4.6. Message Management¶
Caution
This version is already obsolete. Please check the latest guideline.
Table of Contents
4.6.1. Overview¶
Warning
In following cases, there is a risk of inability to identify error cause during the production phase or during the testing just before entering into production phase (however, such risks may not surface during the development phase).
- When only one error message is defined
- When only two types of error messages (“Important” and “Warning”) are defined
Thus, if messages are changed when the number of developers in the team is less, the cost to modify these messages would increase as the development progresses. It is, therefore, recommended to define the messages in advance at a detailed level.
4.6.1.1. Types of messages¶
| Message type | Category | Overview |
|---|---|---|
| info | Information message | This message is displayed when a process is executed normally by the user. |
| warn | Warning message | This message is displayed to indicate waring to be focused on; however the process can be continued. (Example: Notification indicating that the password is about to expire) |
| error | Input error message | This message is displayed on input screen when value entered by the user is invalid. |
| Business error message | This message is displayed to indicate error in the business logic | |
| System error message | This message is displayed when system errors (database connection failure etc.) occur and recovery is not possible by user operations. |
4.6.1.2. Types of messages depending on patterns¶
Message output patterns are shown below.
Message patterns, message display contents and the message type are shown below.
| Symbol | Pattern | Display contents | Message type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
(A)
|
Title
|
Screen title
|
-
|
|
Label
|
Screen field name
Report field name
Comment
Guidance
|
-
|
|
|
(B)
|
Dialog
|
Confirmation message
|
info
|
|
(C)
|
Result message
|
Successful completion
|
info
|
|
(D)
|
Warning
|
warn
|
|
|
(E)
|
Single field validation error
|
error
|
|
|
(F)
|
Correlation check error
|
error
|
|
|
(G)
|
Business error
|
error
|
|
|
(H)
|
System error
|
error
|
|
4.6.1.3. Message ID¶
- To change the message without modifying the source code.
- To be able to identify the message output location easily
- To support internationalization
From maintenance perspective, it is strongly recommended that you define the message IDs by creating and standardizing the rules.
4.6.1.3.1. Title¶
Format
Prefix Delimiter Business process name Delimiter Screen name title.nnn*.nnn*Description
Field Position Contents Remarks Prefix1st - 5th digit (5 digits)“title” (fixed)Business process nameVariable length:OptionalDirectory under prefix of viewResolver defined in spring-mvc.xml (parent directory of JSP)Screen nameVariable length:OptionalJSP name“aaa” when file name is “aaa.jsp”Example
# In case of "/WEB-INF/views/admin/top.jsp" title.admin.top=Admin Top # In case of "/WEB-INF/views/staff/createForm.jsp" title.staff.createForm=Staff Register Input
Tip
This example is valid when using Tiles. For details, refer to Screen Layout using Tiles. When not using Tiles, follow the Labels rules explained later.
4.6.1.3.2. Labels¶
The method of defining message ID to be used in screen label and fixed text of reports is described below.
Format
Prefix Delimiter Project code Delimiter Business process name Delimiter Field name label.xx.nnn*.nnn*Description
Field Position Contents Remarks Prefix1st - 5th digit (5 digits)“label” (Fixed)Project code7th - 8th digit (2 digits)Enter 2 alphabets of project nameBusiness process nameVariable length:OptionalField nameVariable length:OptionalLabel name, CaptionNote
When including the field name into validation error message, define messages as follows.
- model attribute name of form + “.” + field name
staffForm.staffName = Staff name
- filed name
staffName = Staff name
Example
# Form field name on Staff Registration screen # Project code=em (Event Management System) label.em.staff.staffName=Staff name # In case of a caption to be displayed on Tour Search screen # Project code=tr (Tour Reservation System) label.tr.tourSearch.tourSearchMessage=You can search tours with the specified conditions.
Note
In case of multiple projects, define a project code to avoid duplication of message ID. Even if there is a single project, it is recommended to define a project code for future enhancements.
4.6.1.3.3. Result messages¶
4.6.1.3.3.1. Messages commonly used in business processes¶
To avoid duplication of messages, the messages which are common in multiple business processes are explained below.
Format
Message type Delimiter Project code Delimiter Common message code Delimiter Error level Sr. No. x.xx.fw.9999Description
Field Position Contents Remarks Message type1st digit (1 digit)info : iwarn : werror : eProject code3rd - 4th digit (2 digits)Enter 2 alphabets of project nameCommon message code6th - 7th digit (2 digits)“fw” (fixed)Error level9th digit (1 digit)0-1 : Normal message2-4 : Business error (semi-normal message)5-7 : Input validation error8 : Business error (error)9 : System errorSr. No.10th -12th digit (3 digits)Use as per serial number (000-999)Even if the message is deleted, serial number field should be blank and it should not be deleted.Example
# When registration is successful (Normal message) i.ex.fw.0001=Registered successfully. # Insufficient server resources w.ex.fw.9002=Server busy. Please, try again. # When system error occurs (System error) e.ex.fw.9001=A system error has occurred.
4.6.1.3.3.2. Messages used individually in each business process¶
The messages used individually in each business process are explained below.
Format
Message type Delimiter Project code Delimiter Business process message code Delimiter Error level Sr. No. x.xx.xx.9999Description
Field Position Contents Remarks Message type1st digit (1 digit)info : iwarn : werror : eProject code3rd -4th digit (2 digits)Enter 2 alphabets of project nameBusiness process message code6th -7th digit (2 digits)2 characters defined for each business process such as Business IDError level9th digit (1 digit)0-1 : Normal message2-4 : Business error (semi-normal message)5-7 : Input validation error8 : Business error (error)9 : System errorSr. No.10th -12th digit (3 digits)Use as per serial number (000-999)Even if the message is deleted, serial number field should be blank and it should not be deleted.Example
# When file upload is successful. i.ex.an.0001={0} upload completed. # When the recommended password change interval has passed. w.ex.an.2001=The recommended change interval has passed password. Please change your password. # When file size exceeds the limit. e.ex.an.8001=Cannot upload, Because the file size must be less than {0}MB. # When there is inconsistency in data. e.ex.an.9001=There are inconsistencies in the data.
4.6.1.3.4. Input validation error message¶
For the messages to be displayed in case of input validation error, refer to Definition of error messages.
Note
Basic policies related to output location of input validation error are as follows:
4.6.2. How to use¶
4.6.2.1. Display of messages set in properties file¶
4.6.2.1.1. Settings at the time of using properties¶
Define implementation class of org.springframework.context.MessageSource which is used for performing message management.
applicationContext.xml
<!-- Message --> <bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource"> <!-- (1) --> <property name="basenames"> <!-- (2) --> <list> <value>i18n/application-messages</value> </list> </property> </bean>
Sr. No. Description (1)Definition ofMessageSource. Here, useResourceBundleMessageSource.(2)Define the base name of message property to be used. Specify it with relative class path.In this example, read “src/main/resources/i18n/application-messages.properties”.
4.6.2.1.2. Display of messages set in properties¶
application-messages.properties
See the example below for defining the messages in
application-messages.properties.label.aa.bb.year=Year label.aa.bb.month=Month label.aa.bb.day=Day
Note
Earlier, it was necessary to convert the characters (such as Japanese characters etc.) that cannot be expressed into “ISO-8859-1” with the help of
native2asciicommand. However, from JDK version 6 onwards, it has become possible to specify the character encoding; hence character conversion is no longer needed. By setting the character encoding to UTF-8, Japanese characters etc. can be used directly in properties file.application-messages.properties
label.aa.bb.year= Year label.aa.bb.month= Month label.aa.bb.day= Day
In such a case, it is necessary to specify the character encoding that can also be read in
ResourceBundleMessageSource.applicationContext.xml
<bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource"> <property name="basenames"> <list> <value>i18n/application-messages</value> </list> </property> <property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8" /> </bean>
ISO-8859-1 is used by default; hence when describing the Japanese characters directly in properties file, make sure that the character encoding is set as value of
defaultEncodingproperty.JSP
Messages set above can be displayed using
<spring:message>tag in JSP. For using it, settings mentioned in Creating common JSP for include must be done.<spring:message code="label.aa.bb.year" /> <spring:message code="label.aa.bb.month" /> <spring:message code="label.aa.bb.day" />
When used with form label, it can be used as follows:
<form:form modelAttribute="sampleForm"> <form:label path="year"> <spring:message code="label.aa.bb.year" /> </form:label>: <form:input path="year" /> <br> <form:label path="month"> <spring:message code="label.aa.bb.month" /> </form:label>: <form:input path="month" /> <br> <form:label path="day"> <spring:message code="label.aa.bb.day" /> </form:label>: <form:input path="day" /> </form:form>
It is displayed in browser as follows:
Tip
When supporting internationalization,
src/main/resources/i18n ├ application-messages.properties (English message) ├ application-messages_fr.properties (French message) ├ ... └ application-messages_ja.properties (Japanese message)properties file should be created for each language as shown above. For details, refer to Internationalization .
4.6.2.2. Display of result messages¶
org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessages and org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessage are provided in common library,
as classes storing the result messages which indicate success or failure of process at server side.
| Class name | Description |
|---|---|
ResultMessages |
Class having list of result messages and message type.
List of Result messages is expressed in terms of
List<ResultMessage> and message type is expressed in terms of org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessageType interface. |
ResultMessage |
Class having result message ID or message text.
|
<t:messagesPanel> tag is also provided as JSP tag library for displaying this result message in JSP.4.6.2.2.1. Using basic result messages¶
The way of creating ResultMessages in Controller, passing them to screen and displaying
the result messages using <t:messagesPanel> tag in JSP, is displayed below.
Controller class
The methods of creating
ResultMessagesobject and passing the messages to screen are given below. An example of Messages used individually in each business process should be defined in application-messages.properties.package com.example.sample.app.message; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessages; @Controller @RequestMapping("message") public class MessageController { @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET) public String hello(Model model) { ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error().add("e.ex.an.9001"); // (1) model.addAttribute(messages); // (2) return "message/index"; } }
Sr. No. Description (1)CreateResultMessageswherein message type is “error” andset result messages wherein message ID is “e.ex.an.9001”.This process is same as follows:ResultMessages.error().add(ResultMessage.fromCode("e.ex.an.9001"));Since it is possible to skip the creation ofResultMessageobject if message ID is specified, it is recommended to skip the same.(2)AddResultMessagesto Model.It is ok even if the attribute is not specified. (Attribute name is “resultMessages”)JSP
Write WEB-INF/views/message/index.jsp as follows:
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Result Message Example</title> </head> <body> <h1>Result Message</h1> <t:messagesPanel /><!-- (1) --> </body> </html>
Sr. No. Description (1)<t:messagesPanel>tag is used with default settings.By default, “resultMessages” object is displayed.Therefore, attribute name need not be specified whenResultMessagesis set in Model from Controller with default settings.It is displayed in browser as follows:
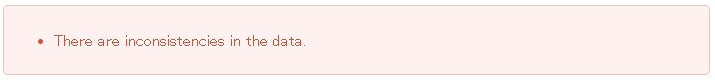
HTML output by
<t:messagesPanel>is shown below. (The format makes the explanation easier).<div class="alert alert-error"><!-- (1) --> <ul><!-- (2) --> <li>There are inconsistencies in the data.</li><!-- (3) --> </ul> </div>
Sr. No. Description (1)“alert-error”class is assigned in accordance with the message type. “error error-[Message type]” is assigned to<div>tag class by default.(2)Result message list is output using<ul>tag.(3)The message corresponding to message ID is resolved fromMessageSource.<t:messagesPanel>outputs only HTML with class; hence it is necessary to customize the look and feel using CSS as per the output class (explained later).Note
Message text can be hard-coded such as
ResultMessages.error().add(ResultMessage.fromText("There are inconsistencies in the data."));; however, to enhance maintainability, it is recommended to createResultMessageobject using message key, and to fetch the message text from properties file.
For inserting a value in message placeholder, set second or subsequent arguments of add method as follows:
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error().add("e.ex.an.8001", 1024);
model.addAttribute(messages);
In such a case, the HTML shown below is output using <t:messagesPanel /> tag.
<div class="alert alert-error">
<ul>
<li>Cannot upload, Because the file size must be less than 1,024MB.</li>
</ul>
</div>
Warning
Points to be noted when inserting values in placeholder using terasoluna-gfw-web 1.0.0.RELEASE
When using terasoluna-gfw-web 1.0.0.RELEASE, if the user entered value is inserted in the placeholder, there is a risk of XSS vulnerability.If the user entered value is likely to include XSS vulnerable characters, then the value should not be inserted in the placeholder.
When using terasoluna-gfw-web 1.0.1.RELEASE or higher version, XSS vulnerability does not occur even after inserting the user entered value in the placeholder.
Note
ResourceBundleMessageSourceusesjava.text.MessageFormatat the time of creating a message; hence1024is displayed as1,024with comma. When comma is not required, perform settings in properties file as shown below.e.ex.an.8001=Cannot upload, Because the file size must be less than {0,number,#}MB.For details, refer to Javadoc.
It is also possible to set multiple result messages as shown below.
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error()
.add("e.ex.an.9001")
.add("e.ex.an.8001", 1024);
model.addAttribute(messages);
In such a case, HTML is output as follows (no need to change JSP).
<div class="alert alert-error">
<ul>
<li>There are inconsistencies in the data.</li>
<li>Cannot upload, Because the file size must be less than 1,024MB.</li>
</ul>
</div>
In order to display info message, it is desirable to create ResultMessages object using ResultMessages.info() method as shown below.
ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.info().add("i.ex.an.0001", "XXXX");
model.addAttribute(messages);
HTML shown below is output.
<div class="alert alert-info"><!-- (1) -->
<ul>
<li>XXXX upload completed.</li>
</ul>
</div>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
The output class name has changed to “alert alert-info” in accordance with the message type.
|
Fundamentally the following message types are created.
| Message type | Creation of ResultMessages object |
Default class name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
success
|
ResultMessages.success() |
alert alert-success
|
-
|
info
|
ResultMessages.info() |
alert alert-info
|
-
|
warn
|
ResultMessages.warn() |
alert alert-warn
|
This type is deprecated because added “warning” as new message type from terasoluna-gfw-common 5.0.0.RELEASE.
This message type might be removed in the future.
|
warning
|
ResultMessages.warning() |
alert alert-warning
|
Added this message type to support Alerts component of Bootstrap(CSS Framework) from the terasoluna-gfw-common 5.0.0.RELEASE.
|
error
|
ResultMessages.error() |
alert alert-error
|
-
|
danger
|
ResultMessages.danger() |
alert alert-danger
|
-
|
CSS should be defined according to the message type. Example of applying CSS is given below.
.alert {
margin-bottom: 15px;
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid;
border-radius: 4px;
text-shadow: 0 1px 0 #ffffff;
}
.alert-info {
background: #ebf7fd;
color: #2d7091;
border-color: rgba(45, 112, 145, 0.3);
}
.alert-warning {
background: #fffceb;
color: #e28327;
border-color: rgba(226, 131, 39, 0.3);
}
.alert-error {
background: #fff1f0;
color: #d85030;
border-color: rgba(216, 80, 48, 0.3);
}
Example wherein
ResultMessages.error().add("e.ex.an.9001")is output using<t:messagesPanel />Example wherein
ResultMessages.warning().add("w.ex.an.2001")is output using<t:messagesPanel />Example wherein
ResultMessages.info().add("i.ex.an.0001", "XXXX")is output using<t:messagesPanel />Note
“success” and “danger” are provided to have diversity in style. In this guideline, success is synonymous with info and error is synonymous with danger.
Tip
Alerts component of Bootstrap 3.0.0 which is a CSS framework can be used with default settings of
<t:messagePanel />.Warning
In this example, message keys are hardcoded. However, in order to improve maintainability, it is recommended to define message keys in constant class.
Refer to Auto-generation tool of message key constant class.
4.6.2.2.2. Specifying attribute name of result messages¶
ResultMessages to Model.ResultMessages cannot represent more than one message type.ResultMessages of different message types on 1 screen, it is necessary to specify the attribute name explicitly and set it in Model.Controller (Add to MessageController)
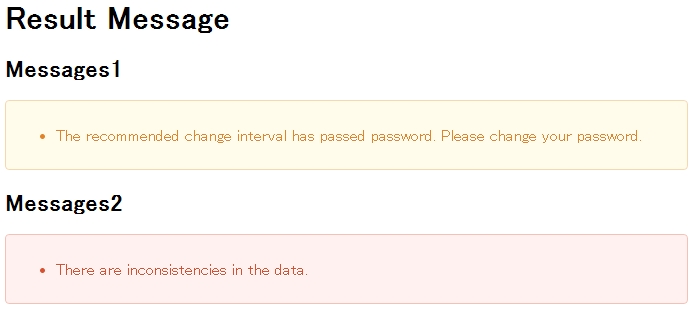
@RequestMapping(value = "showMessages", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String showMessages(Model model) { model.addAttribute("messages1", ResultMessages.warning().add("w.ex.an.2001")); // (1) model.addAttribute("messages2", ResultMessages.error().add("e.ex.an.9001")); // (2) return "message/showMessages"; }
Sr. No. Description (1)AddResultMessagesof “warning” message type to Model with attribute name “messages1”.(2)AddResultMessagesof “info” message type to Model with attribute name “messages2”.JSP (WEB-INF/views/message/showMessages.jsp)
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Result Message Example</title> <style type="text/css"> .alert { margin-bottom: 15px; padding: 10px; border: 1px solid; border-radius: 4px; text-shadow: 0 1px 0 #ffffff; } .alert-info { background: #ebf7fd; color: #2d7091; border-color: rgba(45, 112, 145, 0.3); } .alert-warning { background: #fffceb; color: #e28327; border-color: rgba(226, 131, 39, 0.3); } .alert-error { background: #fff1f0; color: #d85030; border-color: rgba(216, 80, 48, 0.3); } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Result Message</h1> <h2>Messages1</h2> <t:messagesPanel messagesAttributeName="messages1" /><!-- (1) --> <h2>Messages2</h2> <t:messagesPanel messagesAttributeName="messages2" /><!-- (2) --> </body> </html>
Sr. No. Description (1)DisplayResultMessageshaving attribute name “messages1”.(2)DisplayResultMessageshaving attribute name “messages2”.It is displayed in browser as follows:
4.6.2.2.3. Displaying business exception messages¶
org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.BusinessException and org.terasoluna.gfw.common.exception.ResourceNotFoundException storesResultMessages internally.BusinessException wherein ResultMessages is set should be thrown in Service class.BusinessException in Controller class and add the result message fetched from the caught exception to Model.Service class
@Service @Transactional public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { // omitted public void create(...) { // omitted... if (...) { // illegal state! ResultMessages messages = ResultMessages.error() .add("e.ex.an.9001"); // (1) throw new BusinessException(messages); } } }
Sr. No. Description (1)Create error message usingResultMessagesand set inBusinessException.Controller class
@RequestMapping(value = "create", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String create(@Validated UserForm form, BindingResult result, Model model) { // omitted try { userService.create(user); } catch (BusinessException e) { ResultMessages messages = e.getResultMessages(); // (1) model.addAttribute(messages); return "user/createForm"; } // omitted }
Sr. No. Description (1)FetchResultMessagesheld byBusinessExceptionand add to Model.
Normally, this method should be used to display error message instead of creating
ResultMessages object in Controller.
4.6.3. How to extend¶
4.6.3.1. Creating independent message types¶
First, create independent message type class wherein org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessageType interface is implemented
as follows:
import org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.ResultMessageType;
public enum ResultMessageTypes implements ResultMessageType { // (1)
NOTICE("notice");
private ResultMessageTypes(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
private final String type;
@Override
public String getType() { // (2)
return this.type;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.type;
}
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Define Enum wherein
ResultMessageType interface is implemented. A new message type can be created using constant class; however it is recommended to create it using Enum. |
(2)
|
Return value of
getType corresponds to class name of CSS which is output. |
ResultMessages using this message type as mentioned below.ResultMessages messages = new ResultMessages(ResultMessageTypes.NOTICE) // (1)
.add("w.ex.an.2001");
model.addAttribute(messages);
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify
ResultMessageType in constructor of ResultMessages. |
In such a case, HTML shown below is output in <t:messagesPanel /> .
<div class="alert alert-notice">
<ul>
<li>The recommended change interval has passed password. Please change your password.</li>
</ul>
</div>
Tip
For extension method, refer to
org.terasoluna.gfw.common.message.StandardResultMessageType.
4.6.4. Appendix¶
4.6.4.1. Changing attribute of <t:messagesPanel> tag¶
<t:messagesPanel> tag contains various attributes for changing the display format.
| Option | Contents | Default setting value |
|---|---|---|
| panelElement | Result message display panel elements | div |
| panelClassName | CSS class name of result message display panel. | alert |
| panelTypeClassPrefix | Prefix of CSS class name | alert- |
| messagesType | Message type. When this attribute is set, the set message type is given preference over the message type of ResultMessages object. |
|
| outerElement | Outer tag of HTML configuring result messages list | ul |
| innerElement | Inner tag of HTML configuring result messages list | li |
| disableHtmlEscape | Flag for disabling HTML escaping.
By setting the flag to
true, HTML escaping is no longer performed for the message to be output.This attribute is used to create different message styles by inserting HTML into the message to be output.
When the flag is set to true, XSS vulnerable characters should not be included in the message.
This attribute can be used with terasoluna-gfw-web 1.0.1.RELEASE or higher version.
|
false |
For example, following CSS is provided in CSS framework “BlueTrip”.
.error,.notice,.success {
padding: .8em;
margin-bottom: 1.6em;
border: 2px solid #ddd;
}
.error {
background: #FBE3E4;
color: #8a1f11;
border-color: #FBC2C4;
}
.notice {
background: #FFF6BF;
color: #514721;
border-color: #FFD324;
}
.success {
background: #E6EFC2;
color: #264409;
border-color: #C6D880;
}
<div class="error">...</div> should be output.<t:messagesPanel> tag can be used as follows (no need to modify the Controller):<t:messagesPanel panelClassName="" panelTypeClassPrefix="" />
HTML shown below is output.
<div class="error">
<ul>
<li>There are inconsistencies in the data.</li>
</ul>
</div>
It is displayed in browser as follows:
When you do not want to use <ul> tag to display the message list,
it can be customized using outerElement attribute and innerElement attribute.
When the attributes are set as follows:
<t:messagesPanel outerElement="" innerElement="span" />
HTML shown below is output.
<div class="alert alert-error">
<span>There are inconsistencies in the data.</span>
<span>Cannot upload, Because the file size must be less than 1,024MB.</span>
</div>
Set the CSS as follows:
.alert > span {
display: block; /* (1) */
}
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Set
<span> tag which is a child element of “alert” class to Block-level element. |
It is displayed in browser as follows:
true, the output will be as follows:- jsp
<spring:message var="informationMessage" code="i.ex.od.0001" /> <t:messagesPanel messagesAttributeName="informationMessage" messagesType="alert alert-info" disableHtmlEscape="true" />
- properties
i.ex.od.0001 = Please confirm order content. <font style="color: red; font-size: 16px;">If this orders submitted, cannot cancel.</font>
- Output image
4.6.4.2. Display of result message wherein ResultMessages is not used¶
Apart from ResultMessages object, <t:messagesPanel> tag can also output the following objects.
java.lang.Stringjava.lang.Exceptionjava.util.List
<t:messagesPanel> tag is used to output the ResultMessages object; however<t:messagesPanel> tag similar to the result messages.<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Login</title>
<style type="text/css">
/* (1) */
.alert {
margin-bottom: 15px;
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid;
border-radius: 4px;
text-shadow: 0 1px 0 #ffffff;
}
.alert-error {
background: #fff1f0;
color: #d85030;
border-color: rgba(216, 80, 48, 0.3);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<c:if test="${param.containsKey('error')}">
<t:messagesPanel messagesType="error"
messagesAttributeName="SPRING_SECURITY_LAST_EXCEPTION" /><!-- (2) -->
</c:if>
<form:form
action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/authentication"
method="post">
<fieldset>
<legend>Login Form</legend>
<div>
<label for="username">Username: </label><input
type="text" id="username" name="username">
</div>
<div>
<label for="username">Password:</label><input
type="password" id="password" name="password">
</div>
<div>
<input type="submit" value="Login" />
</div>
</fieldset>
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Re-define the CSS. It is strongly recommended to mention it in CSS file.
|
(2)
|
In
messagesAttributeName attribute, specify the attribute name wherein Exception object is stored.Unlike the
ResultMessages object, it does not contain the information of message type; henceit is necessary to explicitly specify the message type in
messagesType attribute. |
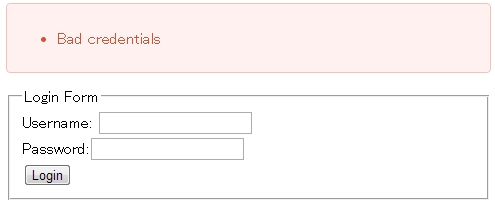
The HTML output in case of an authentication error will be,
<div class="alert alert-error"><ul><li>Bad credentials</li></ul></div>
and it will be displayed in the browser as follows:
Tip
For details on JSP for login, refer to Authentication.
4.6.4.3. Auto-generation tool of message key constant class¶
In all earlier examples, message keys were hard-coded strings; however it is recommended that you define the message keys in constant class.
This section introduces the program that auto-generates message key constant class from properties file and the corresponding usage method. You can customize and use them based on the requirements.
Creation of message key constant class
First, create an empty message key constant class. Here, it is
com.example.common.message.MessageKeys.package com.example.common.message; public class MessageKeys { }
Creation of auto-generation class
Next, create
MessageKeysGenclass in the same package asMessageKeysclass and write the logic as follows:package com.example.common.message; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.regex.Pattern; import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils; public class MessageKeysGen { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // message properties file InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("src/main/resources/i18n/application-messages.properties"); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream)); Class<?> targetClazz = MessageKeys.class; File output = new File("src/main/java/" + targetClazz.getName().replaceAll(Pattern.quote("."), "/") + ".java"); System.out.println("write " + output.getAbsolutePath()); PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(FileUtils.openOutputStream(output)); try { pw.println("package " + targetClazz.getPackage().getName() + ";"); pw.println("/**"); pw.println(" * Message Id"); pw.println(" */"); pw.println("public class " + targetClazz.getSimpleName() + " {"); String line; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { String[] vals = line.split("=", 2); if (vals.length > 1) { String key = vals[0].trim(); String value = vals[1].trim(); pw.println(" /** " + key + "=" + value + " */"); pw.println(" public static final String " + key.toUpperCase().replaceAll(Pattern.quote("."), "_").replaceAll(Pattern.quote("-"), "_") + " = \"" + key + "\";"); } } pw.println("}"); pw.flush(); } finally { IOUtils.closeQuietly(br); IOUtils.closeQuietly(pw); } } }
Provision of message properties file
Define the messages in src/main/resource/i18m/application-messages.properties. The settings are carried out as follows:
i.ex.an.0001={0} upload completed. w.ex.an.2001=The recommended change interval has passed password. Please change your password. e.ex.an.8001=Cannot upload, Because the file size must be less than {0}MB. e.ex.an.9001=There are inconsistencies in the data.
Execution of auto-generation class
MessageKeysclass is overwritten as follows:package com.example.common.message; /** * Message Id */ public class MessageKeys { /** i.ex.an.0001={0} upload completed. */ public static final String I_EX_AN_0001 = "i.ex.an.0001"; /** w.ex.an.2001=The recommended change interval has passed password. Please change your password. */ public static final String W_EX_AN_2001 = "w.ex.an.2001"; /** e.ex.an.8001=Cannot upload, Because the file size must be less than {0}MB. */ public static final String E_EX_AN_8001 = "e.ex.an.8001"; /** e.ex.an.9001=There are inconsistencies in the data. */ public static final String E_EX_AN_9001 = "e.ex.an.9001"; }