6.1. Spring Security Overview¶
Caution
This version is already obsolete. Please check the latest guideline.
Table of Contents
Spring Security is a framework which is used while implementing the security countermeasure function in the application. Spring Security can also be used in stand-alone application, but generally it is used while implementing the security countermeasures for Web application deployed in servlet container. This chapter describes only those functions provided by Spring Security which are considered to be frequently used in general Web application.
Tip
Functions not introduced in the guideline
Spring Security also provides many functions not introduced in this guideline. Refer Spring Security Reference to know all functions provided by Spring Security.
Note
Spring Security version
This guideline assumes the use of Spring Security 4.0 or higher version. Various changes have been applied for upgrading version of Spring Security to 4.0 and the samples described later also have used Spring Security 4.
Refer Migrating from Spring Security 3.x to 4.x (XML Configuration) for the changes.
6.1.1. Spring Security functions¶
6.1.1.1. Basic functions of security countermeasures¶
Spring Security provides the following functions as the basic functions of security countermeasures.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Authentication function | A function that checks whether the application user is valid. |
| Authorization function | A function that controls access to the resources and processes provided by the application. |
6.1.1.2. Function to strengthen security countermeasures¶
Spring Security provides several functions besides the basic functions of authentication and authorization to enhance Web application security.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Session management function | A function that protects the user from session hijacking attack and session fixation attack, A function to control session lifecycle (generate, discard, time out). |
| CSRF countermeasure function | A function to protect the user from Cross site request forgeries (CSRF) attack. |
| Security header output function | A function to link with security countermeasure function of Web browser and protect the user from the attack where the browser function is misused. |
6.1.2. Spring Security architecture¶
Overview of Spring Security architecture and the role of key components those configure Spring Security are described before explaining each function in detail.
Note
The developers need not be directly aware of the contents described over here while using the default operation provided by Spring Security as it is or while using the mechanism to support the configuration of Spring Security. Therefore, this section can be skipped while reading when the user first wants to know how to use each function.
However, since the contents described here are required while customizing the default operation of Spring Security, it is recommended that the application architect should go through it once.
6.1.2.1. Spring Security module¶
First, the module provided by Spring Security used as a framework stack is introduced.
6.1.2.1.1. Set of framework stack modules¶
Framework stack module is as follows. This guideline also describes the method to implement security countermeasures using these modules.
| Module name | Description |
|---|---|
spring-security-core |
A core component required to implement authentication and authorization functions has been stored. A component included in this module can also be used in the applications executed in stand-alone environment. |
spring-security-web |
A component required to implement security countermeasures of Web application has been stored. A component included in this module performs the process that depends on Web layer (like servlet API). |
spring-security-config |
A component (like the class that supports configuration or the class that analyses XML namespace) to support the setup of components provided by each module has been stored. If this module is used, bean for Spring Security can be defined easily. |
spring-security-taglibs |
A JSP tag library to access the authentication information and authorization function has been stored. |
spring-security-acl |
A component required for authorized control of domain objects like Entity using Access Control List (ACL) has been stored. Since this module is included in the framework stack for the sake of dependency, the method of using this module is not described in this guideline. |
6.1.2.1.2. Set of modules used according to the requirements¶
The following modules those are not included in the framework stack, are also provided to support the authentication methods used in general. Use of these modules also needs to be reviewed as per the security requirements.
| Module name | Description |
|---|---|
spring-security-remoting |
A component required to access DNS via JNDI, to access Website for which Basic authentication is necessary and to access the methods via RMI wherein security countermeasures are implemented using Spring Security has been stored. |
spring-security-aspects |
A component required to use AspectJ function while applying the authorization function for the Java methods has been stored. This module is not required when Spring AOP is used as ACF. |
spring-security-messaging[5] |
A component to add security countermeasures for Web Socket function of Spring has been stored. |
spring-security-data[5] |
A component to enable accessing authentication information from Spring Data function has been stored. |
spring-security-ldap |
A component required to implement authentication using Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) has been stored. |
spring-security-openid |
A component required to implement authentication using OpenID[1] has been stored. |
spring-security-cas |
A component required to link with Central Authentication Service (CAS)[2] has been stored. |
spring-security-crypto |
A component for encryption, key generation and password encoding using hash algorithm has been stored.
Class contained in this module is also included in spring-security-core in framework stack module. |
6.1.2.1.3. Test module¶
A module to support the test has been added from Spring Security 4.0.
| Module name | Description |
|---|---|
spring-security-test[5] |
A component to support the testing of class that depends on Spring Security has been stored.
If this module is used, the authentication information required at the time of JUnit testing can be setup easily.
Note that, a component which is used by linking with component (MockMvc) for testing of Spring MVC is also included. |
6.1.2.2. Framework processing¶
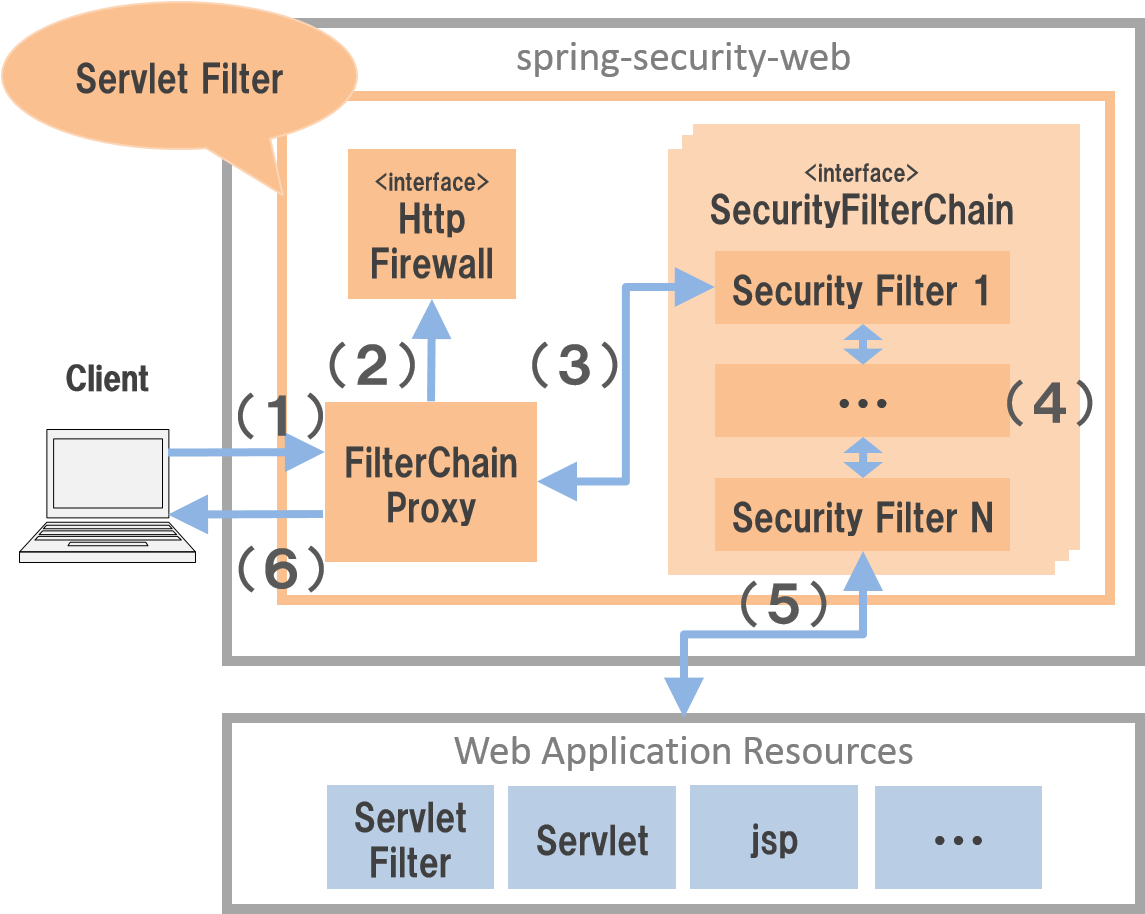
Spring Security has adopted the architecture that implements security countermeasures for Web application using the servlet filter mechanism and executes the processes in the following flow.
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
| (1) | Client sends a request to the Web application. |
| (2) | FilterChainProxy class (servlet filter) of Spring Security receives the request,
calls method of HttpFirewall interface and incorporates the firewall function for HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse. |
| (3) | FilterChainProxy class assigns process to Security Filter (servlet filter) class for security countermeasures provided by Spring Security. |
| (4) | Security Filter consists of multiple classes and subsequent servlet filter is called if servlet filter process is successfully completed. |
| (5) | When the last Security Filter process is successfully completed, subsequent process (like servlet filter or servlet) is called and the resources in the Web application are accessed. |
| (6) | FilterChainProxy class sends response of resources returned by the Web application to the client. |
The key component that configures the framework process for the Web application is as follows. For details, refer Spring Security Reference -The Security Filter Chain-.
6.1.2.2.1. FilterChainProxy¶
FilterChainProxy class is a servlet filter class that is an entry point of the framework process for the Web application.
This class controls the entire flow of the framework process and assigns specific security countermeasure process to Security Filter.
6.1.2.2.2. HttpFirewall¶
HttpFirewall interface incorporates the firewall function for HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse.
By default, DefaultHttpFirewall class is used and the checks for Directory traversal attack and HTTP response splitting attack are implemented.
6.1.2.2.3. SecurityFilterChain¶
SecurityFilterChain interface manages Security Filter list to be applied to the request received by FilterChainProxy.
By default, DefaultSecurityFilterChain class is used and the Security Filter list to be applied is managed for each pattern of request URL.
For example, security countermeasures for the details those vary according to the URL can be applied if the bean is defined as follows.
- Definition example of xxx-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/spring-security.xml
<sec:http pattern="/api/**">
<!-- ... -->
</sec:http>
<sec:http pattern="/ui/**">
<!-- ... -->
</sec:http>
6.1.2.2.4. Security Filter¶
Security Filter class is a servlet filter class that provides a process required to implement framework function and security countermeasure function.
Spring Security is a mechanism to implement the security countermeasures for the Web application by linking multiple Security Filters. Here, core class required to implement authentication and authorization functions is introduced. For details, refer Spring Security Reference -Core Security Filters-.
| Class name | Description |
|---|---|
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter |
A class that provides a process to share the authentication information across the requests.
Authentication information is shared across the requests by storing it in HttpSession, in the default implementation. |
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter |
A class that performs the authentication process using user name and password specified in the request parameter. It is used at the time of form authentication. |
LogoutFilter |
A class that performs logout process. |
FilterSecurityInterceptor |
A class to execute authorization process for HTTP request (HttpServletRequest). |
ExceptionTranslationFilter |
A class that handles the exception occurred in FilterSecurityInterceptor and controls response returned to the client.
It returns response that prompts authentication in case of access by unauthenticated user and
response that notifies authorization error in case of access by authenticated user in the default implementation. |
6.1.3. Spring Security setup¶
A setup method to apply Spring Security to the Web application is explained.
Here, the simplest method of setup that applies Spring Security to the Web application and displays the default login screen provided by Spring Security is explained. Customization method and extension method required in real application development are described sequentially in the following sections.
Note
When the development project is created from Blank project , the setting described here is already configured. For how to create a development project, refer ‘Create Web application development project’ .
6.1.3.1. Applying dependent library¶
First, the common library that uses Spring Security as dependency is applied. Refer Building blocks of Common Library for the relation between Spring Security and common library.
This guideline assumes that the development project is created using Maven.
- Setup example of xxx-domain/pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.terasoluna.gfw</groupId>
<artifactId>terasoluna-gfw-security-core</artifactId> <!-- (1) -->
</dependency>
- Setup example of xxx-web/pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.terasoluna.gfw</groupId>
<artifactId>terasoluna-gfw-security-web</artifactId> <!-- (2) -->
</dependency>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
| (1) | Add terasoluna-gfw-security-core to dependency when Spring Security function is used in domain layer project. |
| (2) | Add terasoluna-gfw-security-web to dependency when Spring Security function is used in application layer project. |
Note
This guideline assumes that the library version is managed using Spring IO Platform, therefore <version> element is omitted.
6.1.3.2. Creating a bean definition file¶
XML file is created as below to define a bean for the component of Spring Security. (extracted from Blank project)
- Definition example of xxx-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/spring-security.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:sec="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security.xsd
"> <!-- (1) -->
<sec:http> <!-- (2) -->
<sec:form-login /> <!-- (3) -->
<sec:logout /> <!-- (4) -->
<sec:access-denied-handler ref="accessDeniedHandler"/> <!-- (5) -->
<sec:custom-filter ref="userIdMDCPutFilter" after="ANONYMOUS_FILTER"/> <!-- (6) -->
<sec:session-management /> <!-- (7) -->
</sec:http>
<sec:authentication-manager /> <!-- (8) -->
<bean id="accessDeniedHandler" class="org.springframework.security.web.access.DelegatingAccessDeniedHandler"> <!-- (9) -->
<!-- omitted -->
</bean>
<bean id="userIdMDCPutFilter" class="org.terasoluna.gfw.security.web.logging.UserIdMDCPutFilter"> <!-- (10) -->
<!-- omitted -->
</bean>
</beans>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
| (1) | Enable XML namespace provided by Spring Security.
A name sec is assigned in the above example.
A bean for component of Spring Security can be defined easily if XML namespace is used. |
| (2) | Define <sec:http> tag.
A bean for the component required to use Spring Security is automatically defined if <sec:http> tag is defined. |
| (3) | Define <sec:form-login> tag and perform settings related to login where form authentication is used.
Refer Form authentication for details |
| (4) | Define <sec:logout> tag and perform settings related to logout.
Refer Logout for details. |
| (5) | Define <sec:access-denied-handler> tag and define settings to control at the time of access error.
Refer Applying AccessDeniedHandler and Transition destination at the time of authorization error for details. |
| (6) | Define a filter for common library to store the user information to be output in a log, in MDC. |
| (7) | Define <sec:session-management> tag and perform settings related to session management.
Refer Session Management for details |
| (8) | Define <sec:authentication-manager> tag and define a bean for component for authentication function.
Error occurs at the time of starting a server if this tag is not defined. |
| (9) | Define a bean for the component that handles access error. |
| (10) | Define a bean for the component of common library to store the user information to be output in a log in MDC. |
Note
Access to static resources
When the static resources like CSS are used in JSF, the access rights must be assigned to the folder where they are stored. Refer Settings not to apply security countermeasures for details.
Define to generate DI container of Spring using a bean definition file thus created.
- Setup example of xxx-web/src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml
<!-- (1) -->
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- (2) -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
classpath*:META-INF/spring/applicationContext.xml
classpath*:META-INF/spring/spring-security.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
| (1) | Specify ContextLoaderListener class as the listener class of servlet container. |
| (2) | Add a bean definition file for Spring Security to contextClass parameter of servlet container besides applicationContext.xml. |
6.1.3.3. Settings for servlet filter¶
Finally, the servlet filter class (FilterChainProxy) provided by Spring Security is registered in servlet container.
- Setup example of xxx-web/src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml
<!-- (1) -->
<filter>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<filter-class>
org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy
</filter-class>
</filter>
<!-- (2) -->
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
| (1) | Register bean (FilterChainProxy) managed in DI container of Spring in the servlet container
using DelegatingFilterProxy provided by Spring Framework.
Specify the name (springSecurityFilterChain) of bean managed in DI container of Spring in the servlet filter name. |
| (2) | Specify the pattern of URL where Spring Security is to be applied. Apply Spring Security to all requests in the above example. |
6.1.3.4. Settings not to apply security countermeasures¶
The resource path (like the path to access css file or image file) for which the security countermeasures are not required,
can be controlled using <sec:http> tag so that the security function (Security Filter) of Spring Security is not applied.
- Definition example of xxx-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/spring-security.xml
<sec:http pattern="/resources/**" security="none"/> <!-- (1) (2) -->
<sec:http>
<!-- omitted -->
</sec:http>
| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1)
|
Specify the pattern of the path where the security function is not applied in
pattern attribute. |
(2)
|
Specify
none in security attribute.The security function (Security Filter) of Spring Security is not applied if
none is specified. |