6.9. Encryption¶
Caution
This version is already obsolete. Please check the latest guideline.
Index
6.9.1. Overview¶
Encryption is required for confidential information like personal data, passwords etc in the following cases.
- Sending/receiving confidential information through a network medium like Internet
- Storing confidential information in external resources like database, file etc
The guideline explains following processes.
- Encryption and decryption by common key encryption methods which use class offered by Spring Security
- Generation of pseudo-random numbers which use class offered by Spring Security
- Encryption and decryption by public key encryption method which use JCA (Java Cryptography Architecture)
- Encryption and decryption by hybrid encryption method which use JCA
For details of Encryption function of Spring Security, refer Spring Security Reference -Spring Security Crypto Module-.
6.9.1.1. Encryption method¶
Encryption method is explained below.
6.9.1.1.1. Common key encryption method¶
6.9.1.1.2. Public key encryption method¶
6.9.1.1.3. Hybrid encryption method¶
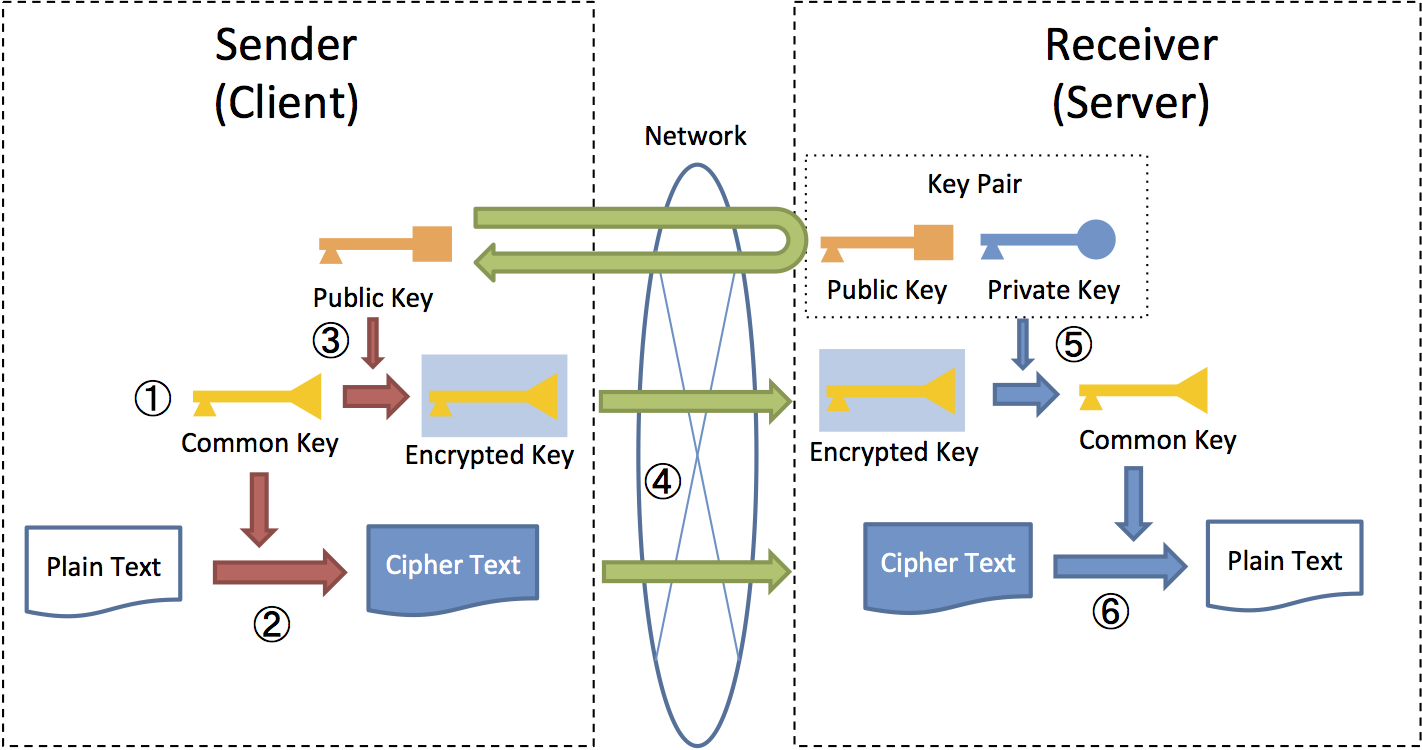
For example, in HTTPS communication, common key generated at the client side is sent after encrypting it with public key on the server side and common key is decrypted at the server by using secret key paired with public key. The subsequent communication is done by a common key encryption method which uses a shared common key.
This method consists of
- Confidential information which is likely to be large in size is encrypted by a common key encryption method wherein the processing cost is less
- A common key with smaller size wherein safe distribution is required is encrypted by using a public key encryption method with high security strength
Since common key used while decrypting confidential information is protected by secret key, security strength of public key encryption method is retained while achieving a high-speed encryption and decryption process than public key encryption method.
Process flow of hybrid encryption method from encryption to decryption is shown in the following figure..
- Sender generates a common key for encryption of plain text.
- Plain text is encrypted by common key generated by sender.
- Sender uses public key of receiving side to encrypt common key.
- Sender sends encrypted text along with encrypted common key.
- Receiving side decrypts encrypted common key by using secret key on receiving side.
- Receiving side decrypts encrypted text by decrypted common key
6.9.1.2. Encryption algorithm¶
Encryption algorithm is explained.
6.9.1.2.1. DES / 3DES¶
6.9.1.2.2. AES¶
Note
AES with GCM
GCM (Galois/Counter Mode) is an encryption mode generally accepted for feasible parallel processing and excellent processing efficiency as compared to CEC and can be used in AES.
6.9.1.2.3. RSA¶
6.9.1.2.4. DSA / ECDSA¶
6.9.1.3. Pseudo-random number (Generator)¶
6.9.1.4. javax.crypto.Cipher class¶
Cipher class offers encryption and decryption functions, and specifies a combination of encryption algorithms like AES or RSA, encryption modes like ECB or CBC and padding methods like PKCS1."<Encryption algorithm>/<Encryption mode>/<Padding method>" or "<Encryption algorithm>" format. For example, "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding" or "RSA" are used.
For details, refer to JavaDoc of Cipher class.6.9.1.5. Encryption function in Spring Security¶
6.9.1.5.1. Components for encryption and decryption¶
Spring Security offers following interfaces as a function for encryption and decryption using common key encryption method.
org.springframework.security.crypto.encrypt.TextEncryptor(For text)org.springframework.security.crypto.encrypt.BytesEncryptor(For byte array)
Also, following classes are offered as implementation classes for these interfaces and Cipher class is used internally.
org.springframework.security.crypto.encrypt.HexEncodingTextEncryptor(For text)org.springframework.security.crypto.encrypt.AesBytesEncryptor(For byte array)
6.9.1.5.2. Components to generate random numbers¶
Spring Security offers following interfaces as functions to generate random numbers (key).
org.springframework.security.crypto.keygen.StringKeyGenerator(for text)org.springframework.security.crypto.keygen.BytesKeyGenerator(for byte array)
Also, following classes are offered as implementation classes for these interfaces.
org.springframework.security.crypto.keygen.HexEncodingStringKeyGenerator(for text)org.springframework.security.crypto.keygen.SecureRandomBytesKeyGenerator(for byte array. Generate a different key length bygenerateKeymethod and return)org.springframework.security.crypto.keygen.SharedKeyGenerator(for byte array. Return same key length set by constructor, usinggenerateKeymethod)
Note
Spring Security RSA
spring-security-rsa offers API for public key encryption method and hybrid encryption method which use RSA as an encryption algorithm. spring-security-rsa is currently not managed as official repository of Spring <https://github.com/spring-projects>_. Later, how to use the repository will be explained in the guideline after moving it under official repository of Spring.
spring-security-rsa offers 2 classes given below.
org.springframework.security.crypto.encrypt.RsaRawEncryptorA class that offers encryption and decryption functions which use public key encryption method.
org.springframework.security.crypto.encrypt.RsaSecretEncryptorA class that offers encryption and decryption functions which use hybrid encryption method.
6.9.2. How to use¶
An unlimited strength JCE jurisdiction policy file must be applied for handling key length 256 bits of AES in some Java products like Oracle.
Note
JCE jurisdiction policy file
Default encryption algorithm strength is restricted in some Java products due to relation with import regulations. If a more powerful algorithm is to be used, an unlimited strength JCE jurisdiction policy file must be obtained and installed in JDK/JRE. For details, refer Java Cryptography Architecture Oracle Providers Documentation.
Download destination for JCE jurisdiction policy file
6.9.2.1. Common key encryption method¶
6.9.2.1.1. Encryption of character string¶
Encrypt text (string).
public static String encryptText( String secret, String salt, String plainText) { TextEncryptor encryptor = Encryptors.text(secret, salt); // (1) return encryptor.encrypt(plainText); // (2) }
Sr. No. Description (1)CallEncryptors#textmethod by specifying common key and salt, and generate instance ofTextEncryptorclass.Since initialization vector of generated instance is random, a varied result is returned at the time of encryption. It should be noted that CEC is used as an encryption mode.Common key and salt specified during encryption are also used at the time of decryption.(2)Encrypt plain text by usingencryptmethod.Note
Regarding encryption results
Return value of
encryptmethod (encryption results) return a different value for each execution, however, if key and salt are identical, decryption process results will be similar as well (can be correctly decrypted).
Fetch identical encryption results.
This method is used in the processes such as searching the database etc.using encrypted results. However, whether to use the method must be reviewed considering possible reduction in the security strength.
public static void encryptTextResult( String secret, String salt, String plainText) { TextEncryptor encryptor = Encryptors.queryableText(secret, salt); // (1) System.out.println(encryptor.encrypt(plainText)); // (2) System.out.println(encryptor.encrypt(plainText)); // }
Sr.No. Description (1)When identical value must be fetched as encryption results, generate an instance ofTextEncryptorclass by usingEncryptors#queryableTextmethod.(2)The instance generated byEncryptors#queryableTextmethod returns identical values as the encryption results forencryptmethod.
Encrypt text (string) by using AES which uses GCM.
AES using GCM can be used in Spring Security4.0.2 and subsequent versions. Processing efficiency is superior to CEC as explained in AES.
public static String encryptTextByAesWithGcm(String secret, String salt, String plainText) { TextEncryptor aesTextEncryptor = Encryptors.delux(secret, salt); // (1) return aesTextEncryptor.encrypt(plainText); // (2) }
Sr. No. Description (1)CallEncryptors#deluxmethod by specifying common key and salt, and generate an instance ofTextEncryptorclass.Common key and salt specified during encryption are also used at the time of decryption.(2)Encrypt plain text by usingencryptmethod.Note
Java support for AES which uses GCM
AES using GCM can be used in Java SE8 and subsequent versions. For details, refer JDK 8 security enhancement.
6.9.2.1.2. Decryption of string¶
Decrypt encryption text of text (string).
public static String decryptText(String secret, String salt, String cipherText) { TextEncryptor decryptor = Encryptors.text(secret, salt); // (1) return decryptor.decrypt(cipherText); // (2) }
Sr. No. Description (1)CallEncryptors#textmethod by specifying common key and salt, and generate an instance ofTextEncryptorclass.Specify values used at the time of encryption as common key and salt.(2)Decrypt encrypted text by usingdecryptmethod.
Decrypt encrypted text of text (string) by using AES which uses GCM.
public static String decryptTextByAesWithGcm(String secret, String salt, String cipherText) { TextEncryptor aesTextEncryptor = Encryptors.delux(secret, salt); // (1) return aesTextEncryptor.decrypt(cipherText); // (2) }
Sr. No. Description (1)CallEncryptors#deluxmethod by specifying common key and salt, and generate an instance ofTextEncryptorclass.Specify values at the time of encryption as common key and salt.(2)Decrypt encrypted text by usingdecryptmethod.
6.9.2.1.3. Encryption of byte array¶
Encrypt byte array.
public static byte[] encryptBytes(String secret, String salt, byte[] plainBytes) { BytesEncryptor encryptor = Encryptors.standard(secret, salt); // (1) return encryptor.encrypt(plainBytes); // (2) }
Sr. No. Description (1)CallEncryptors#standardmethod by specifying common key and salt, and generate an instance ofBytesEncryptorclass.Common key and salt specified during encryption are also used at the time of decryption.(2)Encrypt plain text of byte array by usingencryptmethod.
Encrypt byte array by using AES which uses GCM.
public static byte[] encryptBytesByAesWithGcm(String secret, String salt, byte[] plainBytes) { BytesEncryptor aesBytesEncryptor = Encryptors.stronger(secret, salt); // (1) return aesBytesEncryptor.encrypt(plainBytes); // (2) }
Sr. No. Description (1)CallEncryptors#strongermethod by specifying common key and salt, and generate an instance ofBytesEncryptorclass.Common key and salt specified during encryption are also used at the time of decryption.(2)Encrypt plain text of byte array by usingencryptmethod.
6.9.2.1.4. Decryption of byte array¶
Decrypt encrypted text of byte array.
public static byte[] decryptBytes(String secret, String salt, byte[] cipherBytes) { BytesEncryptor decryptor = Encryptors.standard(secret, salt); // (1) return decryptor.decrypt(cipherBytes); // (2) }
Sr. No. Description Encryptors#standardmethod by specifying common key and salt, and generate an instance ofBytesEncryptorclass.Specify values used at the time of encryption as common key and salt.decryptmethod.
Decrypt byte array using AES which use GCM.
public static byte[] decryptBytesByAesWithGcm(String secret, String salt, byte[] cipherBytes) { BytesEncryptor aesBytesEncryptor = Encryptors.stronger(secret, salt); // (1) return aesBytesEncryptor.decrypt(cipherBytes); // (2) }
Sr. No. Description (1)CallEncryptors#strongermethod by specifying common key and salt, and generate an instance ofBytesEncryptorclass.Specify values used at the time of encryption as common key and salt.(2)Decrypt encrypted text of byte array by usingdecryptmethod.
6.9.2.2. Public key encryption method¶
6.9.2.2.1. Preliminary preparation (Generation of key pairs using JCA)¶
Generate key pairs (a combination of public key / secret key) using JCA, perform encryption and decryption process by using public key and secret key respectively.
public void generateKeysByJCA() { try { KeyPairGenerator generator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA"); // (1) generator.initialize(2048); // (2) KeyPair keyPair = generator.generateKeyPair(); // (3) PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic(); PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate(); byte[] cipherBytes = encryptByPublicKey("Hello World!", publicKey); // (4) String plainText = decryptByPrivateKey(cipherBytes, privateKey); // (5) System.out.println(plainText); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9002", "No Such setting error.", e); } }
Sr. No. Description (1)Specify RSA algorithm and generate an instance ofKeyPairGeneratorclass.(2)Specify 2048 bits as a key length.(3)Generate key pairs.(4)Use public key and perform encryption process. Processing details will be described later.(5)Use secret key and perform decryption process. Processing details will be described later.Note
When the encrypted data is to be handled as string
When encrypted data is to be handled as string like in external system linkage etc, Base64 encoding can be listed as one of the measures.
java.util.Base64of Java standard is used in case of subsequent versions of Java SE8. In the earlier versions,org.springframework.security.crypto.codec.Base64of Spring Security is used.A method used for Base64 encoding and decoding is explained using
java.util.Base64of Java standard.- Base64 encoding
// omitted byte[] cipherBytes = encryptByPublicKey("Hello World!", publicKey); // Encryption process String cipherString = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(cipherBytes); // Convert encrypted text of byte array to string // omitted
- Base64 decoding
// omitted byte[] cipherBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(cipherString); // Convert encrypted text of string to byte array String plainText = decryptByPrivateKey(cipherBytes, privateKey); // Decryption process // omitted
6.9.2.2.2. Encryption¶
Use public key and encrypt character string.
public byte[] encryptByPublicKey(String plainText, PublicKey publicKey) { try { Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding"); // (1) cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey); // (2) return cipher.doFinal(plainText.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); // } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException | NoSuchPaddingException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9002", "No Such setting error.", e); } catch (InvalidKeyException | IllegalBlockSizeException | BadPaddingException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9003", "Invalid setting error.", e); } }
Sr.No. Description (1)Specify encryption algorithm, encryption mode and padding method, and generate an instance ofCipherclass.(2)Execute encryption process.
6.9.2.2.3. Decryption¶
Use secret key and decrypt byte array.
public String decryptByPrivateKey(byte[] cipherBytes, PrivateKey privateKey) { try { Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding"); // (1) cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey); // (2) byte[] plainBytes = cipher.doFinal(cipherBytes); // return new String(plainBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException | NoSuchPaddingException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9002", "No Such setting error.", e); } catch (InvalidKeyException | IllegalBlockSizeException | BadPaddingException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9003", "Invalid setting error.", e); } }
Sr. No. Description (1)Specify encryption algorithm, encryption mode and padding method, and generate an instance ofCipherclass.(2)Execute decryption process.
6.9.2.2.4. OpenSSL¶
Note
OpenSSL
The software must be installed for creating key pairs by OpenSSL. It can be downloaded from the following site.
Download destination for OpenSSL
Create key pairs by OpenSSL as a preliminary preparation.
$ openssl genrsa -out private.pem 2048 # (1) $ openssl pkcs8 -topk8 -nocrypt -in private.pem -out private.pk8 -outform DER # (2) $ openssl rsa -pubout -in private.pem -out public.der -outform DER # (3)
Sr. No. Description (1)Generate secret key of 2048 bits (DER format) by OpenSSL..(2)Convert secret key to PKCS#8 format for reading it from Java application.(3)Generate public key (DER format) from secret key.
Read public key created by OpenSSL in the application and perform encryption process by using public key that has been read.
public void useOpenSSLDecryption() { try { KeySpec publicKeySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec( Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("public.der"))); // (1) KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA"); PublicKey publicKey = keyFactory.generatePublic(publicKeySpec); // (2) byte[] cipherBytes = encryptByPublicKey("Hello World!", publicKey); // (3) Files.write(Paths.get("encryptedByJCA.txt"), cipherBytes); System.out.println("Please execute the following command:"); System.out .println("openssl rsautl -decrypt -inkey hoge.pem -in encryptedByJCA.txt"); } catch (IOException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9001", "input/output error.", e); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9002", "No Such setting error.", e); } catch (InvalidKeySpecException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9003", "Invalid setting error.", e); } }
Sr.No. Description (1)Read binary data from public key file.(2)Generate an instance ofPublicKeyclass from binary data.(3)Perform encryption process by using public key.
Check that details encrypted by JCA can be decrypted by OpenSSL.
$ openssl rsautl -decrypt -inkey private.pem -in encryptedByJCA.txt # (1)
Sr. No. Description (1)Decrypt by OpenSSL by using a secret key.
Perform encryption process by using OpenSSL commands.
$ echo Hello | openssl rsautl -encrypt -keyform DER -pubin -inkey public.der -out encryptedByOpenSSL.txt # (1)
Sr. No. Description (1)Encrypt by OpenSSL by using a public key.
Read secret key created by OpenSSL in the application and perform decryption process by using a secret key that has been read.
public void useOpenSSLEncryption() { try { KeySpec privateKeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec( Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("private.pk8"))); // (1) KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA"); PrivateKey privateKey = keyFactory.generatePrivate(privateKeySpec); // (2) String plainText = decryptByPrivateKey( Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("encryptedByOpenSSL.txt")), privateKey); // (3) System.out.println(plainText); } catch (IOException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9001", "input/output error.", e); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9002", "No Such setting error.", e); } catch (InvalidKeySpecException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9003", "Invalid setting error.", e); } }
Sr. No. Description (1)Read binary data from secret key file of PKCS #8 format and generate an instance ofPKCS8EncodedKeySpecclass.(2)Generate an instance ofPrivateKeyclass fromKeyFactoryclass.(3)Perform decryption process by using a secret key.
6.9.2.3. Hybrid encryption method¶
6.9.2.3.1. Encryption¶
public byte[] encrypt(byte[] plainBytes, PublicKey publicKey, String salt) { byte[] random = KeyGenerators.secureRandom(32).generateKey(); // (1) BytesEncryptor aes = Encryptors.standard( new String(Hex.encode(random)), salt); // (2) try (ByteArrayOutputStream result = new ByteArrayOutputStream()) { final Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA"); // (3) cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey); // (4) byte[] secret = cipher.doFinal(random); // (5) byte[] data = new byte[2]; // (6) data[0] = (byte) ((secret.length >> 8) & 0xFF); // data[1] = (byte) (secret.length & 0xFF); // result.write(data); // result.write(secret); // (7) result.write(aes.encrypt(plainBytes)); // (8) return result.toByteArray(); // (9) } catch (IOException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9001", "input/output error.", e); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException | NoSuchPaddingException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9002", "No Such setting error.", e); } catch (InvalidKeyException | IllegalBlockSizeException | BadPaddingException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9003", "Invalid setting error.", e); } }
Sr. No. Description KeyGenerators#secureRandommethod by specifyinh 32 bytes as a key length and generate an instance ofBytesKeyGeneratorclass.CallBytesKeyGenerator#generateKeymethod and generate a common key.For details, refer to Random number generation.BytesEncryptorclass.Cipherclass.Cipherclass.
6.9.2.3.2. Decryption¶
public byte[] decrypt(byte[] cipherBytes, PrivateKey privateKey, String salt) { try (ByteArrayInputStream input = new ByteArrayInputStream(cipherBytes); ByteArrayOutputStream output = new ByteArrayOutputStream()) { byte[] b = new byte[2]; // (1) input.read(b); // int length = ((b[0] & 0xFF) << 8) | (b[1] & 0xFF); // byte[] random = new byte[length]; // (2) input.read(random); // final Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA"); // (3) cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey); // (4) String secret = new String(Hex.encode(cipher.doFinal(random))); // (5) byte[] buffer = new byte[cipherBytes.length - random.length - 2]; // (6) input.read(buffer); // BytesEncryptor aes = Encryptors.standard(secret, salt); // (7) output.write(aes.decrypt(buffer)); // (8) return output.toByteArray(); // (9) } catch (IOException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9001", "input/output error.", e); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException | NoSuchPaddingException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9002", "No Such setting error.", e); } catch (InvalidKeyException | IllegalBlockSizeException | BadPaddingException e) { throw new SystemException("e.xx.xx.9003", "Invalid setting error.", e); } }
Sr. No. Description Cipherclass.Cipherclass.BytesEncryptorclass.
6.9.2.4. Random number generation¶
6.9.2.4.1. Generation of string type pseudo-random number¶
public static void createStringKey() { StringKeyGenerator generator = KeyGenerators.string(); // (1) System.out.println(generator.generateKey()); // (2) System.out.println(generator.generateKey()); // }
Sr. No. Description StringKeyGeneratorclass.If key is generated by this generator, a different value is obtained for each instance.Key length cannot be specified, a key of length 8 byte is always generated.generateKeymethod.
6.9.2.4.2. Generation of byte array type pseudo-randon number¶
Generate a different key.
public static void createDifferentBytesKey() { BytesKeyGenerator generator = KeyGenerators.secureRandom(); // (1) System.out.println(Arrays.toString(generator.generateKey())); // (2) System.out.println(Arrays.toString(generator.generateKey())); // }
Sr. No. Description (1)CallKeyGenerators#secureRandommethod and generate an instance of key (pseudo-random number) generatorBytesKeyGeneratorclass.If key is generated by this generator, a different value is obtained for each instance.When key length is not specified, a key of length - 8 bytes is generated by default.(2)Generate a key by usinggenerateKeymethod.
Generate identical key.
public static void createSameBytesKey() { BytesKeyGenerator generator = KeyGenerators.shared(32); // (1) System.out.println(Arrays.toString(generator.generateKey())); // (2) System.out.println(Arrays.toString(generator.generateKey())); // }
Sr. No. Description (1)Specify 32 bytes as key length, callKeyGenerators#sharedmethod and generate an instance of key (pseudo-random number) generatorBytesKeyGeneratorclass.If key is generated by this generator, same value is obtained for each instance.Specifying key length is mandatory.(2)Generate key by usinggenerateKeymethod.