6.6. CSRF Countermeasures¶
Table of contents
6.6.1. Overview¶
This chapter explains Cross site request forgeries (hereafter referred to as CSRF) countermeasures function offered by Spring Security.
CSRF is an attack that forces a user to perform unwanted actions on a different website in which the user is logged in. by implementing a script in the Website or by automatic transfer (HTTP redirect).
Following are the methods to prevent server side CSRF attack.
- Embedding confidential information (token)
- Re-entering password
- ‘Referer’ check
CSRF countermeasures function handles the malicious request sent from the Web page provided by the attacker as an invalid request. Following methods can be used to attack if CSRF countermeasures are not implemented in a Web application.
- User logs in to the Web application for which CSRF countermeasures are not implemented.
- User opens the Web page provided by the attacker under the skilful guidance of the attacker.
- The Web page prepared by the attacker sends a forged request to the Web application for which CSRF countermeasures have not been implemented, using techniques such as automatic submission of form.
- Web applications for which CSRF countermeasures are not implemented handle forged request by the attacker as a legitimate request.
Tip
In OWASP[1], the method to use token pattern is recommended.
[1] OWASP is an abbreviation of Open Web Application Security Project. It is a not-for-profit international organization dedicated to enable organizations to develop and maintain applications that can be trusted. It advocates measures such as effective approach etc. with respect to security. https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Main_Page
Note
CSRF countermeasures at the time of login
CSRF countermeasures should be implemented not only for the login request but also for the login process. If CSRF countermeasures are not implemented for login process, user is forced to login using the account created by the attacker even before the user realizes it and there is a possibility of the operation history of login being stolen.
Warning
CSRF measures at the time of the multi-part request (file upload)
About CSRF measures during file upload, file upload Servlet Filter settingshould be followed.
6.6.1.1. CSRF countermeasures of Spring Security¶
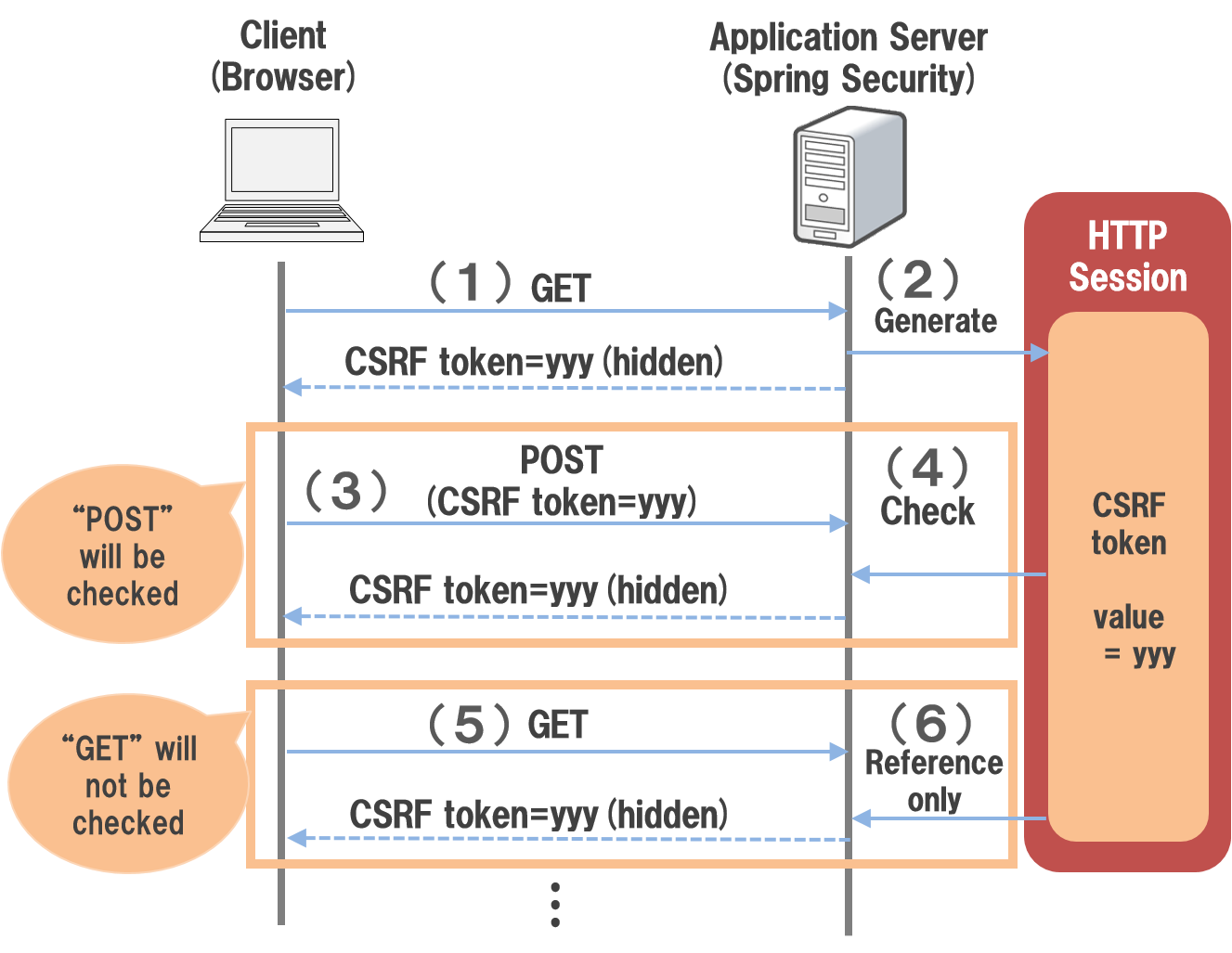
Spring Security issues a fixed token value (CSRF token) generated randomly for each session and sends the issued CSRF token as a request parameter (hidden field in the HTML form). Accordingly, a system to determine whether the request is from a normal Web page or from the Web page created by the attacker, is adopted.
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Client accesses the application server using the HTTP GET method.
|
(2)
|
Spring Security generates a CSRF token and stores it in HTTP session.
The generated CSRF token links with the client using the hidden tag of HTML form.
|
(3)
|
The client sends a request to the application server by clicking a button on the HTML form.
Since the CSRF token is embedded in a hidden field in the HTML form, CSRF token value is sent as a request parameter.
|
(4)
|
Spring Security checks if the CSRF token value specified in the request parameter and the CSRF token value retained in the HTTP session are same when it is accessed using HTTP POST method.
If the token value does not match, an error is thrown as an invalid request (request from the attacker).
|
(5)
|
Client accesses the application server using the HTTP GET method.
|
(6)
|
Spring Security does not check the CSRF token value when it is accessed using GET method.
|
Note
CSRF token using Ajax
Since Spring Security can set the CSRF token value in request header, it is possible to implement CSRF countermeasures for the requests for Ajax etc.
6.6.1.1.1. Target request of token check¶
In the default implementation of Spring Security, check CSRF token for the request that uses the following HTTP methods.
- POST
- PUT
- DELETE
- PATCH
Note
Reason for not checking CSRF token
GET, HEAD, OPTIONS, TRACE methods are not checked as these methods are not used to implement the request to change the application status.
6.6.2. How to use¶
6.6.2.1. Applying CSRF countermeasures¶
By using the RequestDataValueProcessorimplementation class for CSRF token, the token can be automatically inserted as ‘hidden’ field using <form:form>tag of Spring tag library.
- Setting example of spring-mvc.xml
<bean id="requestDataValueProcessor"
class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.mvc.support.CompositeRequestDataValueProcessor"> <!-- (1) -->
<constructor-arg>
<util:list>
<bean
class="org.springframework.security.web.servlet.support.csrf.CsrfRequestDataValueProcessor" /> <!-- (2) -->
<bean
class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.token.transaction.TransactionTokenRequestDataValueProcessor" />
</util:list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Define a bean for
org.terasoluna.gfw.web.mvc.support.CompositeRequestDataValueProcessor for which multipleorg.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestDataValueProcessor provided by common library can be defined. |
(2)
|
Set the bean definition
org.springframework.security.web.servlet.support.csrf.CsrfRequestDataValueProcessor as the first argument of constructor. |
CSRF countermeasures function is enabled as a default by the settings described above from Spring Security 4.0 and subsequent versions. Therefore, CSRF countermeasures function should be disabled explicitly if you do not want to use it.
Define a bean as given below if CSRF countermeasures function is not to be used.
- Definition example of spring-security.xml
<sec:http>
<!-- omitted -->
<sec:csrf disabled="true"/> <!-- Disabled by setting true in the 'disabled' attribute -->
<!-- omitted -->
</sec:http>
6.6.2.2. Linking CSRF token value¶
Spring Security provides the following two methods to link the CSRF token value between the client and server.
- Output the CSRF token value as a hidden field in the HTML form and link as a request parameter
- Output CSRF token information as HTML meta tag and link by setting the token value in the request header at the time of Ajax communication
6.6.2.2.1. Coordination by using Spring MVC¶
Spring Security has provided several components to coordinate with Spring MVC. How to use the component to coordinate with CSRF countermeasures function is described below.
6.6.2.2.2. Coordination while using HTML form¶
CSRF token value can also be linked using HTML form without using Linkage with Spring MVC. If you want to send a request using HTML form, output the CSRF token value as a hidden field in the HTML form and coordinate as a request parameter.
- Implementation example of JSP
<%@ taglib prefix="sec" uri="http://www.springframework.org/security/tags" %>
<form action="<c:url value="/login" />" method="post">
<!-- omitted -->
<sec:csrfInput /> <!-- (1) -->
<!-- omitted -->
</form>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify
<sec:csrfInput> element in <form> element of HTML. |
The hidden fields are output as shown below if <sec:csrfInput> element provided by Spring Security is specified.
CSRF token value is linked as a request parameter by displaying the hidden fields in the HTML form.
By default, the name of the request parameter to link CSRF token value is _csrf .
- Output example of HTML
<form action="/login" method="post">
<!-- omitted -->
<!-- CSRF token value hidden field -->
<input type="hidden"
name="_csrf"
value="63845086-6b57-4261-8440-97a3c6fa6b99" />
<!-- omitted -->
</form>
Warning
Points to be noted while using GET method
When GET is used as the HTTP method, <sec: csrfInput>element should not be specified.
If <sec:csrfInput> element is specified, there is a high risk of CSRF token value being stolen since CSRF token value is included in the URL.
6.6.2.2.3. Coordination while using Ajax¶
If you want to send a request using Ajax, output the CSRF token information as HTML meta tag, and link by setting the token value fetched from meta tag in the request header at the time of Ajax communication.
First, output the CSRF token information in HTML meta tag by using the JSP tag library provided by Spring Security.
- Implementation example of JSP
<%@ taglib prefix="sec" uri="http://www.springframework.org/security/tags" %>
<head>
<!-- omitted -->
<sec:csrfMetaTags /> <!-- (1) -->
<!-- omitted -->
</head>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify
<sec:csrfMetaTags> element in <head> element of HTML. |
If <sec:csrfMetaTags> element is specified, the meta tags are output as shown below.
By default, the name of the request header to link CSRF token value is X-CSRF-TOKEN.
- Output example of HTML
<head>
<!-- omitted -->
<meta name="_csrf_parameter" content="_csrf" />
<meta name="_csrf_header" content="X-CSRF-TOKEN" /> <!-- Header name -->
<meta name="_csrf"
content="63845086-6b57-4261-8440-97a3c6fa6b99" /> <!-- Token value -->
<!-- omitted -->
</head>
Then, fetch the CSRF token information from meta tag using JavaScript and set the CSRF token value in the request header at the time of Ajax communication. (Implementation example using jQuery is described here)
- Implementation example of JavaScript
$(function () {
var headerName = $("meta[name='_csrf_header']").attr("content"); // (1)
var tokenValue = $("meta[name='_csrf']").attr("content"); // (2)
$(document).ajaxSend(function(e, xhr, options) {
xhr.setRequestHeader(headerName, tokenValue); // (3)
});
});
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Fetch the request header name for coordinating with the CSRF token value.
|
(2)
|
Fetch CSRF token value.
|
(3)
|
Set CSRF token value in request header.
|
6.6.2.3. Controlling transition destination in case of token check error¶
In order to control the transition destination in case of token check error, handle AccessDeniedException which is an exception that occurs in CSRF token check error and specify the transition destination corresponding to that exception.
Exception that occurs at the time of CSRF token check error is as follows.
| Class name | Description |
|---|---|
InvalidCsrfTokenException |
Exception class to be used when the token value sent by the client does not match with the token value stored at server side (Mainly invalid request).
|
MissingCsrfTokenException |
Exception class to be used when the token value is not stored at server side (Mainly session timeout).
|
It is possible to set the transition destination for each exception by handling the exception mentioned above using DelegatingAccessDeniedHandler class and assigning implementation class of AccessDeniedHandler interface respectively.
Define a Bean as shown below if you want to transit to an exclusive error page (JSP) at the time of CSRF token check error. (The following definition example is an excerpt from a blank project)
- Definition example of spring-security.xml
<sec:http>
<!-- omitted -->
<sec:access-denied-handler ref="accessDeniedHandler"/> <!-- (1) -->
<!-- omitted -->
</sec:http>
<bean id="accessDeniedHandler"
class="org.springframework.security.web.access.DelegatingAccessDeniedHandler"> <!-- (2) -->
<constructor-arg index="0"> <!-- (3) -->
<map>
<!-- (4) -->
<entry
key="org.springframework.security.web.csrf.InvalidCsrfTokenException">
<bean
class="org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandlerImpl">
<property name="errorPage"
value="/WEB-INF/views/common/error/invalidCsrfTokenError.jsp" />
</bean>
</entry>
<!-- (5) -->
<entry
key="org.springframework.security.web.csrf.MissingCsrfTokenException">
<bean
class="org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandlerImpl">
<property name="errorPage"
value="/WEB-INF/views/common/error/missingCsrfTokenError.jsp" />
</bean>
</entry>
</map>
</constructor-arg>
<!-- (6) -->
<constructor-arg index="1">
<bean
class="org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandlerImpl">
<property name="errorPage"
value="/WEB-INF/views/common/error/accessDeniedError.jsp" />
</bean>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify the Bean name for
AccessDeniedHandler to control each Exception in ref attribute of <sec:access-denied-handler> tag.If all the transition destinations in case of an error are on the same screen, the transition destination should be specified in
error-page attribute.Refer to Transition destination at the time of authorization error when the exceptions are not handled by
<sec:access-denied-handler>. |
(2)
|
Using
DelegatingAccessDeniedHandler , define the exception that occurred (AccessDeniedException subclass) and the exception handler (AccessDeniedHandler Implementation class). |
(3)
|
Using the first argument of constructor, define the exception for which transition destination is to be specified separately (
AccessDeniedException subclass) and the corresponding exception handler (AccessDeniedHandler implementation class) in Map format. |
(4)
|
Specify sub class of
AccessDeniedException in key.Specify
org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandlerImpl which is an implementation class of AccessDeniedHandler , as the value.Specify the view to be displayed in
value by specifying errorPage in name of property.Refer to Controlling transition destination in case of token check error for the Exception to be mapped.
|
(5)
|
Define if an Exception different from Exception of (4) is to be controlled.
In this example, a different transition destination has been set in
InvalidCsrfTokenException, MissingCsrfTokenException respectively. |
(6)
|
Specify the exception handler (
AccessDeniedHandler implementation class) at the time of default exception (subclass of AccessDeniedException not specified in (4)(5)) and the transition destination using second argument of constructor. |
Note
Detection of request with an invalid session
When “Detection of request with invalid session” process of session management function is enabled, implementation class of AccessDeniedHandler interface to be linked with “Detection of request with invalid session” process is used for MissingCsrfTokenException.
Therefore, if MissingCsrfTokenException is thrown, redirect to path (invalid-session-url) specified while enabling “Detection of request with invalid session” process.
Note
When status code other than 403 is to be returned
If status code other than 403 is to be returned when the CSRF token in request does not match, it is necessary to create an independent AccessDeniedHandler which implements org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandler interface.