> <!-- (3) --> <property name="exceptionMappings"> <!-- (4) --> <map> <entry key="ResourceNotFoundException" value="common/error/resourceNotFoundError" /> <entry key="BusinessException" value="common/error/businessError" /> <entry key="InvalidTransactionTokenException" value="common/error/transactionTokenError" /> <entry key=".DataAccessException" value="common/error/dataAccessError" /> </map> </property> <property name="statusCodes"> <!-- (5) --> <map> <entry key="common/error/resourceNotFoundError" value="404" /> <entry key="common/error/businessError" value="409" /> <entry key="common/error/transactionTokenError" value="409" /> <entry key="common/error/dataAccessError" value="500" /> </map> </property> <property name="excludedExceptions"> <!-- (6) --> <array> <value>org.springframework.web.util.NestedServletException</value> </array> </property> <property name="defaultErrorView" value="common/error/systemError" /> <!-- (7) --> <property name="defaultStatusCode" value="500" /> <!-- (8) --> </bean> <!-- Settings View Resolver. --> <mvc:view-resolvers> <mvc:jsp prefix="/WEB-INF/views/" /> <!-- (9) --> </mvc:view-resolvers>
Sr. No. Description SystemExceptionResolverto bean definition.applicationContext.xml.<mvc:annotation-driven>is specified, automatically registered class is given higher priority.Hint
Method to disable exception handling carried out by DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
When exception handling is carried out by
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver, HTTP response code is set; however since View is not resolved, it needs to be resolved using Error Page element ofweb.xml. When it is required to resolve the View usingHandlerExceptionResolverand not inweb.xml, then priority order ofSystemExceptionResolvershould be set to “1”. By doing this, the handling process can be executed beforeDefaultHandlerExceptionResolver. For mapping of HTTP response codes when handling is done byDefaultHandlerExceptionResolver, refer to HTTP response code set by DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver.org.springframework.web.util.NestedServletExceptionis excluded from the handling in order to notify to servlet container without handling the fatal error bySystemExceptionResolver.For reasons of exclusion from handling, refer to “Regarding handling of fatal errors using @ExceptionHandler and SystemExceptionResolver”.Warning
Behavior when nothing is specified
Please note that it will be handled as “200”(OK).
Actual
Viewdepends onViewResolversettings.In above settings, destination pages will be as given below.
/WEB-INF/views/common/error/systemError.jsp/WEB-INF/views/common/error/resourceNotFoundError.jsp/WEB-INF/views/common/error/businessError.jsp/WEB-INF/views/common/error/transactionTokenError.jsp/WEB-INF/views/common/error/dataAccessError.jspTip
<mvc:view-resolvers>is an XML element added from Spring Framework 4.1. If<mvc:view-resolvers>element is used, it is possible to defineViewResolverin simple manner.Example of definition when
<bean>element is used in a conventional manner is given below.<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/" /> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /> </bean>
AOP settings and interceptor class (HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor) in order to output the log of exceptions handled by HandlerExceptionResolver should be added to bean definition.
- spring-mvc.xml
<!-- Setting AOP. --> <bean id="handlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor"> <!-- (1) --> <property name="exceptionLogger" ref="exceptionLogger" /> <!-- (2) --> </bean> <aop:config> <aop:advisor advice-ref="handlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor" pointcut="execution(* org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver.resolveException(..))" /> <!-- (3) --> </aop:config>
Sr. No. Description HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptorto bean definition.applicationContext.xml.HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptorto resolveException method ofHandlerExceptionResolverinterface.As per default settings, this class will not output the log for common library providedorg.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResultMessagesNotificationExceptionclass and its subclasses.The reason the exceptions of the sub class ofResultMessagesNotificationExceptionare excluded from the log output is because their log output is carried out byorg.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResultMessagesLoggingInterceptor.If default settings need to be changed, refer to About HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor settings.Filter class (
ExceptionLoggingFilter) used to output log of fatal errors and exceptions that are out of the boundary of Spring MVC should be added to bean definition andweb.xml.
- applicationContext.xml
<!-- Filter. --> <bean id="exceptionLoggingFilter" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.ExceptionLoggingFilter" > <!-- (1) --> <property name="exceptionLogger" ref="exceptionLogger" /> <!-- (2) --> </bean>
Sr. No. Description ExceptionLoggingFilterto bean definition.applicationContext.xml.
- web.xml
<filter> <filter-name>exceptionLoggingFilter</filter-name> <!-- (1) --> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> <!-- (2) --> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>exceptionLoggingFilter</filter-name> <!-- (3) --> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> <!-- (4) --> </filter-mapping>
Sr. No. Description ExceptionLoggingFilterdefined inapplicationContext.xml.org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy./*for outputting log of fatal errors and exceptions that are out of the boundary of Spring MVC.
- Output Log
date:2013-09-25 19:51:52 thread:tomcat-http--3 X-Track:f94de92148f1489b9ceeac3b2f17c969 level:ERROR logger:o.t.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionLogger message:[e.xx.fw.9001] An exception occurred processing JSP page /WEB-INF/views/exampleJSPException.jsp at line 13
4.2.3.1.4. Servlet Container Settings¶
Add error-page definition for Servlet Container in order to handle error response (HttpServletResponse#sendError) received through default exception handling functionality of Spring MVC, fatal errors and the exceptions that are out of the boundary of Spring MVC.
- web.xml
Add definitions in order to handle error response (HttpServletResponse#sendError) received through default exception handling functionality of Spring MVC.
<error-page> <!-- (1) --> <error-code>404</error-code> <!-- (2) --> <location>/WEB-INF/views/common/error/resourceNotFoundError.jsp</location> </error-page>
Sr. No. Description Add definitions in order to handle fatal errors and exceptions that are out of the boundary of Spring MVC.
<error-page> <!-- (3) --> <location>/WEB-INF/views/common/error/unhandledSystemError.html</location> </error-page>
Sr. No. Description
Note
About the path specified in location tag
If a fatal error occurs, there is high possibility of getting another error if the path of dynamic contents is specified.; hence in location tag, it is recommended that you specify a path of static contents such as HTML and not dynamic contents such as JSP.
Note
If untraceable error occurs during development
If an unexpected error response (HttpServletResponse#sendError) occurs after carrying out the above settings, there may be cases wherein it cannot be determined what kind of error response occurred.
Error screen specified in location tag is displayed; however if the cause of error cannot be identified from logs, it is possible to verify the error response (HTTP response code) on screen by commenting out the above settings.
When it is necessary to individually handle the exceptions that are out of the boundary of Spring MVC, definition of each exception should be added.
<error-page> <!-- (4) --> <exception-type>java.io.IOException</exception-type> <!-- (5) --> <location>/WEB-INF/views/common/error/systemError.jsp</location> </error-page>
Sr. No. Description
4.2.3.2. Coding Points (Service)¶
The coding points in Service when handling the exceptions are given below.
- Generating Business Exception
- Generating System Exception
- Catch the exception to continue the execution
4.2.3.2.1. Generating Business Exception¶
The method of generating Business Exception is given below.
Note
Notes related to the method of generating business exception
- It is recommended that you generate the business exception by detecting violation of business rules in logic.
- When it is required by the API specification of underlying base framework or existing layer of application, that violation of business rule be notified through an exception, then it is OK to catch the exception and throw it as business exception.Use of an exception to control the processing flow lowers the readability of overall logic and thus may reduce maintainability.
Warning
- It is assumed that business exception is generated in Service by default. In AOP settings,
log of business exception occurred in class with
@Serviceannotation, is being output. Business exceptions should not be logged in Controller etc. This rule can be changed if needed in the project.
- xxxService.java
... @Service public class ExampleExceptionServiceImpl implements ExampleExceptionService { @Override public String throwBusinessException(String test) { ... // int stockQuantity = 5; // int orderQuantity = 6; if (stockQuantity < orderQuantity) { // (1) ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error(); // (2) messages.add("e.ad.od.5001", stockQuantity); // (3) throw new BusinessException(messages); // (4) } ...
Sr. No. Description Tip
For the purpose of explanation,
xxxService.javalogic is written in steps (2)-(4) as shown above, however it can also be written in a single step.throw new BusinessException(ResultMessages.error().add( "e.ad.od.5001", stockQuantity));
xxx.properties
Add the below settings to the properties file.
e.ad.od.5001 = Order number is higher than the stock quantity={0}. Change the order number.
An application log as shown below is output.
date:2013-09-17 22:25:55 thread:tomcat-http--8 X-Track:6cfb0b378c124b918e40ac0c32a1fac7 level:WARN logger:o.t.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionLogger message:[e.xx.fw.8001] ResultMessages [type=error, list=[ResultMessage [code=e.ad.od.5001, args=[5], text=null]]] org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException: ResultMessages [type=error, list=[ResultMessage [code=e.ad.od.5001, args=[5], text=null]]] // stackTrace omitted ... date:2013-09-17 22:25:55 thread:tomcat-http--8 X-Track:6cfb0b378c124b918e40ac0c32a1fac7 level:DEBUG logger:o.t.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver message:Resolving exception from handler [public java.lang.String org.terasoluna.exception.app.example.ExampleExceptionController.home(java.util.Locale,org.springframework.ui.Model)]: org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException: ResultMessages [type=error, list=[ResultMessage [code=e.ad.od.5001, args=[5], text=null]]] date:2013-09-17 22:25:55 thread:tomcat-http--8 X-Track:6cfb0b378c124b918e40ac0c32a1fac7 level:DEBUG logger:o.t.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver message:Resolving to view 'common/error/businessError' for exception of type [org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException], based on exception mapping [BusinessException] date:2013-09-17 22:25:55 thread:tomcat-http--8 X-Track:6cfb0b378c124b918e40ac0c32a1fac7 level:DEBUG logger:o.t.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver message:Applying HTTP status code 409 date:2013-09-17 22:25:55 thread:tomcat-http--8 X-Track:6cfb0b378c124b918e40ac0c32a1fac7 level:DEBUG logger:o.t.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver message:Exposing Exception as model attribute 'exception'
Displayed screen
Catch an exception to generate a business exception
try { order(orderQuantity, itemId ); } catch (StockNotEnoughException e) { // (1) throw new BusinessException(ResultMessages.error().add( "e.ad.od.5001", e.getStockQuantity()), e); // (2) }
Sr. No. Description
4.2.3.2.2. Generating System Exception¶
The method of generating SystemException is given below.
Generate a system exception by detecting a system error in logic.
if (itemEntity == null) { // (1) throw new SystemException("e.ad.od.9012", "not found item entity. item code [" + itemId + "]."); // (2) }
Sr. No. Description
Application log as shown below is output.
date:2013-09-19 21:03:06 thread:tomcat-http--3 X-Track:c19eec546b054d54a13658f94292b24f level:DEBUG logger:o.t.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver message:Resolving exception from handler [public java.lang.String org.terasoluna.exception.app.example.ExampleExceptionController.home(java.util.Locale,org.springframework.ui.Model)]: org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.SystemException: not found item entity. item code [10-123456]. date:2013-09-19 21:03:06 thread:tomcat-http--3 X-Track:c19eec546b054d54a13658f94292b24f level:DEBUG logger:o.t.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver message:Resolving to default view 'common/error/systemError' for exception of type [org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.SystemException] date:2013-09-19 21:03:06 thread:tomcat-http--3 X-Track:c19eec546b054d54a13658f94292b24f level:DEBUG logger:o.t.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver message:Applying HTTP status code 500 date:2013-09-19 21:03:06 thread:tomcat-http--3 X-Track:c19eec546b054d54a13658f94292b24f level:DEBUG logger:o.t.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver message:Exposing Exception as model attribute 'exception' date:2013-09-19 21:03:06 thread:tomcat-http--3 X-Track:c19eec546b054d54a13658f94292b24f level:ERROR logger:o.t.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionLogger message:[e.ad.od.9012] not found item entity. item code [10-123456]. org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.SystemException: not found item entity. item code [10-123456]. at org.terasoluna.exception.domain.service.ExampleExceptionServiceImpl.throwSystemException(ExampleExceptionServiceImpl.java:14) ~[ExampleExceptionServiceImpl.class:na] ... // stackTrace omitted
Displayed screen
Note
It is recommended to have a common system error screen rather than creating multiple screens for system errors.
The screen mentioned in this guideline displays a (business-wise) message ID for system errors and has a fixed message. This is because there is no need to inform the details of error to the operator and it is sufficient to only convey that the system error has occurred. Therefore, in order to enhance the response for inquiry against system errors, the Message ID which acts as a key for the message text is displayed on the screen, in order to make the analysis easier for the development side. Displayed error screens should be designed in accordance with the UI standards of each project.
Catch an exception to generate system exception.
try { return new File(preUploadDir.getFile(), key); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // (1) throw new SystemException("e.ad.od.9007", "not found upload file. file is [" + preUploadDir.getDescription() + "]." e); // (2) }
Sr. No. Description
4.2.3.2.3. Catch the exception to continue the execution¶
@Inject ExceptionLogger exceptionLogger; // (1) // ...InteractionHistory interactionHistory = null; try { interactionHistory = restTemplete.getForObject(uri, InteractionHistory.class, customerId); } catch (RestClientException e) { // (2) exceptionLogger.log(e); // (3) } // (4) Customer customer = customerRepository.findOne(customerId); // ...
Sr. No. Description org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionLoggerprovided by the common library for log output.
An application log as shown below is output.
date:2013-09-19 21:31:47 thread:tomcat-http--3 X-Track:df5271ece2304b12a2c59ff494806397 level:ERROR logger:o.t.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionLogger message:[e.xx.fw.9001] Test example exception org.springframework.web.client.RestClientException: Test example exception ... // stackTrace omittedWarning
When log() is used in
exceptionLogger, since it will be output at error level; by default, it will be output in monitoring log also.date:2013-09-19 21:31:47 X-Track:df5271ece2304b12a2c59ff494806397 level:ERROR message:[e.xx.fw.9001] Test example exception
As shown in following example, if there is no problem in continuing the execution, and if monitoring log is being monitored through application monitoring, it should be set to a level such that it will not get monitored at log output level or defined such that it does not get monitored from the log content (log message).
} catch (RestClientException e) { exceptionLogger.info(e); }As per default settings, monitoring log other than error level will not be output. It is output in application log as follows:date:2013-09-19 22:17:53 thread:tomcat-http--3 X-Track:999725b111b4445b8d10b4ea44639c61 level:INFO logger:o.t.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionLogger message:[e.xx.fw.9001] Test example exception org.springframework.web.client.RestClientException: Test example exception
4.2.3.3. Coding Points (Controller)¶
The coding points in Controller while handling the exceptions are given below.
4.2.3.3.1. Method to handle exceptions at request level¶
@RequestMapping(value = "change", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String change(@Validated UserForm userForm, BindingResult result, RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes, Model model) { // (1) // omitted User user = userHelper.convertToUser(userForm); try { userService.change(user); } catch (BusinessException e) { // (2) model.addAttribute(e.getResultMessages()); // (3) return viewChangeForm(user.getUserId(), model); // (4) } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description
4.2.3.3.2. Method to handle exception at use case level¶
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class) // (1) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CONFLICT) // (2) public ModelAndView handleBusinessException(BusinessException e) { ExtendedModelMap modelMap = new ExtendedModelMap(); // (3) modelMap.addAttribute(e.getResultMessages()); // (4) String viewName = top(modelMap); // (5) return new ModelAndView(viewName, modelMap); // (6) }
Sr. No. Description @ExceptionHandlerannotation. You can also specify multiple exceptions which are in the scope of handling.@ResponseStatusannotation. In the example, “409: Conflict” is specified.Warning
When
java.lang.Exceptionandjavax.servlet.ServletExceptionare to be handled by a method which assigns@ExceptionHandler, the fatal errors cannot be notified to servlet container sinceNestedServletExceptionwhich wraps the fatal error get handled unintentionally. For details, refer to “Regarding handling of fatal errors using @ExceptionHandler and SystemExceptionResolver”.In such a case, in order to notify fatal error to the servlet container, :ref: NestedServletException is excluded from handling by SystemExceptionResolver<exception-handling-how-to-use-application-configuration-app-label> and NestedServletException is handled by the method which assigns @ExceptionHandler and then is thrown again. Implementation example is as below.
@ExceptionHandler(NestedServletException.class) // (1) public void handleNestedServletException(NestedServletException e) throws NestedServletException { throw e; // (2) }
Sr. No. Description @ExceptionHandlerannotation and specifyNestedServletException.class.NestedServletExceptionthus handled again.Regarding capturing Exception and ServletException by multiple controllers
When it is necessary to describe
@ExceptionHandlerwhich throwsNestedServletExceptionagain by multiple controllers, use of@ControllerAdviceshould be considered. For details of@ControllerAdvice, refer to Implementing “@ControllerAdvice”.
4.2.3.4. Coding points (JSP)¶
The coding points in JSP while handling the exceptions are given below.
- Method to display messages on screen using MessagesPanelTag
- Method to display system exception code on screen
Tip
When Internet Explorer is a support browser, implementation should be such that size of the HTML responded as error screen should be 513 bytes or more.
This is because in case of Internet Explorer, if the following three conditions such as
- Response status code is Error (4xx and 5xx)
- Response HTML is 512 bytes or less
- Browser setting “Show Friendly HTTP Error Messages” is valid
are satisfied, the mechanism is such that friendly messages created by Internet Explorer will be displayed.
4.2.3.4.1. Method to display messages on screen using MessagesPanelTag¶
The example below illustrates implementation at the time of outputting ResultMessages to an arbitrary location.
<t:messagesPanel /> <!-- (1) -->
Sr. No. Description <t:messagesPanel> tag should be specified at a location where the message is to be output. For details on usage of <t:messagesPanel> tag, refer to Message Management.
4.2.3.4.2. Method to display system exception code on screen¶
The example below illustrates implementation at the time of displaying exception code (message ID) and fixed message at an arbitrary location.
<p> <c:if test="${!empty exceptionCode}"> <!-- (1) --> [${f:h(exceptionCode)}] <!-- (2) --> </c:if> <spring:message code="e.cm.fw.9999" /> <!-- (3) --> </p>
Sr. No. Description
- Output Screen (With exceptionCode)
- Output Screen (Without exceptionCode)
Note
Messages to be output at the time of system exception
- When a system exception occurs, it is recommended that you display a message which would only convey that a system exception has occurred, without outputting a detailed message from which cause of error can be identified or guessed.
- On displaying a detailed message from which cause of error can be identified or guessed, the vulnerabilities of system are likely to get exposed.
Note
Exception code (message ID)
- When a system exception occurs, it is desirable to output an exception code (message ID) instead of a detailed message.
- By outputting the exception code (message ID), it is possible for development team to respond quickly to the inquiries from system user.
- Only a system administrator can identify the cause of error from exception code (message ID); hence the risk of exposing the vulnerabilities of system is lowered.
4.2.5. Appendix¶
- Exception handling classes provided by the common library
- About SystemExceptionResolver settings
- HTTP response code set by DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
4.2.5.1. Exception handling classes provided by the common library¶
| Sr. No. | Class | Role |
|---|---|---|
(1)
|
ExceptionCode
Resolver
|
An interface for resolving exception code (message ID) of exception class.
An exception code is used for identifying the exception type and is expected to be output to system error screen and log.
It is referenced from
ExceptionLogger, SystemExceptionResolver. |
(2)
|
SimpleMapping
ExceptionCode
Resolver
|
Implementation class of
ExceptionCodeResolver contains the mapping of exception class name and exception code, through which the exception code is resolved.The name of exception class need not be FQCN, it can be a part of FQCN or parent class name.
|
(3)
|
enums.
ExceptionLevel
|
enum indicating exception level corresponding to exception class.
INFO, WARN, ERROR are defined.
|
(4)
|
ExceptionLevel
Resolver
|
Interface for resolving exception level (log level) of exception class.
Exception level is a code for identifying the level of exception and is used to switch the output level of log.
It is referenced from
ExceptionLogger. |
(5)
|
DefaultException
LevelResolver
|
This is an implementation class of
ExceptionLevelResolver which resolves the exception level by first character of exception code.If the first character (case insensitive) is,
1. “i”, treat it as
ExceptionLevel.INFO2. “w”, treat it as
ExceptionLevel.WARN3. “e”, treat it as
ExceptionLevel.ERROR4. a character other than the above, treat as
ExceptionLevel.ERROR level.This class is implemented in accordance with the rules of the message ID described in Message guidelines.
|
(6)
|
ExceptionLogger
|
A class to output log of exceptions.
Monitoring log (only messages) and application log (both messages and stack trace) can be output.
This class is used from Filter or Interceptor classes provided by the framework.
When the execution is to be continued by handling the exceptions in application code, log should be output by using this class.
|
(7)
|
ResultMessages
LoggingInterceptor
|
This is an interceptor class for logging an occurrence of exception which stores
ResultMessages (sub exception of ResultMessagesNotificationException).Output all the logs at WARN level.
It is assumed that this Interceptor will be applied to the methods of class with
@Service annotation.Log is output using
ExceptionLogger. |
(8)
|
BusinessException
|
This is an exception class to notify violation of business rules. This exception should be generated in the logic of domain layer.
It inherits
java.lang.RuntimeException; hence the transactions are rolled back as per default behavior.If you want to commit the transactions, this exception class needs to be specified in noRollbackFor or noRollbackForClassName of
@Transactional annotation. |
(9)
|
Resource
NotFoundException
|
This is an exception class to notify that the specified resource (data) does not exist in the system. This exception should mainly be generated in the logic of domain layer.
It inherits
java.lang.RuntimeException; hence the transactions are rolled back as per default behavior. |
(10)
|
ResultMessages
Notification
Exception
|
This is an abstract exception class to notify that the exception holds the result messages (
ResultMessages), and BusinessException and ResourceNotFoundException inherit it in the common library.It inherits
java.lang.RuntimeException; hence the transactions are rolled back as per default behavior.If this exception class is inherited, log of warn level will be output by
ResultMessagesLoggingInterceptor. |
(11)
|
SystemException
|
This is an exception class to notify a system or application error. This exception should be generated in the logic of application layer or domain layer.
It inherits
java.lang.RuntimeException; hence the transactions are rolled back as per default behavior. |
(12)
|
ExceptionCodeProvider
|
This is an interface indicating that it has a role to hold the exception code; it is implemented by
SystemException in the common library.If an exception class that implements this interface is created, it can be used with the exception handling mechanism of ExceptionCodeResolver, to use the exception code of this exception class as it is.
|
| Sr. No. | Class | Role |
|---|---|---|
(13)
|
SystemException
Resolver
|
This is a class for handling the exceptions that will not be handled by
HandlerExceptionResolver, which is registered automatically when <mvc:annotation-driven> is specified.It inherits
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver provided by Spring MVC and adds the functionality of referencing ResultMessages of exception code from View. |
(14)
|
HandlerException
ResolverLogging
Interceptor
|
This is an Interceptor class to output the log of exceptions handled by
HandlerExceptionResolver.In this Interceptor class, the output level of log is switched based on the classification of HTTP response code resolved by
HandlerExceptionResolver.1. When it is “100-399”, log is output at INFO level.
2. When it is “400-499”, log is output at WARN level.
3. When it is “500-“, log is output at ERROR level.
4. When it is “-99”, log is not output.
By using this Interceptor, it is possible to output the log of all exceptions which are within the boundary of Spring MVC.
Log is output using
ExceptionLogger. |
(15)
|
ExceptionLogging
Filter
|
This is a Filter class to output the log of fatal errors and exceptions that are out of the boundary of Spring MVC.
All logs are output at ERROR level.
When this Filter is used, fatal errors and all exceptions that are out of the boundary of Spring MVC can be output to log.
Log is output using
ExceptionLogger. |
4.2.5.2. About SystemExceptionResolver settings¶
This section describes the settings which are not explained above. The settings should be performed depending on the requirements.
| Sr. No. | Field Name | Property Name | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
(1)
|
Attribute name of result message
|
resultMessagesAttribute
|
Specify the attribute name (String) used for setting message of businessException to Model.
This attribute name is used for accessing result message in View(JSP).
|
resultMessages |
(2)
|
Attribute name of exception code (message ID)
|
exceptionCode
Attribute
|
Specify the attribute name (String) used for setting the exception code (message ID) to HttpServletRequest.
This attribute name is used for accessing the exception code (message ID) in View(JSP).
|
exceptionCode |
(3)
|
Header name of exception code (message ID)
|
exceptionCode
Header
|
Specify the header name (String) used for setting the exception code (message ID) to response header of HttpServletResponse.
|
X-Exception-Code |
(4)
|
Attribute name of exception object
|
exceptionAttribute
|
Specify the attribute name (String) used for setting the handled exception object to Model.
This attribute name is used for accessing the exception object in View(JSP).
|
exception |
(5)
|
List of handler (Controller) objects to be used as this ExceptionResolver
|
mappedHandlers
|
Specify the object list (Set) of handlers that use this ExceptionResolver.
Only the exceptions in the specified handler objects will be handled.
This setting should not be specified.
|
Not specified
When specified, the operation is not guaranteed.
|
(6)
|
List of handler (Controller) classes that use this ExceptionResolver
|
mappedHandlerClasses
|
Specify the class list (Class[]) of handlers that use this ExceptionResolver.
Only the exceptions that occur in the specified handler classes are handled.
This setting should not be specified
|
Not specified
When specified, the operation is not guaranteed.
|
(7)
|
Cache control flag of HTTP response
|
preventResponseCaching
|
Set the flag (true: Yes, false: No) for cache control at the time of HTTP response.
If true: Yes is specified, HTTP response header to disable cache is added.
|
false: No
|
org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver.org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver.org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver.4.2.5.2.1. Attribute name of result message¶
spring-mvc.xml
<bean class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver"> <!-- omitted --> <property name="resultMessagesAttribute" value="resultMessagesForExceptionResolver" /> <!-- (1) --> <!-- omitted --> </bean>
jsp
<t:messagesPanel messagesAttributeName="resultMessagesForExceptionResolver"/> <!-- (2) -->
Sr. No. Description
4.2.5.2.2. Attribute name of exception code (message ID)¶
spring-mvc.xml
<bean class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver"> <!-- omitted --> <property name="exceptionCodeAttribute" value="exceptionCodeForExceptionResolver" /> <!-- (1) --> <!-- omitted --> </bean>
jsp
<p> <c:if test="${!empty exceptionCodeForExceptionResolver}"> <!-- (2) --> [${f:h(exceptionCodeForExceptionResolver)}] <!-- (3) --> </c:if> <spring:message code="e.cm.fw.9999" /> </p>
Sr. No. Description
4.2.5.2.3. Header name of exception code (message ID)¶
spring-mvc.xml
<bean class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver"> <!-- omitted --> <property name="exceptionCodeHeader" value="X-Exception-Code-ForExceptionResolver" /> <!-- (1) --> <!-- omitted --> </bean>
Sr. No. Description
4.2.5.2.4. Attribute name of exception object¶
spring-mvc.xml
<bean class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver"> <!-- omitted --> <property name="exceptionAttribute" value="exceptionForExceptionResolver" /> <!-- (1) --> <!-- omitted --> </bean>
jsp
<p>[Exception Message]</p> <p>${f:h(exceptionForExceptionResolver.message)}</p> <!-- (2) -->
Sr. No. Description
4.2.5.2.5. Cache control flag of HTTP response¶
spring-mvc.xml
<bean class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver"> <!-- omitted --> <property name="preventResponseCaching" value="true" /> <!-- (1) --> <!-- omitted --> </bean>
Sr. No. Description Note
HTTP response header when Yes is specified
If cache control flag of HTTP response is set to Yes, the following HTTP response header is output.
Cache-Control:no-storeAdding a header for cache control using
SystemExceptionResolveris an option to suppress display of unintended error screen due to browser cache, however a header for cache control can also be added for security by using a Spring Security function. For Spring Security function, refer A:ref:SpringSecurityLinkageWithBrowser.
4.2.5.3. About HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor settings¶
This section describes the settings which are not explained above. The settings should be performed depending on the requirements.
| Sr. No. | Field Name | Property Name | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
(1)
|
List of exception classes to be excluded from scope of logging
|
ignoreExceptions
|
Amongst the exceptions handled by
HandlerExceptionResolver, the exception classes which are not to be logged should be specified in list format.When an exception of the specified exception class and sub class occurs, the same is not logged in this class.
Only the exceptions which are logged at a different location (using different mechanism) should be specified here.
|
ResultMessagesNotificationException.classExceptions of
ResultMessagesNotificationException.class and its sub classes are logged by ResultMessagesLoggingInterceptor; hence, as default settings, they are being excluded. |
4.2.5.3.1. List of exception classes to be excluded from scope of logging¶
The settings when exception classes provided in the project are to be excluded from the scope of logging, are as follows:
- spring-mvc.xml
<bean id="handlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor"> <property name="exceptionLogger" ref="exceptionLogger" /> <property name="ignoreExceptions"> <set> <!-- (1) --> <value>org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResultMessagesNotificationException</value> <!-- (2) --> <value>com.example.common.XxxException</value> </set> </property> </bean>
Sr. No. Description ResultMessagesNotificationExceptionspecified in the default settings of common library, should be specified under exception to be excluded.
The settings when all the exception classes are to be logged are as follows:
- spring-mvc.xml
<bean id="handlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor"> <property name="exceptionLogger" ref="exceptionLogger" /> <!-- (3) --> <property name="ignoreExceptions"><null /></property> </bean>
Sr. No. Description nullin ignoreExceptions properties.Ifnullis specified, all the exception classes will become target for logging.
4.2.5.4. HTTP response code set by DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver¶
The mapping between framework exceptions handled using DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver and HTTP status code is shown below.
| Sr. No. | Handled framework exceptions | HTTP Status Code |
|---|---|---|
(1)
|
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.multiaction.NoSuchRequestHandlingMethodException
|
404
|
(2)
|
org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException
|
405
|
(3)
|
org.springframework.web.HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException
|
415
|
(4)
|
org.springframework.web.HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException
|
406
|
(5)
|
org.springframework.web.bind.MissingServletRequestParameterException
|
400
|
(6)
|
org.springframework.web.bind.ServletRequestBindingException
|
400
|
(7)
|
org.springframework.beans.ConversionNotSupportedException
|
500
|
(8)
|
org.springframework.beans.TypeMismatchException
|
400
|
(9)
|
org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotReadableException
|
400
|
(10)
|
org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotWritableException
|
500
|
(11).
|
org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException
|
400
|
(12)
|
org.springframework.web.multipart.support.MissingServletRequestPartException
|
400
|
(13)
|
org.springframework.validation.BindException
|
400
|
(14)
|
org.springframework.web.servlet.NoHandlerFoundException
|
404
|
(15)
|
org.springframework.web.context.request.async.AsyncRequestTimeoutException
|
503
|