10.2. Tutorial (Todo Application REST)¶
Caution
This version is already obsolete. Please check the latest guideline.
Index
- Introduction
- Environment creation
- REST API creation
- API specification
- DispatcherServlet for REST API
- Definition of Spring Security for REST API
- Creation of REST API package
- Creation of Resource class
- Creation of Controller class
- Implementation of exception handling
- Change Domain layer implementation
- Error message definition
- Create a package that contains the error handling class
- Creating REST API error handling class
- Creating JavaBean for holding the REST API error information
- Implementation of putting error information to the HTTP response BODY
- Error handling of Input errors
- Business exception error handling
- Resource not found exception error handling
- System exception error handling
- In the end…
10.2.1. Introduction¶
10.2.1.1. Points to study in this tutorial¶
- Basic RESTful web service development using TERASOLUNA Server Framework for Java (5.x)
10.2.1.2. Target readers¶
- Those who have Implemented the Tutorial (Todo Application).
10.2.1.3. Verification environment¶
| Type | Product |
|---|---|
| REST Client | DHC REST Client 1.2.3 |
| Product other than the above | Similar to Tutorial (Todo Application) |
10.2.2. Environment creation¶
Assumes that Java, STS, Maven, Google Chrome are already installed since the Tutorial (Todo Application) is implemented.
10.2.2.1. Install DHC¶
As a REST client, install [DHC] advanced features of Google Chrome.
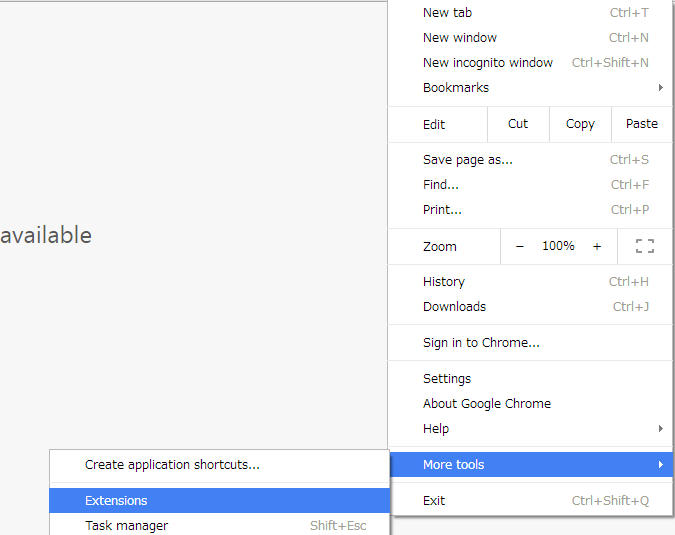
Select [Tools] -> [Extensions] of Chrome browser.
Click [Get more extensions] link.
Search by entering [dev http client] in search form.
Click the [+ ADD TO CHROME] button of DHC REST Client.
Click [Add app] button.
When you open the application list (Open by specifying [chrome://apps/] in your browser address bar) of Chrome, DHC has been added.
10.2.2.2. Project creation¶
In this tutorial, the RESTful Web Services are created for [Tutorial (Todo Application)].
Therefore, if [Tutorial (Todo Application)] project is not exists, re-create project by executing [Tutorial (Todo Application)].
Note
If project is re-created by executing [Tutorial (Todo Application)], it is possible to proceed further this tutorial by performing re-creation till the domain layer creation.
10.2.3. REST API creation¶
In this tutorial, creating REST API for publishing the data on Web which are managed in the todo table (here onwards called as [Todo Resources]).
API name
|
HTTP
method
|
Path
|
Status
code
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
GET Todos
|
GET
|
/api/v1/todos |
200
(OK)
|
Fetch all records of Todo Resource.
|
POST Todos
|
POST
|
/api/v1/todos |
201
(Created)
|
Create new Todo Resource.
|
GET Todo
|
GET
|
/api/v1/todos/{todoId} |
200
(OK)
|
Fetch one record of Todo Resource.
|
PUT Todo
|
PUT
|
/api/v1/todos/{todoId} |
200
(OK)
|
Update Todo Resource in completed status
|
DELETE Todo
|
DELETE
|
/api/v1/todos/{todoId} |
204
(No Content)
|
Delete Todo Resource.
|
Tip
The {todoId} included in path is called as path variable and can deal with any changeable value.
The GET /api/v1/todos/123 and GET /api/v1/todos/456 can be handle with same API using the path variable.
In this tutorial, We are dealing with ID (Todo ID) as the path variable in order to uniquely identifying the Todo.
10.2.3.1. API specification¶
10.2.3.1.1. GET Todos¶
[Request]
> GET /todo/api/v1/todos HTTP/1.1
[Response]
Return list of created Todo Resource in JSON format.
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
[{"todoId":"9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558","todoTitle":"Hello World!","finished":false,"createdAt":"2014-02-25T02:21:48.493+0000"}]
10.2.3.1.2. POST Todos¶
[Request]
Specify newly creation Todo Resource content (Title) in JSON format.
> POST /todo/api/v1/todos HTTP/1.1
> Content-Type: application/json
> Content-Length: 29
>
{"todoTitle": "Study Spring"}
[Response]
Return created Todo Resource in JSON format.
< HTTP/1.1 201 Created
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"todoId":"d6101d61-b22c-48ee-9110-e106af6a1404","todoTitle":"Study Spring","finished":false,"createdAt":"2014-02-25T04:05:58.752+0000"}
10.2.3.1.3. GET Todo¶
[Request]
todoId] path variable that you want to fetch.9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558 is specified in [todoId] path variable.> GET /todo/api/v1/todos/9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558 HTTP/1.1
[Response]
Return Todo Resource in JSON format that matches with the [todoId] path variable.
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"todoId":"9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558","todoTitle":"Hello World!","finished":false,"createdAt":"2014-02-25T02:21:48.493+0000"}
10.2.3.1.4. PUT Todo¶
[Request]
todoId] path variable that you want to update.> PUT /todo/api/v1/todos/9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558 HTTP/1.1
[Response]
Return Todo Resource in JSON format that matches with the [todoId] path variable after updating in completed status (true of finished field).
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"todoId":"9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558","todoTitle":"Hello World!","finished":true,"createdAt":"2014-02-25T02:21:48.493+0000"}
10.2.3.1.5. DELETE Todo¶
[Request]
Specify ID of the Todo Resource in [todoId] path variable that you want to delete.
> DELETE /todo/api/v1/todos/9aef3ee3-30d4-4a7c-be4a-bc184ca1d558 HTTP/1.1
[Response]
In the DELETE Todo, since the Todo Resource is deleted and resource that can return is no longer exists, interface specification does not return the response BODY.
< HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
10.2.3.1.6. Error Response¶
In the Tutorial (Todo Application), error messages are hardcoded in the program but in this tutorial, it is modified such a way that the error messages are retrieved from the property file based on error code.
[Response specification at the time of input check error]
< HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"code":"E400","message":"[E400] The requested Todo contains invalid values.","details":[{"code":"NotNull","message":"todoTitle may not be null.",target:"todoTitle"}]}
[Response specification at the time of business error]
< HTTP/1.1 409 Conflict
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"code":"E002","message":"[E002] The requested Todo is already finished. (id=353fb5db-151a-4696-9b4a-b958358a5ab3)"}
[Response specification at the time of resources undetected]
< HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"code":"E404","message":"[E404] The requested Todo is not found. (id=353fb5db-151a-4696-9b4a-b958358a5ab2)"}
[Response specification at the time of system error]
< HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server Error
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
<
{"code":"E500","message":"[E500] System error occurred."}
10.2.3.2. DispatcherServlet for REST API¶
First, add the definition of DispatcherServlet for processing the REST API request.
10.2.3.2.1. Modification of web.xml¶
src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
version="3.0">
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.terasoluna.gfw.web.logging.HttpSessionEventLoggingListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!-- Root ApplicationContext -->
<param-value>
classpath*:META-INF/spring/applicationContext.xml
classpath*:META-INF/spring/spring-security.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
<filter>
<filter-name>MDCClearFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.terasoluna.gfw.web.logging.mdc.MDCClearFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>MDCClearFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter>
<filter-name>exceptionLoggingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>exceptionLoggingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter>
<filter-name>XTrackMDCPutFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.terasoluna.gfw.web.logging.mdc.XTrackMDCPutFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>XTrackMDCPutFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!-- (1) -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>restApiServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!-- ApplicationContext for Spring MVC (REST) -->
<param-value>classpath*:META-INF/spring/spring-mvc-rest.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<!-- (2) -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>restApiServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/api/v1/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!-- ApplicationContext for Spring MVC -->
<param-value>classpath*:META-INF/spring/spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<jsp-config>
<jsp-property-group>
<url-pattern>*.jsp</url-pattern>
<el-ignored>false</el-ignored>
<page-encoding>UTF-8</page-encoding>
<scripting-invalid>false</scripting-invalid>
<include-prelude>/WEB-INF/views/common/include.jsp</include-prelude>
</jsp-property-group>
</jsp-config>
<error-page>
<error-code>500</error-code>
<location>/WEB-INF/views/common/error/systemError.jsp</location>
</error-page>
<error-page>
<error-code>404</error-code>
<location>/WEB-INF/views/common/error/resourceNotFoundError.jsp</location>
</error-page>
<error-page>
<exception-type>java.lang.Exception</exception-type>
<location>/WEB-INF/views/common/error/unhandledSystemError.html</location>
</error-page>
<session-config>
<!-- 30min -->
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config>
</web-app>
| Sr. No | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify the SpringMVC configuration file for REST at the initialization parameter [
contextConfigLocation].In this tutorial, [
META-INF/spring/spring-mvc-rest.xml] is specified located at class path. |
(2)
|
Specify the URL pattern that maps to the
DispatcherServlet for REST API at <url-pattern> element.In this tutorial, if it starts from
/api/v1/, request is considered as a REST API request and mapped with the DispatcherServlet for REST API. |
10.2.3.2.2. Creation of spring-mvc-rest.xml¶
src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/spring-mvc.xmlfile.
src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/spring-mvc-rest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder
location="classpath*:/META-INF/spring/*.properties" />
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:argument-resolvers>
<bean
class="org.springframework.data.web.PageableHandlerMethodArgumentResolver" />
<bean
class="org.springframework.security.web.method.annotation.AuthenticationPrincipalArgumentResolver" />
</mvc:argument-resolvers>
<mvc:message-converters register-defaults="false">
<!-- (1) -->
<bean
class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter">
<!-- (2) -->
<property name="objectMapper">
<bean class="com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper">
<property name="dateFormat">
<!-- (3) -->
<bean class="com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.util.StdDateFormat"/>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:default-servlet-handler />
<context:component-scan base-package="todo.api" /> <!-- (3) -->
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**" />
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/resources/**" />
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/**/*.html" />
<bean
class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.logging.TraceLoggingInterceptor" />
</mvc:interceptor>
<!-- REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**" />
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/resources/**" />
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/**/*.html" />
<bean
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.support.OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor" />
</mvc:interceptor>
REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA -->
</mvc:interceptors>
<!-- Setting AOP. -->
<bean id="handlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor"
class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor">
<property name="exceptionLogger" ref="exceptionLogger" />
</bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="handlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor"
pointcut="execution(* org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver.resolveException(..))" />
</aop:config>
</beans>
| Sr. No | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Set the class( Multiple |
(2)
|
Specify the In this tutorial, Data format customized |
(3)
|
Specify format of the Date field into In this tutorial, ISO-8601 format used while serializing |
(4)
|
Scan the components under the package of the REST API In this tutorial, the package of REST API is |
10.2.3.3. Definition of Spring Security for REST API¶
src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/spring-security.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<sec:http pattern="/resources/**" security="none"/>
<!-- (1) -->
<sec:http
pattern="/api/v1/**"
create-session="stateless">
<sec:http-basic />
<sec:csrf disabled="true"/>
</sec:http>
<sec:http>
<sec:form-login />
<sec:logout />
<sec:access-denied-handler ref="accessDeniedHandler"/>
<sec:custom-filter ref="userIdMDCPutFilter" after="ANONYMOUS_FILTER"/>
<sec:session-management />
</sec:http>
<sec:authentication-manager></sec:authentication-manager>
<!-- Change View for CSRF or AccessDenied -->
<bean id="accessDeniedHandler"
class="org.springframework.security.web.access.DelegatingAccessDeniedHandler">
<constructor-arg index="0">
<map>
<entry
key="org.springframework.security.web.csrf.InvalidCsrfTokenException">
<bean
class="org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandlerImpl">
<property name="errorPage"
value="/WEB-INF/views/common/error/invalidCsrfTokenError.jsp" />
</bean>
</entry>
<entry
key="org.springframework.security.web.csrf.MissingCsrfTokenException">
<bean
class="org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandlerImpl">
<property name="errorPage"
value="/WEB-INF/views/common/error/missingCsrfTokenError.jsp" />
</bean>
</entry>
</map>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1">
<bean
class="org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandlerImpl">
<property name="errorPage"
value="/WEB-INF/views/common/error/accessDeniedError.jsp" />
</bean>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- Put UserID into MDC -->
<bean id="userIdMDCPutFilter" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.security.web.logging.UserIdMDCPutFilter">
</bean>
</beans>
| Sr. No | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Add the definition of Spring Security for REST API.
Specify the URL pattern of the REST API request path at
pattern attribute of the <sec:http> element.In this tutorial, request path starts with
/api/v1/ is considered as a REST API request.Furthermore, session is no longer used in the processing of Spring Security by specifying
stateless at create-session attribute.Specify
disabled="true" in <sec:csrf> element for invalidating CSRF countermeasures. |
10.2.3.4. Creation of REST API package¶
Create a package that stores the REST API classes.
api that contains the REST API classes and recommended to create a package of each resource (lowercase resource name) under it.todo.api.todo package is created.
Note
Usually following three types of classes are stored in the created package. The following naming rules are recommended for the classes.
[Resource name]Resource[Resource name]RestController[Resource name]Helper(if required)
Since name of the resource is Todo in this tutorial,
TodoResourceTodoRestController
is created
The TodoRestHelper is not created in this tutorial.
10.2.3.5. Creation of Resource class¶
TodoResource class for implementing Todo Resource.src/main/java/todo/api/todo/TodoResource.java
package todo.api.todo;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
public class TodoResource implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String todoId;
@NotNull
@Size(min = 1, max = 30)
private String todoTitle;
private boolean finished;
private Date createdAt;
public String getTodoId() {
return todoId;
}
public void setTodoId(String todoId) {
this.todoId = todoId;
}
public String getTodoTitle() {
return todoTitle;
}
public void setTodoTitle(String todoTitle) {
this.todoTitle = todoTitle;
}
public boolean isFinished() {
return finished;
}
public void setFinished(boolean finished) {
this.finished = finished;
}
public Date getCreatedAt() {
return createdAt;
}
public void setCreatedAt(Date createdAt) {
this.createdAt = createdAt;
}
}
Note
The reason for creating a Resource class in spite of the existence of the DomainObject class (Todo class in this tutorial),
business process is not consistent with the interface to be used in the input and output of the client.
If it is used wrongly, application layer will be impacted to the domain layer and also decrease the maintainability. It is recommended to perform the data conversion using BeanMapper such as Dozer by creating DomainObject and Resource class separately.
The role of the Resource class is similar to the Form class but eventually it is differing like
Form class represent the <form> tag of HTML in JavaBean and Resource class is the input and output of the REST API in JavaBean.
However, it is a JavaBean having annotation of the Bean Validation and the Controller class is approximately the same as the Form class because stored in the same package.
10.2.3.6. Creation of Controller class¶
Create a TodoRestController class that provides a REST API of TodoResource.
src/main/java/todo/api/todo/TodoRestController.java
package todo.api.todo;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController // (1)
@RequestMapping("todos") // (2)
public class TodoRestController {
}
| Sr. No | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify the
@RestController annotation.Refer to the Creation of RestController class for the details of
@RestController. |
(2)
|
Specify the resource path.
Since
/api/v1/ is defined in web.xml, it is mapped with the /<contextPath>/api/v1/todos path by perform this setting. |
10.2.3.6.1. Implementation of GET Todos¶
Implement the processing of API(GET Todos) into getTodos method of TodoRestController that fetches all records of created Todo Resource.
src/main/java/todo/api/todo/TodoRestController.java
package todo.api.todo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.dozer.Mapper;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import todo.domain.model.Todo;
import todo.domain.service.todo.TodoService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("todos")
public class TodoRestController {
@Inject
TodoService todoService;
@Inject
Mapper beanMapper;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET) // (1)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) // (2)
public List<TodoResource> getTodos() {
Collection<Todo> todos = todoService.findAll();
List<TodoResource> todoResources = new ArrayList<>();
for (Todo todo : todos) {
todoResources.add(beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class)); // (3)
}
return todoResources; // (4)
}
}
| Sr. No | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Set the
RequestMethod.GET to method attribute for handling the GET request. |
(2)
|
Specify
@ResponseStatus annotation to the HTTP status code for response.To set “200 OK” as a HTTP status, set the
HttpStatus.OK to the value attribute. |
(3)
|
Converting
Todo object returned from findAll method of TodoService into TodoResource object type that represent JSON response.It is convenient to use the
org.dozer.Mapper interface of Dozer for converting Todo and TodoResource. |
(4)
|
By returning the
List<TodoResource> object, it is serialized into JSON by MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter defined in spring-mvc-rest.xml. |
Check the operation of the implemented API by booting Application Server.
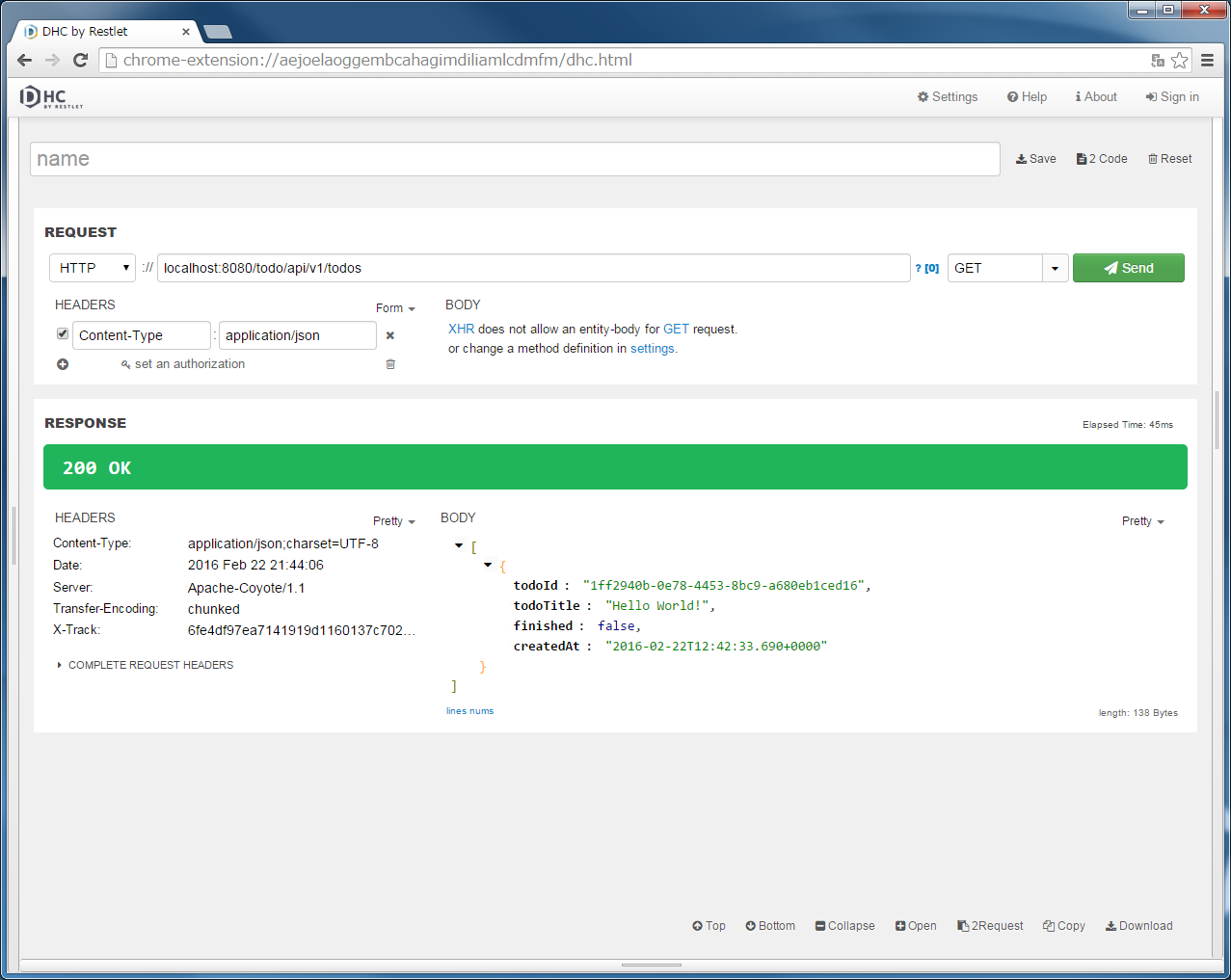
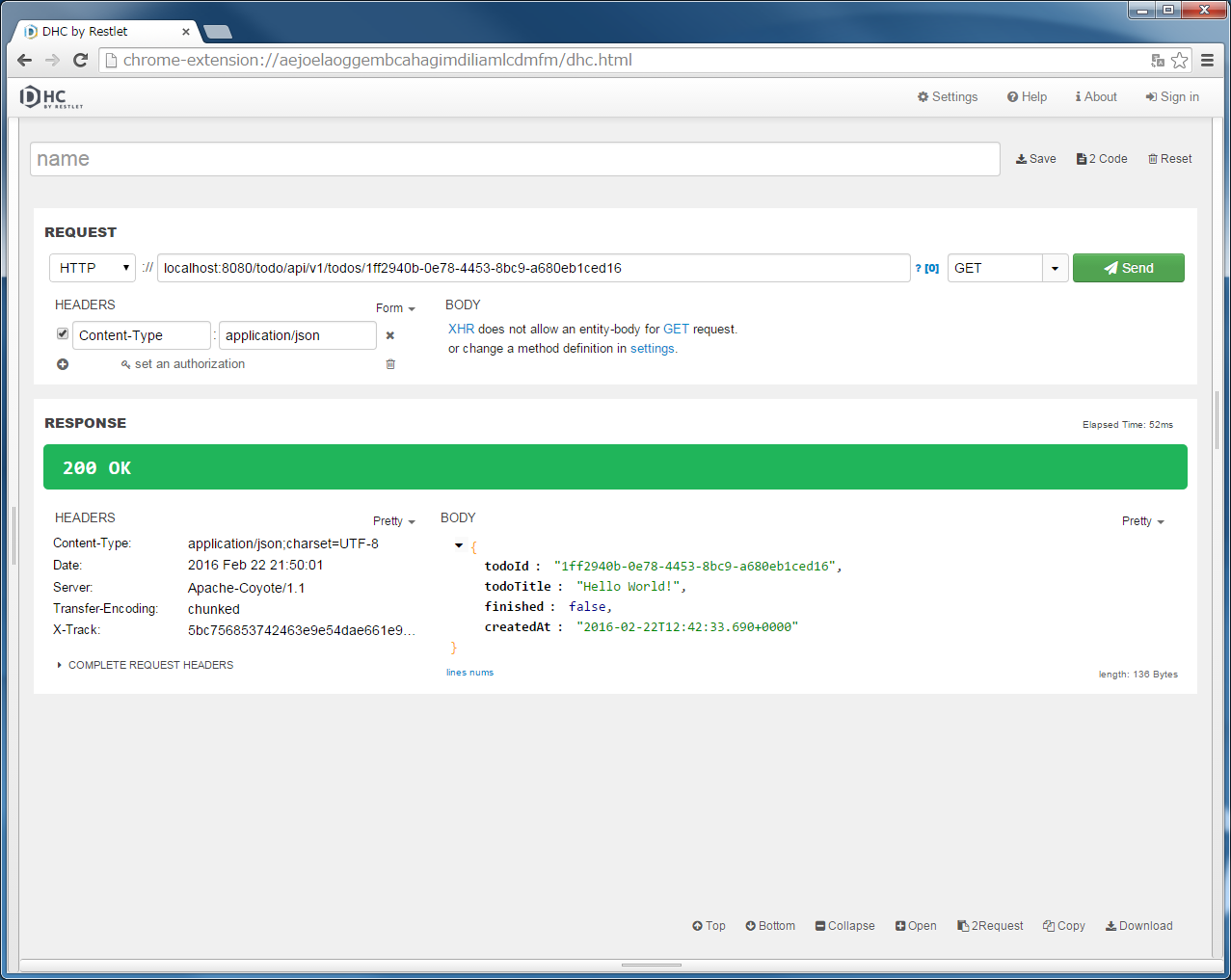
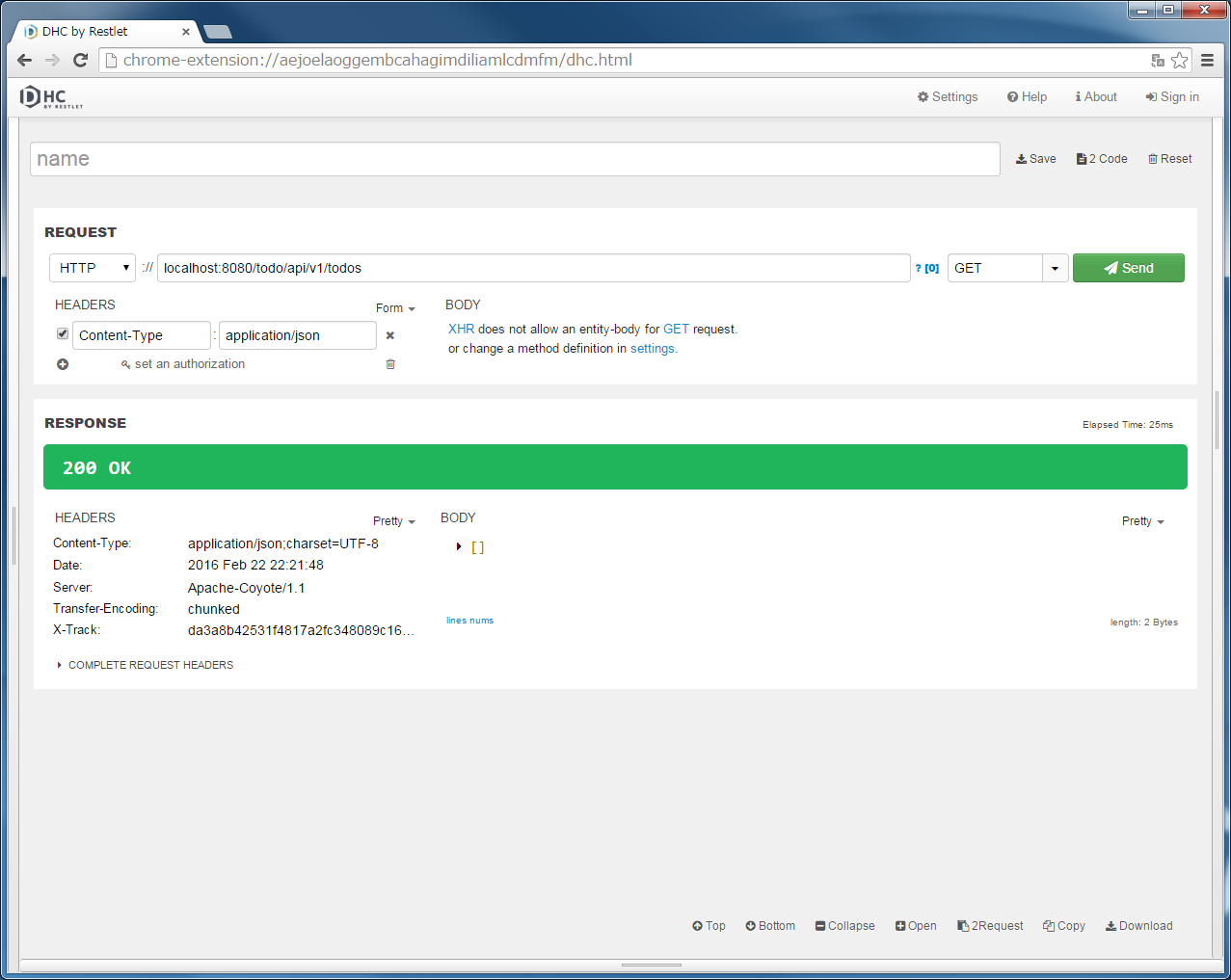
"localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos" in the URL, specify GET in method and click the “Send” button.[] is returned.Since the Spring Security setting has been changed to not use the session therefore want to focus on the point that "Set-Cookie: JSESSIONID=xxxx" is not exists in the [RESPONSE] [HEADERS].
10.2.3.6.2. Implementation of POST Todos¶
Implement the processing of API(GET Todos) into postTodos method of TodoRestController that create new Todo Resource.
src/main/java/todo/api/todo/TodoRestController.java
package todo.api.todo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.dozer.Mapper;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import todo.domain.model.Todo;
import todo.domain.service.todo.TodoService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("todos")
public class TodoRestController {
@Inject
TodoService todoService;
@Inject
Mapper beanMapper;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public List<TodoResource> getTodos() {
Collection<Todo> todos = todoService.findAll();
List<TodoResource> todoResources = new ArrayList<>();
for (Todo todo : todos) {
todoResources.add(beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class));
}
return todoResources;
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST) // (1)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED) // (2)
public TodoResource postTodos(@RequestBody @Validated TodoResource todoResource) { // (3)
Todo createdTodo = todoService.create(beanMapper.map(todoResource, Todo.class)); // (4)
TodoResource createdTodoResponse = beanMapper.map(createdTodo, TodoResource.class); // (5)
return createdTodoResponse; // (6)
}
}
| Sr. No | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Set the
RequestMethod.POST to method attribute for handling the POST request. |
(2)
|
Specify
@ResponseStatus annotation to the HTTP status code for response.To set “201 Created” as a HTTP status, set the
HttpStatus.CREATED to the value attribute. |
(3)
|
In order to map the HTTP request Body(JSON) with JavaBean, grant
@RequestBody annotation to the mapping targeted TodoResource class.Furthermore, grant
@Validated annotation for input check. It is necessary to handle exception separately. |
(4)
|
Create new Todo resource by executing
create method of TodoService after converting TodoResource into Todo class. |
(5)
|
Converting
Todo object created by create method of TodoService into TodoResource type that represent JSON response. |
(6)
|
By returning the
TodoResource object, it is serialized into JSON by MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter defined in spring-mvc-rest.xml. |
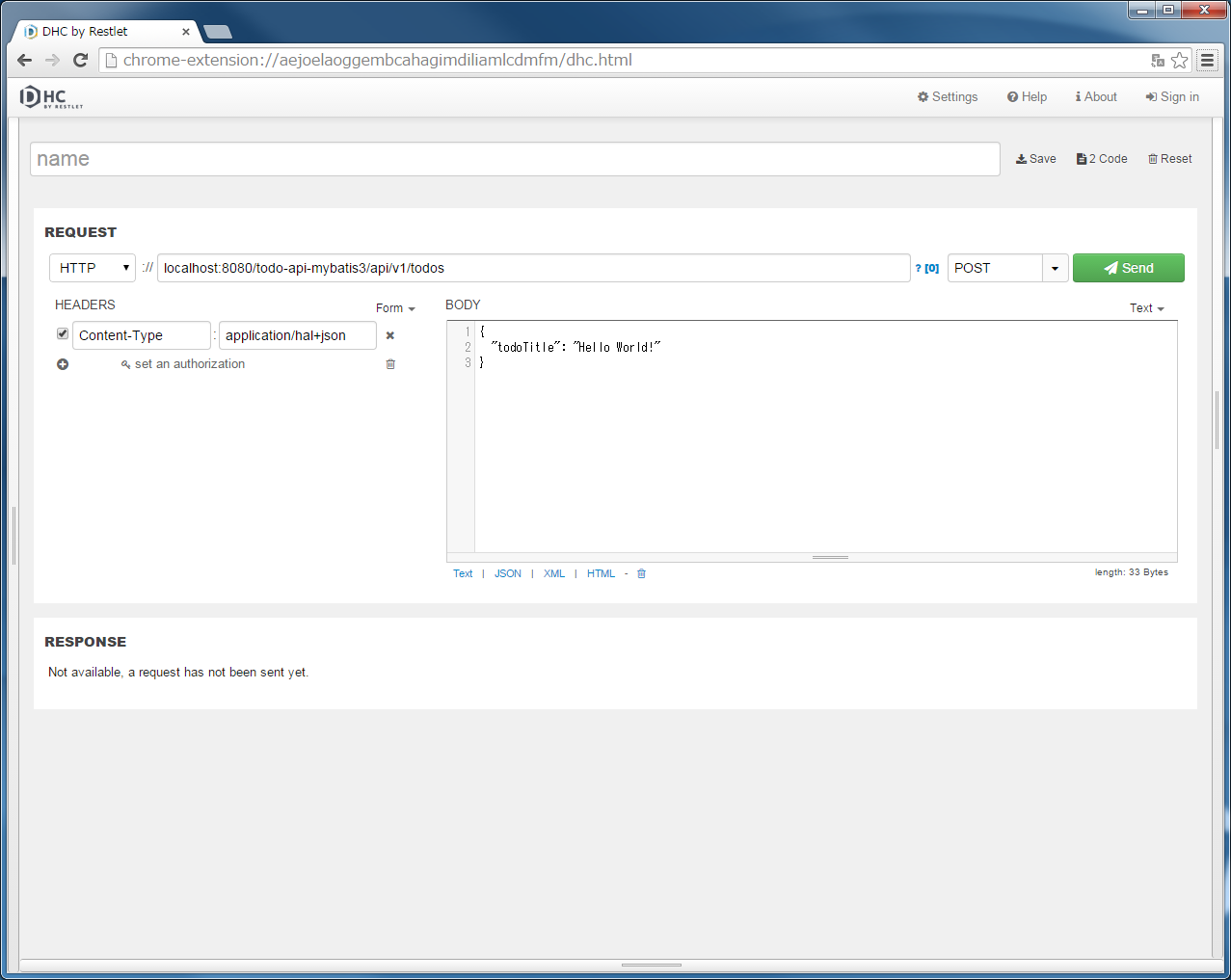
"localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos" in the URL and specify POST in method.{
"todoTitle": "Hello World!"
}
Furthermore, Add HTTP header by [+] button of [REQUEST] [HEADERS] and click “Send” button after setting [application/json] in the [Content-Type].
HTTP status returned “201 Created” and JSON of the newly created Todo resource displays in [Body] of [RESPONSE] part.
If GET Todos gets executed now, newly created Todo Resource returns as an array.
10.2.3.6.3. Implementation of GET Todo¶
Since method (findOne) for retrieving single item is not created in TodoService of the Tutorial (Todo Application),
add the following highlighted parts in TodoService and TodoServiceImpl.
findOne method.src/main/java/todo/domain/service/todo/TodoService.javapackage todo.domain.service.todo;
import java.util.Collection;
import todo.domain.model.Todo;
public interface TodoService {
Collection<Todo> findAll();
Todo findOne(String todoId);
Todo create(Todo todo);
Todo finish(String todoId);
void delete(String todoId);
}
findOne method.src/main/java/todo/domain/service/todo/TodoServiceImpl.javapackage todo.domain.service.todo;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.UUID;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessage;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessages;
import todo.domain.model.Todo;
import todo.domain.repository.todo.TodoRepository;
@Service
@Transactional
public class TodoServiceImpl implements TodoService {
private static final long MAX_UNFINISHED_COUNT = 5;
@Inject
TodoRepository todoRepository;
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public Todo findOne(String todoId) {
Todo todo = todoRepository.findOne(todoId);
if (todo == null) {
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error();
messages.add(ResultMessage
.fromText("[E404] The requested Todo is not found. (id="
+ todoId + ")"));
throw new ResourceNotFoundException(messages);
}
return todo;
}
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public Collection<Todo> findAll() {
return todoRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public Todo create(Todo todo) {
long unfinishedCount = todoRepository.countByFinished(false);
if (unfinishedCount >= MAX_UNFINISHED_COUNT) {
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error();
messages.add(ResultMessage
.fromText("[E001] The count of un-finished Todo must not be over "
+ MAX_UNFINISHED_COUNT + "."));
throw new BusinessException(messages);
}
String todoId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Date createdAt = new Date();
todo.setTodoId(todoId);
todo.setCreatedAt(createdAt);
todo.setFinished(false);
todoRepository.create(todo);
/* REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA
todoRepository.save(todo);
REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA */
return todo;
}
@Override
public Todo finish(String todoId) {
Todo todo = findOne(todoId);
if (todo.isFinished()) {
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error();
messages.add(ResultMessage
.fromText("[E002] The requested Todo is already finished. (id="
+ todoId + ")"));
throw new BusinessException(messages);
}
todo.setFinished(true);
todoRepository.update(todo);
/* REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA
todoRepository.save(todo);
REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA */
return todo;
}
@Override
public void delete(String todoId) {
Todo todo = findOne(todoId);
todoRepository.delete(todo);
}
}
getTodo method of TodoRestController .src/main/java/todo/api/todo/TodoRestController.javapackage todo.api.todo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.dozer.Mapper;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import todo.domain.model.Todo;
import todo.domain.service.todo.TodoService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("todos")
public class TodoRestController {
@Inject
TodoService todoService;
@Inject
Mapper beanMapper;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public List<TodoResource> getTodos() {
Collection<Todo> todos = todoService.findAll();
List<TodoResource> todoResources = new ArrayList<>();
for (Todo todo : todos) {
todoResources.add(beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class));
}
return todoResources;
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public TodoResource postTodos(@RequestBody @Validated TodoResource todoResource) {
Todo createdTodo = todoService.create(beanMapper.map(todoResource, Todo.class));
TodoResource createdTodoResponse = beanMapper.map(createdTodo, TodoResource.class);
return createdTodoResponse;
}
@RequestMapping(value="{todoId}", method = RequestMethod.GET) // (1)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public TodoResource getTodo(@PathVariable("todoId") String todoId) { // (2)
Todo todo = todoService.findOne(todoId); // (3)
TodoResource todoResource = beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class);
return todoResource;
}
}
| Sr. No | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
In order to get the
todoId from path, specify the path variable in the value attribute of the @RequestMapping annotation.Set the
RequestMethod.GET to method attribute for handling the GET request. |
(2)
|
Specify the path variable name to retrieve
todoId in the value attribute of the @PathVariable annotation. |
(3)
|
You can use the
todoId obtained from path variable to get one Todo resource. |
"localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos/{todoId}" in the URL and specify GET in method.{todoId}, run the POST Todos or GET Todos to get actual ID, copy & paste the todoId from the Response, and click the “Send” button.HTTP status returned “200 OK” and JSON of the indicated Todo resource displays in [Body] of [RESPONSE] part.
10.2.3.6.4. Implementation of PUT Todo¶
Implement the processing of API(PUT Todo) into putTodo method of TodoRestController that updates(updating into completed status) one record of Todo Resource.
src/main/java/todo/api/todo/TodoRestController.java
package todo.api.todo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.dozer.Mapper;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import todo.domain.model.Todo;
import todo.domain.service.todo.TodoService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("todos")
public class TodoRestController {
@Inject
TodoService todoService;
@Inject
Mapper beanMapper;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public List<TodoResource> getTodos() {
Collection<Todo> todos = todoService.findAll();
List<TodoResource> todoResources = new ArrayList<>();
for (Todo todo : todos) {
todoResources.add(beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class));
}
return todoResources;
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public TodoResource postTodos(@RequestBody @Validated TodoResource todoResource) {
Todo createdTodo = todoService.create(beanMapper.map(todoResource, Todo.class));
TodoResource createdTodoResponse = beanMapper.map(createdTodo, TodoResource.class);
return createdTodoResponse;
}
@RequestMapping(value="{todoId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public TodoResource getTodo(@PathVariable("todoId") String todoId) {
Todo todo = todoService.findOne(todoId);
TodoResource todoResource = beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class);
return todoResource;
}
@RequestMapping(value="{todoId}", method = RequestMethod.PUT) // (1)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public TodoResource putTodo(@PathVariable("todoId") String todoId) { // (2)
Todo finishedTodo = todoService.finish(todoId); // (3)
TodoResource finishedTodoResource = beanMapper.map(finishedTodo, TodoResource.class);
return finishedTodoResource;
}
}
| Sr. No | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
In order to get the
todoId from path, specify the path variable in the value attribute of the @RequestMappingannotation.Set the
RequestMethod.PUT to method attribute for handling the PUT request. |
(2)
|
Specify the path variable name to retrieve
todoId in the value attribute of the @PathVariable annotation. |
(3)
|
You can use the
todoId obtained from path variable to update the Todo resource in completed status. |
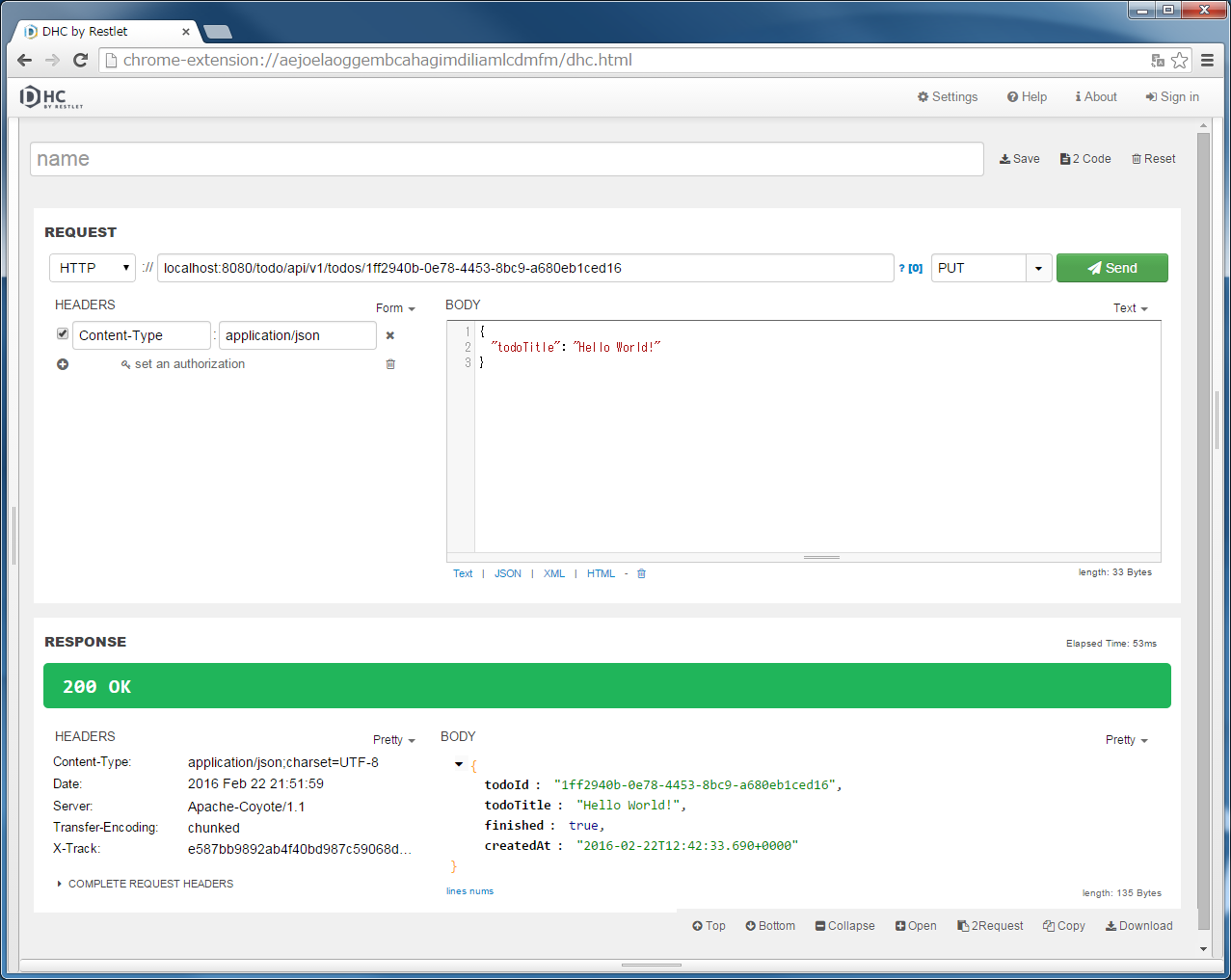
"localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos/{todoId}" in the URL and specify PUT in method.{todoId}, run the POST Todos or GET Todos to get actual ID, copy & paste the todoId from the Response, and click the “Send” button.finished is updated to true.10.2.3.6.5. Implementation of DELETE Todo¶
Lastly, implement the processing of API(DELETE Todo) into deleteTodo method of TodoRestController that delete one record of Todo Resource.
src/main/java/todo/api/todo/TodoRestController.java
package todo.api.todo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.dozer.Mapper;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import todo.domain.model.Todo;
import todo.domain.service.todo.TodoService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("todos")
public class TodoRestController {
@Inject
TodoService todoService;
@Inject
Mapper beanMapper;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public List<TodoResource> getTodos() {
Collection<Todo> todos = todoService.findAll();
List<TodoResource> todoResources = new ArrayList<>();
for (Todo todo : todos) {
todoResources.add(beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class));
}
return todoResources;
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public TodoResource postTodos(@RequestBody @Validated TodoResource todoResource) {
Todo createdTodo = todoService.create(beanMapper.map(todoResource, Todo.class));
TodoResource createdTodoResponse = beanMapper.map(createdTodo, TodoResource.class);
return createdTodoResponse;
}
@RequestMapping(value="{todoId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public TodoResource getTodo(@PathVariable("todoId") String todoId) {
Todo todo = todoService.findOne(todoId);
TodoResource todoResource = beanMapper.map(todo, TodoResource.class);
return todoResource;
}
@RequestMapping(value="{todoId}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public TodoResource putTodo(@PathVariable("todoId") String todoId) {
Todo finishedTodo = todoService.finish(todoId);
TodoResource finishedTodoResource = beanMapper.map(finishedTodo, TodoResource.class);
return finishedTodoResource;
}
@RequestMapping(value="{todoId}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE) // (1)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) // (2)
public void deleteTodo(@PathVariable("todoId") String todoId) { // (3)
todoService.delete(todoId); // (4)
}
}
| Sr. No | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
In order to get the
todoId from path, specify the path variable in the value attribute of the @RequestMapping annotation.Set the
RequestMethod.DELETE to method attribute for handling the DELETE request. |
(2)
|
Specify
@ResponseStatus annotation to the HTTP status code for response.To set “204 No Content” as a HTTP status, set the
HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT to the value attribute. |
(3)
|
The type of return value is a
void because there is no content to be returned in the case of DELETE. |
(4)
|
You can use the
todoId obtained from path variable to delete the Todo resource. |
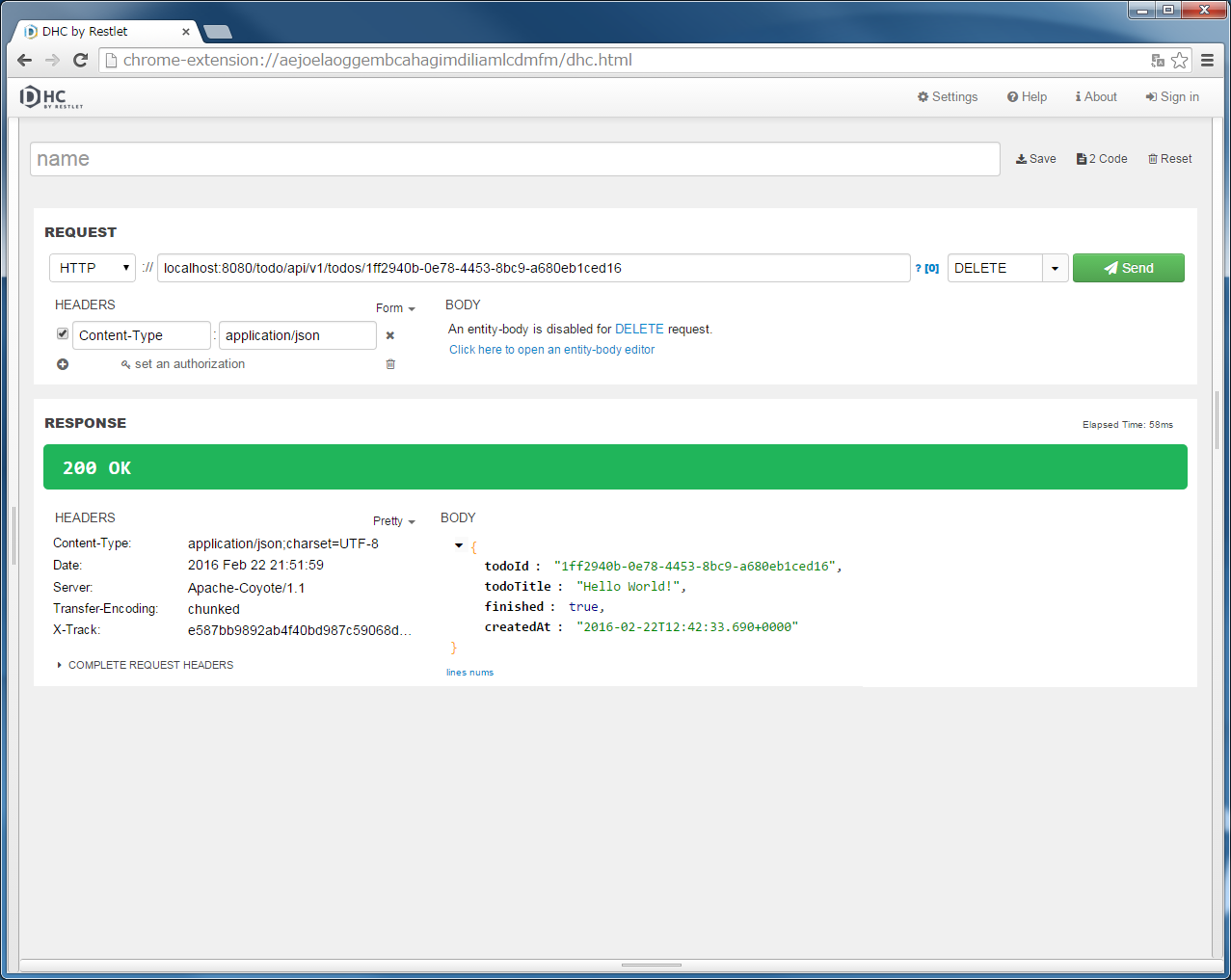
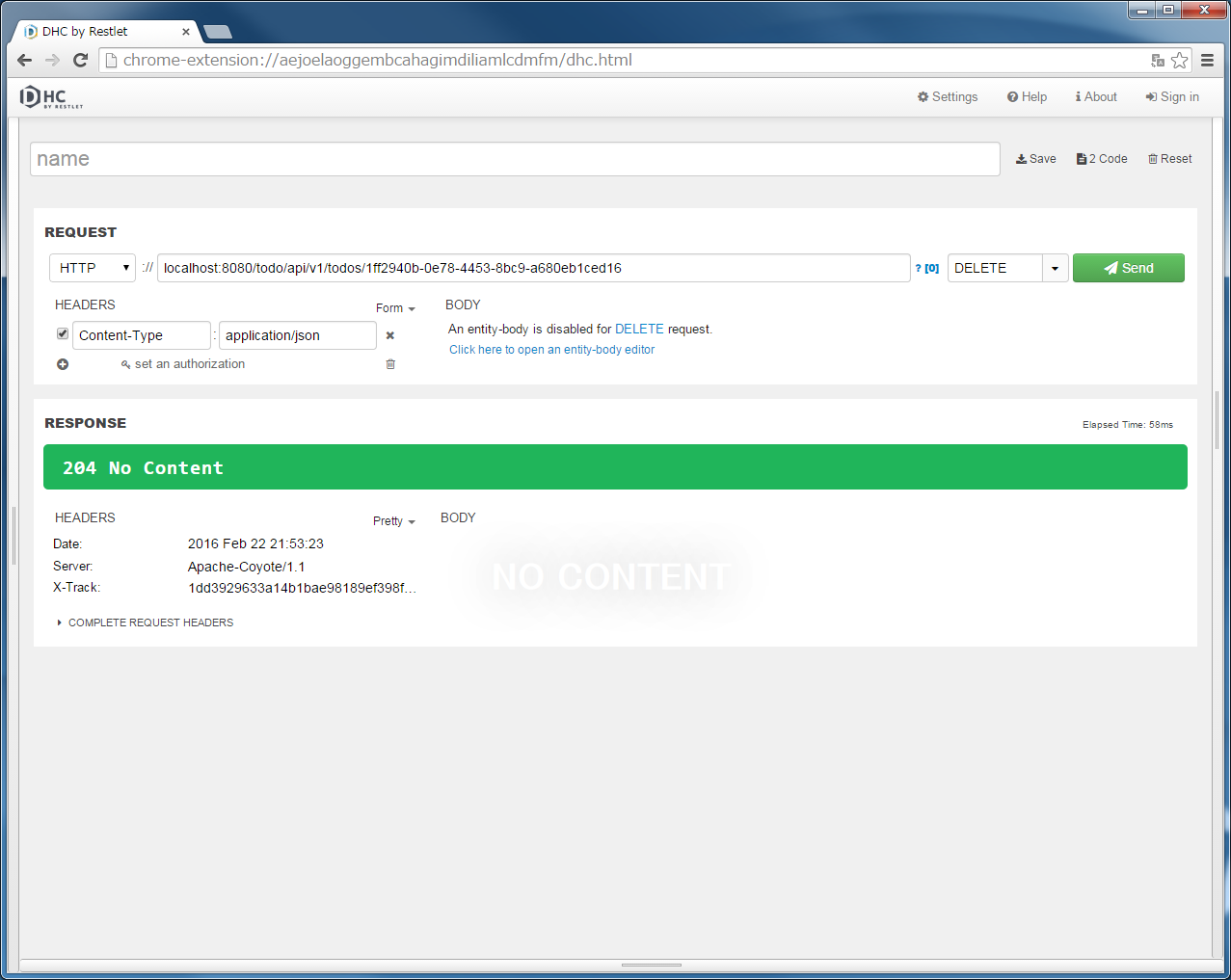
"localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos/{todoId}" in the URL and specify DELETE in method.{todoId}, run the POST Todos or GET Todos to get actual ID, copy & paste the todoId from the Response, and click the “Send” button.HTTP status returned “204 No Content” and [Body] of [RESPONSE] is empty.
"localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos" in the URL and click the “Send” button by specify GET in method.10.2.3.7. Implementation of exception handling¶
10.2.3.7.1. Change Domain layer implementation¶
src/main/java/todo/domain/service/todo/TodoServiceImpl.javapackage todo.domain.service.todo;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.UUID;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessages;
import todo.domain.model.Todo;
import todo.domain.repository.todo.TodoRepository;
@Service
@Transactional
public class TodoServiceImpl implements TodoService {
private static final long MAX_UNFINISHED_COUNT = 5;
@Inject
TodoRepository todoRepository;
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public Todo findOne(String todoId) {
Todo todo = todoRepository.findOne(todoId);
if (todo == null) {
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error();
messages.add("E404", todoId);
throw new ResourceNotFoundException(messages);
}
return todo;
}
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public Collection<Todo> findAll() {
return todoRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public Todo create(Todo todo) {
long unfinishedCount = todoRepository.countByFinished(false);
if (unfinishedCount >= MAX_UNFINISHED_COUNT) {
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error();
messages.add("E001", MAX_UNFINISHED_COUNT);
throw new BusinessException(messages);
}
String todoId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Date createdAt = new Date();
todo.setTodoId(todoId);
todo.setCreatedAt(createdAt);
todo.setFinished(false);
todoRepository.create(todo);
/* REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA
todoRepository.save(todo);
REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA */
return todo;
}
@Override
public Todo finish(String todoId) {
Todo todo = findOne(todoId);
if (todo.isFinished()) {
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error();
messages.add("E002", todoId);
throw new BusinessException(messages);
}
todo.setFinished(true);
todoRepository.update(todo);
/* REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA
todoRepository.save(todo);
REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA */
return todo;
}
@Override
public void delete(String todoId) {
Todo todo = findOne(todoId);
todoRepository.delete(todo);
}
}
10.2.3.7.2. Error message definition¶
Define the error code corresponding to the error messages of the processing result in the message property file.
src/main/resources/i18n/application-messages.properties
e.xx.fw.5001 = Resource not found.
e.xx.fw.7001 = Illegal screen flow detected!
e.xx.fw.7002 = CSRF attack detected!
e.xx.fw.7003 = Access Denied detected!
e.xx.fw.7004 = Missing CSRF detected!
e.xx.fw.8001 = Business error occurred!
e.xx.fw.9001 = System error occurred!
e.xx.fw.9002 = Data Access error!
# typemismatch
typeMismatch="{0}" is invalid.
typeMismatch.int="{0}" must be an integer.
typeMismatch.double="{0}" must be a double.
typeMismatch.float="{0}" must be a float.
typeMismatch.long="{0}" must be a long.
typeMismatch.short="{0}" must be a short.
typeMismatch.boolean="{0}" must be a boolean.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Integer="{0}" must be an integer.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Double="{0}" must be a double.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Float="{0}" must be a float.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Long="{0}" must be a long.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Short="{0}" must be a short.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Boolean="{0}" is not a boolean.
typeMismatch.java.util.Date="{0}" is not a date.
typeMismatch.java.lang.Enum="{0}" is not a valid value.
# For this tutorial
E001 = [E001] The count of un-finished Todo must not be over {0}.
E002 = [E002] The requested Todo is already finished. (id={0})
E400 = [E400] The requested Todo contains invalid values.
E404 = [E404] The requested Todo is not found. (id={0})
E500 = [E500] System error occurred.
E999 = [E999] Error occurred. Caused by : {0}
@NotNull and @Size) that are used in TodoResource class.
src/main/resources/ValidationMessages.properties
javax.validation.constraints.NotNull.message = {0} may not be null.
javax.validation.constraints.Size.message = {0} size must be between {min} and {max}.
10.2.3.7.3. Create a package that contains the error handling class¶
todo.api.common.error error handling class.
10.2.3.7.4. Creating REST API error handling class¶
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler provided by Spring MVC, adding the @ControllerAdvice annotation, and recommended to add (annotations = RestController.class) attribute in order to restrict to the REST API processing.todo.api.common.error.RestGlobalExceptionHandler class inherited from the ResponseEntityExceptionHandler.
src/main/java/todo/api/common/error/RestGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package todo.api.common.error;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
}
10.2.3.7.5. Creating JavaBean for holding the REST API error information¶
ApiError class under the todo.api.common.error package for holding the error information generated by the REST API.ApiError class converted into JSON and return to client.
src/main/java/todo/api/common/error/ApiError.java
package todo.api.common.error;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude;
public class ApiError implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final String code;
private final String message;
@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_EMPTY)
private final String target;
@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_EMPTY)
private final List<ApiError> details = new ArrayList<>();
public ApiError(String code, String message) {
this(code, message, null);
}
public ApiError(String code, String message, String target) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
this.target = target;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public String getTarget() {
return target;
}
public List<ApiError> getDetails() {
return details;
}
public void addDetail(ApiError detail) {
details.add(detail);
}
}
10.2.3.7.6. Implementation of putting error information to the HTTP response BODY¶
By default ResponseEntityExceptionHandler configures only HTTP status (400 or 500 etc) but not configures the HTTP response BODY.
Therefore, output the BODY by overidding the handleExceptionInternal method as follows.
src/main/java/todo/api/common/error/RestGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package todo.api.common.error;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@Inject
MessageSource messageSource;
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(Exception ex,
Object body, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status,
WebRequest request) {
Object responseBody = body;
if (body == null) {
responseBody = createApiError(request, "E999", ex.getMessage());
}
return ResponseEntity.status(status).headers(headers).body(responseBody);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request, String errorCode,
Object... args) {
return new ApiError(errorCode, messageSource.getMessage(errorCode,
args, request.getLocale()));
}
}
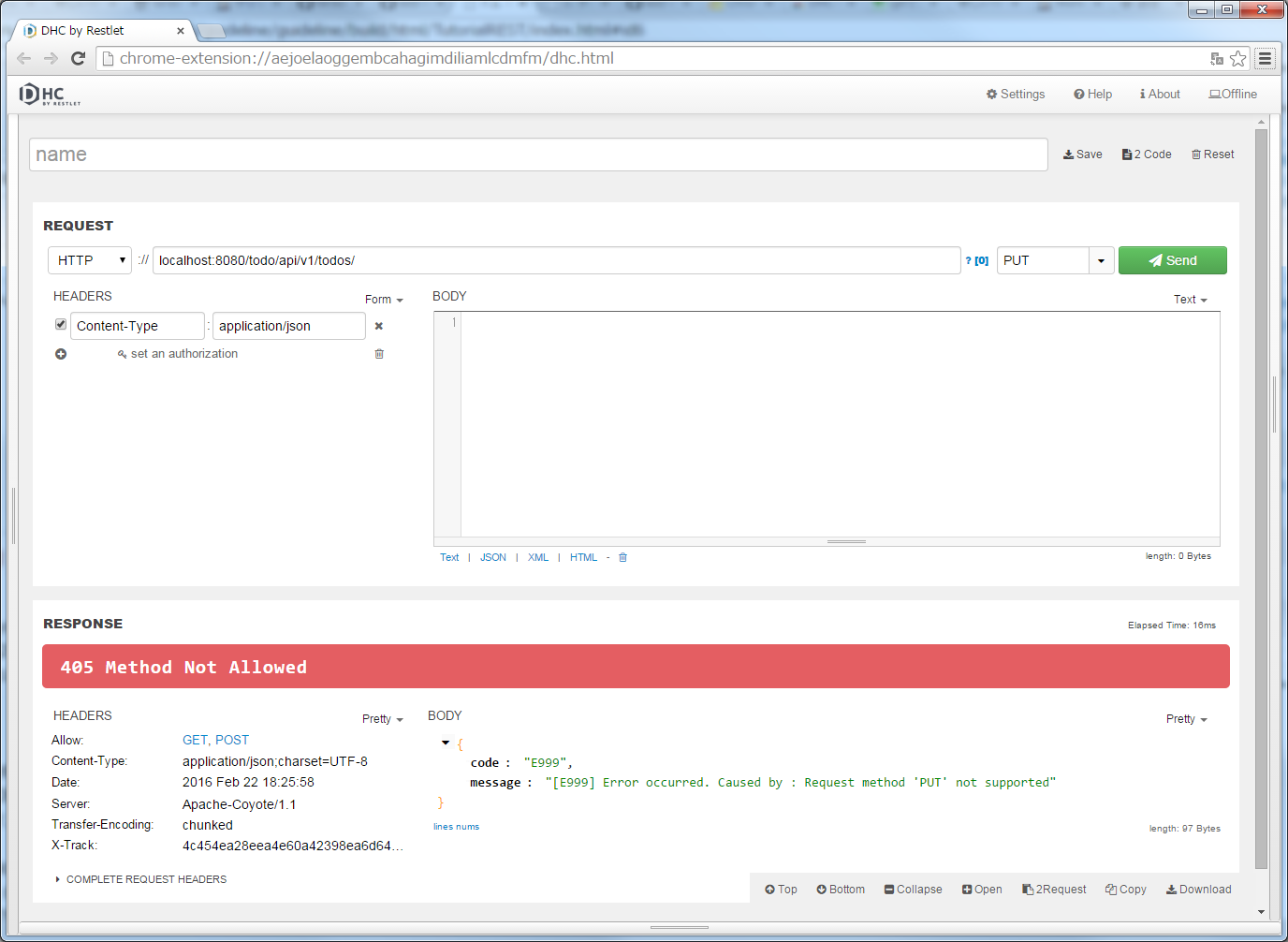
ResponseEntityExceptionHandler .ResponseEntityExceptionHandler , refer HTTP response code set by DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver."localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos" in the URL and click the “Send” button after specifying PUT in method.HTTP status returned “405 Method Not Allowed” and the JSON error information displays in [Body] of [RESPONSE] part.
10.2.3.7.7. Error handling of Input errors¶
Type of input errors as follows.
org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidExceptionorg.springframework.validation.BindExceptionorg.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotReadableExceptionorg.springframework.beans.TypeMismatchException
MethodArgumentNotValidException error handling.MethodArgumentNotValidException is an exception that occurs if there is any input error in the data stored in HTTP request BODY.src/main/java/todo/api/common/error/RestGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package todo.api.common.error;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@Inject
MessageSource messageSource;
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(Exception ex,
Object body, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status,
WebRequest request) {
Object responseBody = body;
if (body == null) {
responseBody = createApiError(request, "E999", ex.getMessage());
}
return ResponseEntity.status(status).headers(headers).body(responseBody);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request, String errorCode,
Object... args) {
return new ApiError(errorCode, messageSource.getMessage(errorCode,
args, request.getLocale()));
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, "E400");
for (FieldError fieldError : ex.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, fieldError, fieldError
.getField()));
}
for (ObjectError objectError : ex.getBindingResult().getGlobalErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, objectError, objectError
.getObjectName()));
}
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request,
DefaultMessageSourceResolvable messageSourceResolvable,
String target) {
return new ApiError(messageSourceResolvable.getCode(), messageSource
.getMessage(messageSourceResolvable, request.getLocale()), target);
}
}
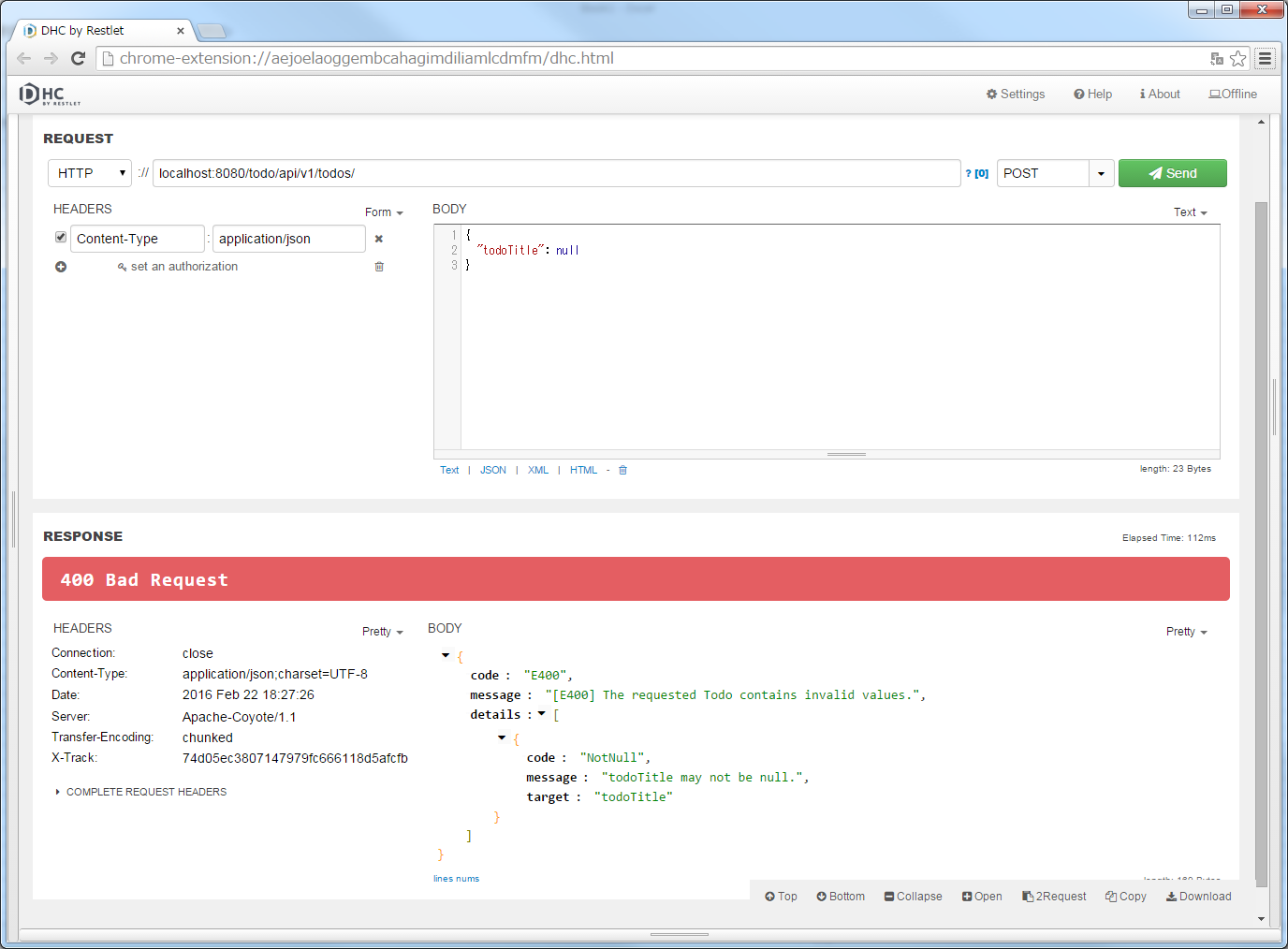
"localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos" in the URL and specify POST in method.{
"todoTitle": null
}
Furthermore, Add HTTP header by [+] button of [REQUEST] [HEADERS] and click “Send” button after setting [application/json] in the [Content-Type].
todoTitle is required field, required error occurred.10.2.3.7.8. Business exception error handling¶
Handling a business exception by adding org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException method in the RestGlobalExceptionHandler .
Set “409 Conflict” in HTTP status if business exception occurred.
src/main/java/todo/api/common/error/RestGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package todo.api.common.error;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResultMessagesNotificationException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessage;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@Inject
MessageSource messageSource;
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(Exception ex,
Object body, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status,
WebRequest request) {
Object responseBody = body;
if (body == null) {
responseBody = createApiError(request, "E999", ex.getMessage());
}
return ResponseEntity.status(status).headers(headers).body(responseBody);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request, String errorCode,
Object... args) {
return new ApiError(errorCode, messageSource.getMessage(errorCode,
args, request.getLocale()));
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, "E400");
for (FieldError fieldError : ex.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, fieldError, fieldError
.getField()));
}
for (ObjectError objectError : ex.getBindingResult().getGlobalErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, objectError, objectError
.getObjectName()));
}
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request,
DefaultMessageSourceResolvable messageSourceResolvable,
String target) {
return new ApiError(messageSourceResolvable.getCode(), messageSource
.getMessage(messageSourceResolvable, request.getLocale()), target);
}
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleBusinessException(BusinessException ex,
WebRequest request) {
return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.CONFLICT, request);
}
private ResponseEntity<Object> handleResultMessagesNotificationException(
ResultMessagesNotificationException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ResultMessage message = ex.getResultMessages().iterator().next();
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, message.getCode(), message
.getArgs());
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
}
"localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos/{todoId}" in the URL and specify PUT in method.{todoId}, run the POST Todos or GET Todos to get actual ID, copy & paste the todoId from the Response, and click the “Send” button twice.todoId of the Todos.HTTP status returned “409 Conflict” as a response of the 2nd request and JSON error information displays in [Body] of [RESPONSE] part.
10.2.3.7.9. Resource not found exception error handling¶
Resource not found exception handles by adding org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException method in the RestGlobalExceptionHandler.
Set “404 NotFound” in HTTP status if Resource not found exception occurred.
src/main/java/todo/api/common/error/RestGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package todo.api.common.error;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResultMessagesNotificationException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessage;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@Inject
MessageSource messageSource;
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(Exception ex,
Object body, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status,
WebRequest request) {
Object responseBody = body;
if (body == null) {
responseBody = createApiError(request, "E999", ex.getMessage());
}
return ResponseEntity.status(status).headers(headers).body(responseBody);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request, String errorCode,
Object... args) {
return new ApiError(errorCode, messageSource.getMessage(errorCode,
args, request.getLocale()));
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, "E400");
for (FieldError fieldError : ex.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, fieldError, fieldError
.getField()));
}
for (ObjectError objectError : ex.getBindingResult().getGlobalErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, objectError, objectError
.getObjectName()));
}
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request,
DefaultMessageSourceResolvable messageSourceResolvable,
String target) {
return new ApiError(messageSourceResolvable.getCode(), messageSource
.getMessage(messageSourceResolvable, request.getLocale()), target);
}
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleBusinessException(BusinessException ex,
WebRequest request) {
return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.CONFLICT, request);
}
private ResponseEntity<Object> handleResultMessagesNotificationException(
ResultMessagesNotificationException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ResultMessage message = ex.getResultMessages().iterator().next();
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, message.getCode(), message
.getArgs());
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleResourceNotFoundException(
ResourceNotFoundException ex, WebRequest request) {
return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, request);
}
}
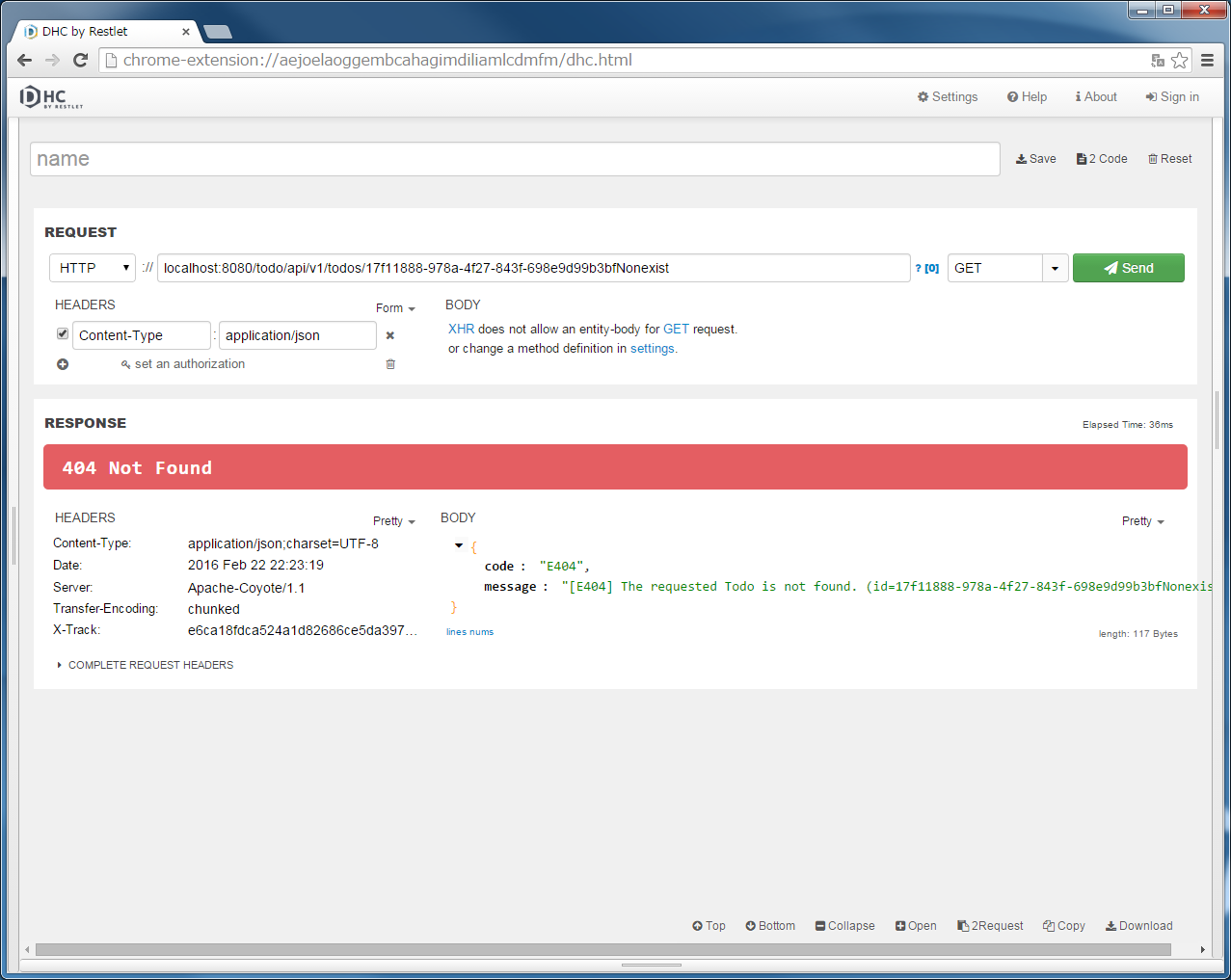
"localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos/{todoId}" in the URL and specify GET in method.HTTP status returned “404 Not Found” and JSON error information displays in [Body] of [RESPONSE] part.
10.2.3.7.10. System exception error handling¶
Lastly, System exception handles by adding java.lang.Exception method in the RestGlobalExceptionHandler.
Set “500 InternalServerError” in HTTP status if System exception occurred.
src/main/java/todo/api/common/error/RestGlobalExceptionHandler.java
package todo.api.common.error;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResultMessagesNotificationException;
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessage;
@ControllerAdvice
public class RestGlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@Inject
MessageSource messageSource;
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(Exception ex,
Object body, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status,
WebRequest request) {
Object responseBody = body;
if (body == null) {
responseBody = createApiError(request, "E999", ex.getMessage());
}
return ResponseEntity.status(status).headers(headers).body(responseBody);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request, String errorCode,
Object... args) {
return new ApiError(errorCode, messageSource.getMessage(errorCode,
args, request.getLocale()));
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, "E400");
for (FieldError fieldError : ex.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, fieldError, fieldError
.getField()));
}
for (ObjectError objectError : ex.getBindingResult().getGlobalErrors()) {
apiError.addDetail(createApiError(request, objectError, objectError
.getObjectName()));
}
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
private ApiError createApiError(WebRequest request,
DefaultMessageSourceResolvable messageSourceResolvable,
String target) {
return new ApiError(messageSourceResolvable.getCode(), messageSource
.getMessage(messageSourceResolvable, request.getLocale()), target);
}
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleBusinessException(BusinessException ex,
WebRequest request) {
return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.CONFLICT, request);
}
private ResponseEntity<Object> handleResultMessagesNotificationException(
ResultMessagesNotificationException ex, HttpHeaders headers,
HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
ResultMessage message = ex.getResultMessages().iterator().next();
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, message.getCode(), message
.getArgs());
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, headers, status, request);
}
@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleResourceNotFoundException(
ResourceNotFoundException ex, WebRequest request) {
return handleResultMessagesNotificationException(ex, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, request);
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleSystemError(Exception ex,
WebRequest request) {
ApiError apiError = createApiError(request, "E500");
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, apiError, new HttpHeaders(),
HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, request);
}
}
src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/todo-infra.properties
database=H2
#database.url=jdbc:h2:mem:todo;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1;INIT=create table if not exists todo(todo_id varchar(36) primary key, todo_title varchar(30), finished boolean, created_at timestamp)
database.url=jdbc:h2:mem:todo;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1
database.username=sa
database.password=
database.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
# connection pool
cp.maxActive=96
cp.maxIdle=16
cp.minIdle=0
cp.maxWait=60000
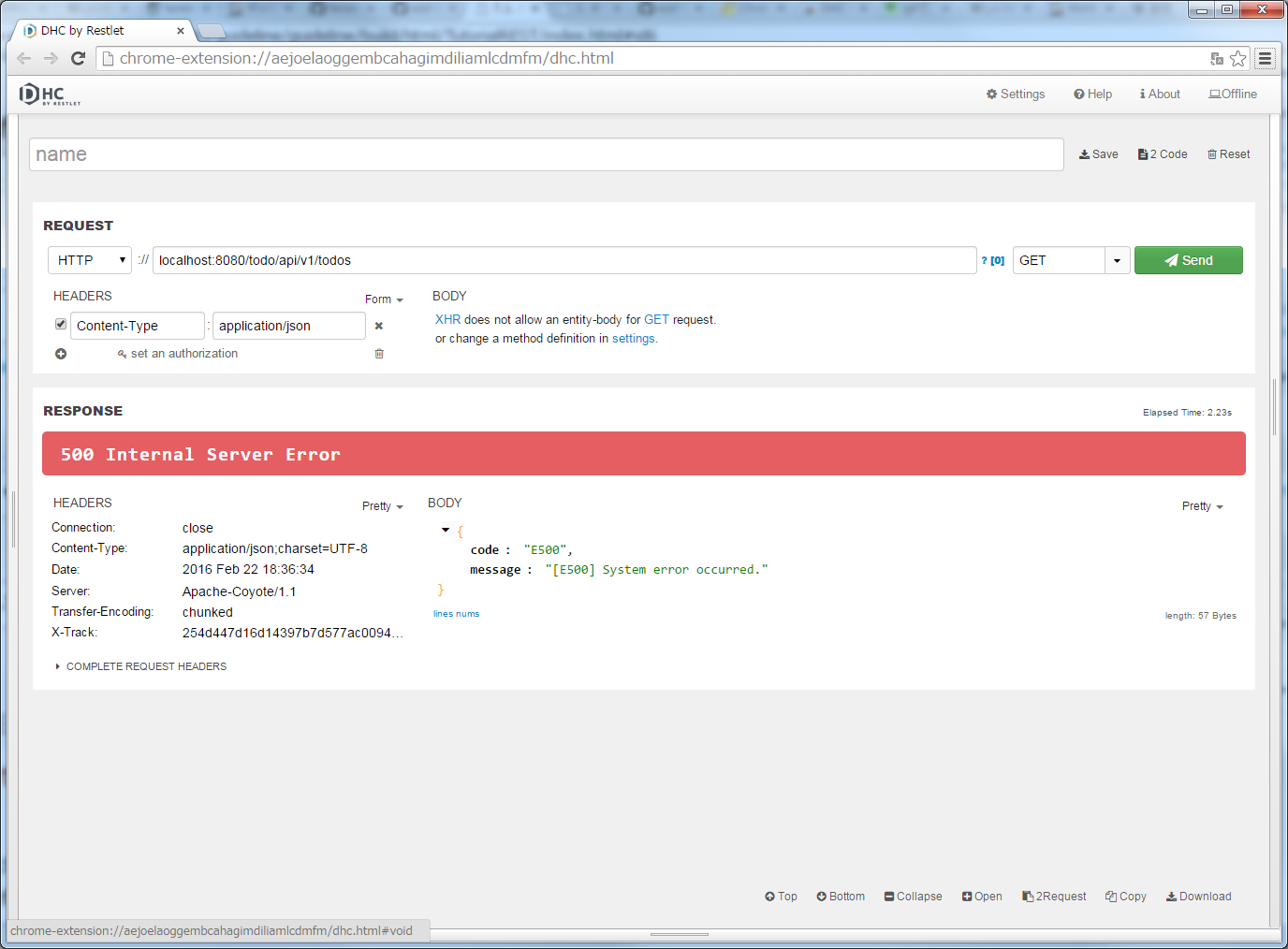
Open the DHC, enter "localhost:8080/todo/api/v1/todos/" in the URL and click the “Send” button after specifying GET in method.
HTTP status returned “500 Internal Server Error” and JSON error information displays in [Body] of [RESPONSE] part.
Note
In case of system error occurred, it is recommended to set a simple error message from which cause of error can not be identified while error message returning to the client. When you set the error message from which cause of error is identified, there is a possibility to exposes the vulnerability of the system to the client and may cause security issues.
It is good to flush the cause of an error into error analysis log.
The default setting of Blank project has been outputting the log by ExceptionLogger provided in the common library therefore setting and implementation for outputting the log is not required.
The log output by ExceptionLogger is as follows.
The cause of the system error can be understood that the Todo table is not exist.
date:2015-01-19 02:08:47 thread:tomcat-http--4 X-Track:aadf5822205d423c95a6531f2f76036f level:ERROR logger:o.t.gfw.common.exception.ExceptionLogger message:[e.xx.fw.9002] ### Error querying database. Cause: org.h2.jdbc.JdbcSQLException: Table "TODO" not found; SQL statement: SELECT todo_id, todo_title, finished, created_at FROM todo [42102-182] ### The error may exist in todo/domain/repository/todo/TodoRepository.xml ### The error may involve todo.domain.repository.todo.TodoRepository.findAll ### The error occurred while executing a query ... (omitted)
10.2.4. In the end…¶
In this tutorial, following contents have been learnt.
- How to develop basic RESTful Web service by TERASOLUNA Server Framework for Java (5.x)
- Implementation of Controller class that offers REST API(GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
- Cross conversion method of JavaBean and JSON
- Error message definition method
- Method of handling a variety of exception with Spring MVC
Here, explained how to implement the basic RESTful Web Services. To learn more about the architecture and design guidelines etc, Refer [RESTful Web Service].