6.1. Database Access (Common)¶
Table of Contents
- Overview
- How to use
- How to extend
- how to solve the problem
- Appendix
Todo
TBD
The following topics in this chapter are currently under study.
- About multiple datasources
- About handling of unique constraint errors and pessimistic exclusion errors when using JPAFor details, refer to Overview - About exception handling.
6.1.1. Overview¶
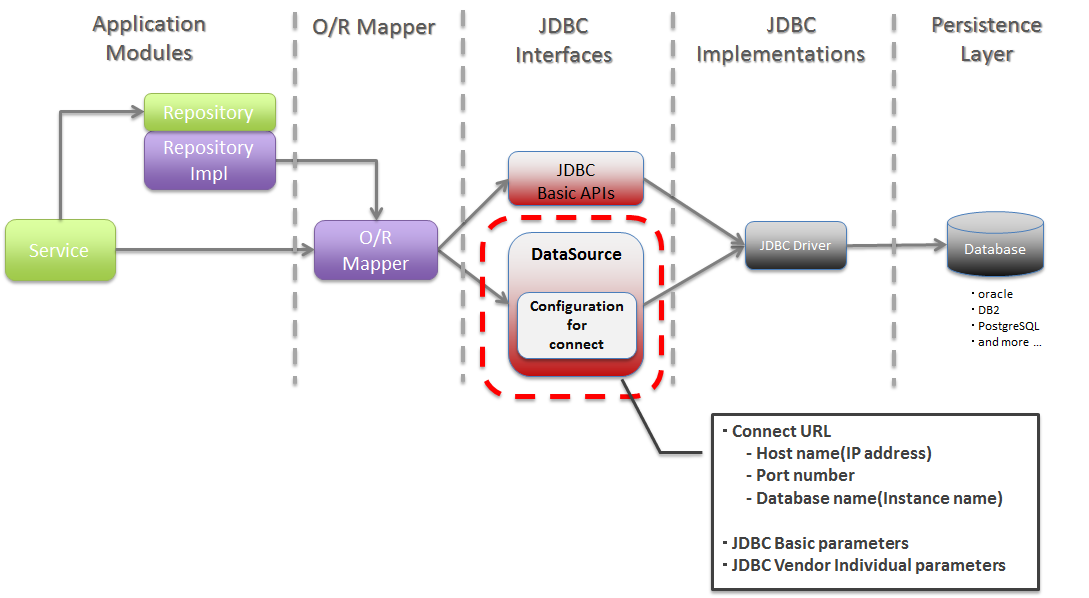
This chapter explains the method of accessing the data stored in RDBMS.
For the O/R Mapper dependent part, refer to
6.1.1.1. About JDBC DataSource¶
6.1.1.1.1. JDBC datasource provided by Application Server¶
Datasources provided by Application Server¶ Sr. No. Application Server Reference page
Apache Tomcat 8.5
Apache Tomcat 8.0
Apache Tomcat 7
Oracle WebLogic Server 12c Refer to Oracle WebLogic Server Product Documentation.
IBM WebSphere Application Server Version 9.0 Refer to WebSphere Application Server Online information center.
JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 7.0 Refer JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 7.0 Product Documentation.
JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 6.4 Refer JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 6.4 Product Documentation.
6.1.1.1.2. JDBC datasource provided by OSS/Third-Party library¶
JDBC datasource provided by OSS/Third-Party library¶ Sr. No. Library name Description
Apache Commons DBCP Refer to Apache Commons DBCP.
6.1.1.1.3. JDBC datasource provided by Spring Framework¶
6.1.1.2. About transaction management¶
6.1.1.3. About declaration of transaction boundary/attribute¶
@Transactional annotation in Service.6.1.1.4. About exclusion control of data¶
6.1.1.5. About exception handling¶
java.sql.SQLException) and O/R Mapper specific exception to data access exception (subclass of (org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException) provided by Spring Framework.DataAccessException.
Subclasses of DB access exception, which are likely to be handled¶ Sr. No. Class name Description
Note
When optimistic locking is to be implemented using MyBatis in O/R Mapper, it should be implemented as Service or Repository process.
As a method of notifying the optimistic locking failure to Controller, this guideline recommends generation of
OptimisticLockingFailureExceptionand exception of its child class.This is to make implementation of application layer (implementation of Controller) independent of O/R Mapper to be used.
Todo
It has been recently found that using JPA (Hibernate) results in occurrence of unexpected errors.
- In case of unique constraint violation,
org.springframework.dao.DataIntegrityViolationExceptionoccurs and notDuplicateKeyException.
See the example below for handling unique constraint violation as business exception.
try { accountRepository.saveAndFlash(account); } catch(DuplicateKeyException e) { // (1) throw new BusinessException(ResultMessages.error().add("e.xx.xx.0002"), e); // (2) }
Sr. No. Description e) in business exception.
6.1.1.6. About multiple datasources¶
Typical case where multiple datasources are required¶ Sr. No. Case Example Feature
When database and schema are divided according to data (tables). When group of tables maintaining customer information and group of tables maintaining invoice information are stored in separate database and schema. The data to be handled in the process is fixed; hence the datasource to be used can be defined statically.
When database and schema to be used are divided according to users (login users). When database and schema are divided according to users (Multitenant etc.). The datasource to be used differs depending on users; hence the datasource to be used dynamically can be defined. Todo
TBD
The following details will be added in future.
- Conceptual diagram
6.1.1.7. About common library classes¶
6.1.2. How to use¶
6.1.2.1. Datasource settings¶
6.1.2.1.1. Settings when using DataSource defined in Application Server¶
xxx-context.xml(Tomcat config file)<!-- (1) --> <Resource type="javax.sql.DataSource" name="jdbc/SampleDataSource" driverClassName="org.postgresql.Driver" url="jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/terasoluna" username="postgres" password="postgres" defaultAutoCommit="false" /> <!-- (2) -->
xxx-env.xml
<jee:jndi-lookup id="dataSource" jndi-name="jdbc/SampleDataSource" /> <!-- (3) -->
Sr. No. Attribute name Description - Define datasource. type Specify resource type. Specify javax.sql.DataSource.name Specify resource name. The name specified here is JNDI name. driverClassName Specify JDBC driver class. In the example, JDBC driver class provided by PostgreSQL is specified. url Specify URL. [Needs to be changed as per environment] username Specify user name. [Needs to be changed as per environment] password Specify password of user. [Needs to be changed as per environment] defaultAutoCommit Specify default value of auto commit flag. Specify ‘false’. It is forcibly set to ‘false’ when it is under Transaction Management. - - Specify JNDI name of datasource. In case of Tomcat, specify the value specified in resource name “(1)-name” at the time of defining datasource.
6.1.2.1.2. Settings when using DataSource for which Bean is defined¶
xxx-env.xml
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"> <!-- (1) (8) --> <property name="driverClassName" value="org.postgresql.Driver" /> <!-- (2) --> <property name="url" value="jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/terasoluna" /> <!-- (3) --> <property name="username" value="postgres" /> <!-- (4) --> <property name="password" value="postgres" /> <!-- (5) --> <property name="defaultAutoCommit" value="false"/> <!-- (6) --> <!-- (7) --> </bean>
Sr. No. Description Specify implementation class of datasource. In the example, datasource class ( org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource) provided by Apache Commons DBCP is specified.Specify JDBC driver class. In the example, JDBC driver class provided by PostgreSQL is specified. Specify URL. [Needs to be changed as per environment] Specify user name. [Needs to be changed as per environment] Specify password of user. [Needs to be changed as per environment] Specify default value of auto commit flag. Specify ‘false’. It is forcibly set to ‘false’ when it is under Transaction Management. PropertyPlaceholderConfigurerof Spring Reference Document.
6.1.2.2. Settings to enable transaction management¶
For basic settings to enable transaction management, refer to Settings for using transaction management of Domain Layer Implementation.
For PlatformTransactionManager, the class to be used changes depending on the O/R Mapper used; hence for detailed settings, refer to:
6.1.2.3. JDBC debug log settings¶
Warning
When Log4jdbcProxyDataSource offered by log4jdbc-remix is used, substantial overheads are likely to occur even if the log level is set in the configuration other than debug. Therefore, it is recommended to use this setting for debugging, and connect to database without passing through Log4jdbcProxyDataSource while its release during performance test enviroment and commercial environment.
6.1.2.3.2. log4jdbc logger settings¶
logback.xml
<!-- (1) --> <logger name="jdbc.sqltiming"> <level value="debug" /> </logger> <!-- (2) --> <logger name="jdbc.sqlonly"> <level value="warn" /> </logger> <!-- (3) --> <logger name="jdbc.audit"> <level value="warn" /> </logger> <!-- (4) --> <logger name="jdbc.connection"> <level value="warn" /> </logger> <!-- (5) --> <logger name="jdbc.resultset"> <level value="warn" /> </logger> <!-- (6) --> <logger name="jdbc.resultsettable"> <level value="debug" /> </logger>
Sr. No. Description Warning
Large amount of log is output depending on the type of logger; hence only the required logger should be defined or output.
In the above sample, log level for loggers which output very useful logs during development, is set to
"debug". As for other loggers, the log level needs to be set to"debug"whenever required.When the application is to be released in performance test environment or production environment, log using log4jdbc logger should not be output at the time of normal end of process.
Typically log level should be set to
"warn".
6.1.2.3.3. Settings of log4jdbc option¶
Default operations of log4jdbc can be customized by placing properties file log4jdbc.propertiesunder class path.
log4jdbc.properties
# (1) log4jdbc.dump.sql.maxlinelength=0 # (2)
Sr. No. Description Specify word-wrap setting for SQL statement. If ‘0’ is specified, SQL statement is not wrapped. For option details, refer to log4jdbc project page -Options-.
6.1.3. How to extend¶
6.1.3.1. Settings for using multiple datasources¶
Todo
TBD
Following details will be added in future.
- Transaction management method may change depending on the processing pattern (like Update for multiple datasources, Update for a single datasource, Only for reference, No concurrent access etc.), hence breakdown is planned focusing on that area.
6.1.3.2. Settings to switch the datasource dynamically¶
org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource and implement the conditions by which datasource is switched.determineCurrentLookupKey method with the datasource. For selecting the key, usually context information like authenticated user information, time and locale etc. is to be used.6.1.3.2.1. Implementation of AbstractRoutingDataSource¶
DataSource which is created by extending AbstractRoutingDataSourcein a same way as the normal datasource.- Example of implementing a class that inherits
AbstractRoutingDataSource
package com.examples.infra.datasource; import javax.inject.Inject; import org.joda.time.DateTime; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource; import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.date.jodatime.JodaTimeDateFactory; public class RoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { // (1) @Inject JodaTimeDateFactory dateFactory; // (2) @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { // (3) DateTime dateTime = dateFactory.newDateTime(); int hour = dateTime.getHourOfDay(); if (7 <= hour && hour <= 23) { // (4) return "OPEN"; // (5) } else { return "CLOSE"; } } }
Sr. No. Description Inherit AbstractRoutingDataSource.Use JodaTimeDateFactoryto fetch time. For details, refer to System Date.Implement determineCurrentLookupKeymethod. The datasource to be used is defined by mapping the return value of this method and thekeydefined intargetDataSourcesof the bean definition file described later.In the method, refer to the context information (here Time) and switch the key. Here the implementation should be in accordance with the business requirements. This sample is being implemented so that the time returns different keys as “From 7:00 to 23:59” and “From 0:00 to 6:59”. Return the keyto be mapped withtargetDataSourcesof the bean definition file described later.
6.1.3.2.2. Datasource definition¶
Define the AbstractRoutingDataSourceextended class which was created, in bean definition file.
xxx-env.xml
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.examples.infra.datasource.RoutingDataSource"> <!-- (1) --> <property name="targetDataSources"> <!-- (2) --> <map> <entry key="OPEN" value-ref="dataSourceOpen" /> <entry key="CLOSE" value-ref="dataSourceClose" /> </map> </property> <property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="dataSourceDefault" /> <!-- (3) --> </bean>
Sr. No. Description Define a class that inherits AbstractRoutingDataSourcecreated earlier.Define the datasource to be used. As for key, define the value that can be returned usingdetermineCurrentLookupKeymethod. Invalue-ref, specify the datasource to be used for eachkey. Define in accordance with the number of datasources to be switched based on Datasource settings.This datasource is used, when keyspecified indetermineCurrentLookupKeymethod does not exist intargetDataSources. In case of implementation example, default setting is not used; however, this timedefaultTargetDataSourceis being used for description purpose.
6.1.4. how to solve the problem¶
6.1.4.1. How to resolve N+1¶
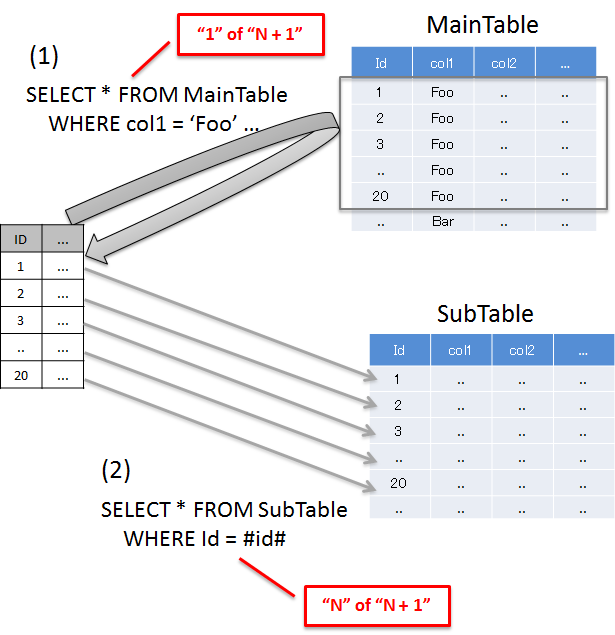
N+1 occurs when more number of SQL statements need to be executed in accordance with the number of records to be fetched from the database. This problem causes high load on the database and deteriorates response time.
Details are given below.
Sr. No. Description 'Foo'records and the total records fetched are 20.
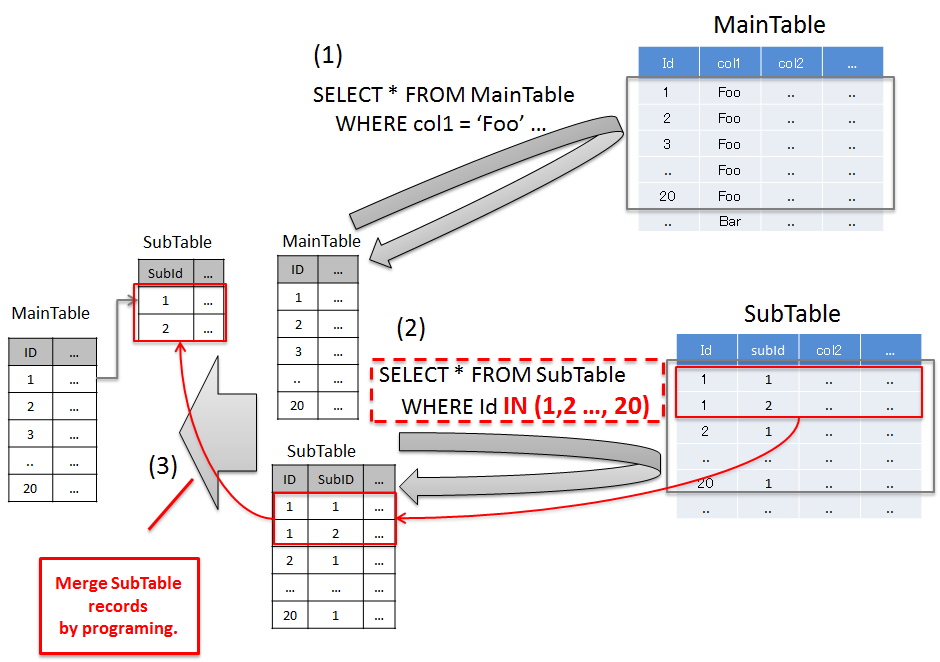
Typical example to resolve N+1 is given below.
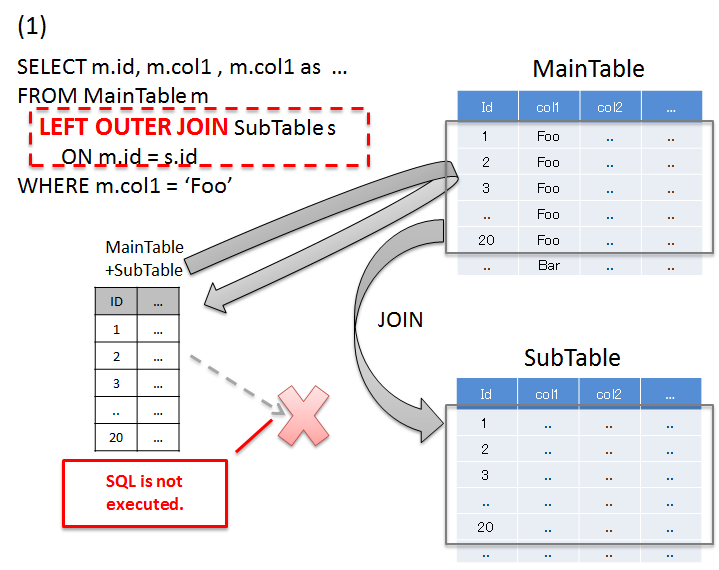
6.1.4.1.1. Resolving N+1 using JOINs (Join Fetch)¶
Sr. No. Description 'Foo'records and records of SubTable that match the id of the records matching with search conditions.When there are duplicate column names, it is necessary to assign alias name in order to identify the table to which that column belongs.If JOIN (Join Fetch) is used, all the required data can be fetched by executing SQL once.Warning
When relation with SubTable is 1:N, the problem can be resolved using JOIN (Join Fetch); however the following points should be noted.
- When JOIN is performed on records having 1:N relation, unnecessary data is fetched depending on the number of records in SubTable. For details, refer to Notes during collective fetch.
- When using JPA (Hibernate), if N portions in 1:N are multiple, then it is necessary to use
java.util.Setinstead ofjava.util.Listas a collection type storage N portion.
6.1.5. Appendix¶
6.1.5.1. Escaping during LIKE search¶
When performing LIKE search, the values to be used as search conditions need to be escaped.
Following class is provided by common library as a component to perform escaping for LIKE search.
| Sr. No. | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
org.terasoluna.gfw.common.query.
QueryEscapeUtils
|
Utility class that provide methods to perform escaping of SQL and JPQL. In this class,
is provided. |
|
org.terasoluna.gfw.common.query.
LikeConditionEscape
|
Class to perform escaping for LIKE search. |
Note
LikeConditionEscape is a class added from terasoluna-gfw-common 1.0.2.RELEASE
to fix “Bugs related to handling of wildcard characters for LIKE search”.
LikeConditionEscape class plays a role in absorbing the differences in wildcard characters that occur due to difference in database and database versions.
6.1.5.1.1. Specifications of escaping of common library¶
Specifications of escaping provided by common library are as follows:
- Escape character is
"~". - Characters to be escaped by default are 2, namely
"%","_".
Note
Till terasoluna-gfw-common 1.0.1.RELEASE, the characters to be escaped were 4, namely "%" , "_" , "%" , "_" ; however,
it is changed to 2 characters namely "%" , "_" from terasoluna-gfw-common 1.0.2.RELEASE
in order to fix the “Bugs related to handling of wildcard characters for LIKE search “.
In addition, a method for escaping that includes double byte characters "%" , "_" as characters to be escaped, is also provided.
See the example of escaping below.
[Example of escaping with default specifications]
Example of escaping when default values used as characters to be escaped is given below.
"a""a"OFF Escaping not done as the string does not contain character to be escaped.
"a~""a~~"ON Escaping done as the string contains escape character.
"a%""a~%"ON Escaping done as the string contains character to be escaped.
"a_""a~_"ON Similar to No.3.
"_a%""~_a~%"ON Escaping done as the string contains characters to be escaped. When there are multiple characters to be escaped, escaping is done for all characters.
"a%""a%"OFF Similar to No.1.
From terasoluna-gfw-common 1.0.2.RELEASE,
"%"is handled as character out of escaping scope in default specifications.
"a_""a_"OFF Similar to No.1.
From terasoluna-gfw-common 1.0.2.RELEASE,
"_"is handled as character out of escaping scope in default specifications.
" "" "OFF Similar to No.1.
""""OFF Similar to No.1.
nullnullOFF Similar to No.1.
[Example of escaping when double byte characters are included]
Example of escaping when double byte characters included as characters to be escaped is given below.
For other than Sr. No. 6 and 7, refer to escaping example of default specifications.
"a%""a~%"ON Escaping done as string contains characters to be escaped.
"a_""a~_"ON Similar to No.6.
6.1.5.1.2. About escaping methods provided by common library¶
List of escaping methods for LIKE search of QueryEscapeUtils class and LikeConditionEscape class provided by common library is given below.
Sr. No. Method name Description
toLikeCondition(String)
toStartingWithCondition(String) "%"at the end of the string after escaping.This method is used in order to convert into a value for Forward match search.
toEndingWithCondition(String) "%"at the beginning of the string after escaping.This method is used in order to convert into a value for Backward match search.
toContainingCondition(String) "%"at the beginning and end of the string after escaping.This method is used in order to convert into a value for Partial match search.Note
Methods of No.2, 3, 4 are used when specifying the type of matching (Forward match, Backward match and Partial match) at program side and not at SQL or JPQL side.
6.1.5.1.3. How to use common library¶
For example of escaping at the time of LIKE search, refer to the document for O/R Mapper to be used.
- When using MyBatis3, refer to Escape during LIKE search of Database Access (MyBatis3).
- When using JPA (Spring Data JPA), refer to Escaping at the time of LIKE searchof Database Access (JPA).
Note
API for escaping should be used as per wildcard characters supported by database to be used.
[In case of database that supports only “%” , “_” (single byte characters) as wildcard]
String escapedWord = QueryEscapeUtils.toLikeCondition(word);
Escaping is done by directly using method of QueryEscapeUtilsclass.
[In case of database that also supports “%” , “_” (double byte characters) as wildcard]
String escapedWord = QueryEscapeUtils.withFullWidth() // (2) .toLikeCondition(word); // (3)
Fetch instance of LikeConditionEscapeclass by callingwithFullWidth()method ofQueryEscapeUtilsmethod.Perform escaping by using method of LikeConditionEscapeclass instance fetched in (2).
6.1.5.2. About Sequencer¶
Note
Reason for creating Sequencer as a common library
The reason for creating Sequencer is that there is no mechanism to format the sequence value as string in ID generator functionality of JPA. In actual application development, sometimes the formatted string is also set as primary key; hence Sequencer is provided as common library.
When value set as primary key is number, it is recommended to use ID generator functionality of JPA. For ID generator functionality of JPA, refer to How to add entities of Database Access (JPA).
The primary objective of creating Sequencer is to supplement functions which are not supported by JPA; but it can also be used when sequence value is required in the processes not relating to JPA.
6.1.5.2.1. About classes provided by common library¶
Sr. No. Class name Description
Sequencerinterface for JDBC.This class is used to fetch sequence value by executing SQL in the database.For this class, it is assumed that values are fetched from sequence object of the database; however it is also possible to fetch the values from other than sequence object by calling function stored in the database.
6.1.5.2.2. How to use common library¶
Define a bean for Sequencer.
xxx-infra.xml
<!-- (1) --> <bean id="articleIdSequencer" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.common.sequencer.JdbcSequencer"> <!-- (2) --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> <!-- (3) --> <property name="sequenceClass" value="java.lang.String" /> <!-- (4) --> <property name="nextValueQuery" value="SELECT TO_CHAR(NEXTVAL('seq_article'),'AFM0000000000')" /> <!-- (5) --> <property name="currentValueQuery" value="SELECT TO_CHAR(CURRVAL('seq_article'),'AFM0000000000')" /> </bean>
Sr. No. Description org.terasoluna.gfw.common.sequencer.Sequencer.In the above example, (JdbcSequencer) class for fetching sequence value by executing SQL is specified.java.lang.Stringtype is specified.1,"A0000000001"is returned as return value ofSequencer#getNext()method.2,"A0000000002"is returned as return value ofSequencer#getCurrent()method.
Fetch sequence value from Sequencer for which bean is defined.
- Service
// omitted // (1) @Inject @Named("articleIdSequencer") // (2) Sequencer<String> articleIdSequencer; // omitted @Transactional public Article createArticle(Article inputArticle) { String articleId = articleIdSequencer.getNext(); // (3) inputArticle.setArticleId(articleId); Article savedArticle = articleRepository.save(inputArticle); return savedArticle; }
Sr. No. Description Sequencerobject for which bean is defined.In the above example, since sequence value is fetched as formatted string,java.lang.Stringtype is specified as generics type ofSequencer.@javax.inject.Namedannotation.In the above example, bean name ("articleIdSequencer") defined inxxx-infra.xmlis specified.Sequencer#getNext()method and fetch the subsequent sequence value.In the above example, fetched sequence value is used as Entity ID.When fetching current sequence value, callSequencer#getCurrent()method.Tip
When
Sequencerfor which bean is defined is 1,@Namedannotation can be omitted. When specifying multiple sequencers, bean name needs to be specified using@Namedannotation.
6.1.5.3. Classes provided by Spring Framework for converting to data access exception¶
Classes of Spring Framework which play a role in converting an exception to data access exception, are as follows:
Classes of Spring Framework for converting to data access exception¶ Sr. No. Class name Description
When MyBatis or JdbcTemplateis used, JDBC exception is converted to data access exception of Spring Framework using this class. Conversion rules are mentioned in XML file. XML file used by default isorg/springframework/jdbc/support/sql-error-codes.xmlinspring-jdbc.jar. It is also possible to change the default behavior by placing XML file (sql-error-codes.xml) just below class path.
When JPA (Hibernate implementation) is used, O/R Mapper exception (Hibernate exception) is converted to data access exception of Spring Framework using this class.
If an exception that cannot be converted by HibernateJpaDialecthas occurred, JPA exception is converted to data access exception of Spring Framework using this class.
When JPA (Hibernate implementation) is used, exceptions are converted to JDBC exception and O/R Mapper exception using this class.
6.1.5.4. JDBC datasource classes provided by Spring Framework¶
JDBC datasource classes provided by Spring Framework¶ Sr. No. Class name Description
Datasource class for creating new connection by calling java.sql.DriverManager#getConnectionwhen connection fetch request is received from the application. When connection pooling is required, Application Server datasource or datasource of OSS/Third-Party library should be used.
Child class of DriverManagerDataSource.This class provides implementation of single shared connection. This is a datasource class for unit test which works with single thread. Even in case of Unit Testing, if this class is used when datasource is to be accessed with multithread, care needs to be taken as it may not show the expected behavior.
Datasource class for creating new connection by calling java.sql.Driver#getConnectionwhen connection fetch request is received from the application. When connection pooling is required, Application Server datasource or datasource of OSS/Third-Party library should be used.
JDBC datasource adapter classes provided by Spring Framework¶ Sr. No. Class name Description
Adapter class for converting a datasource which does not store transactions, into a datasource storing Spring Framework transactions.
Adapter class for switching the datasource to be used based on independence level of an active transaction.