7.10. Spring Framework Comprehension Check¶
Caution
This version is already obsolete. Please check the latest guideline.
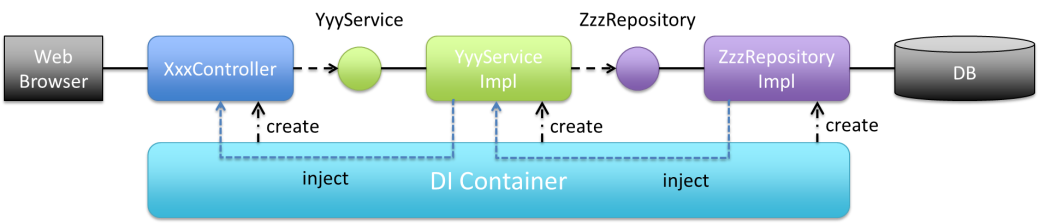
Fill (1)-(4) such that the Bean dependency relation is as follows. Skip import statement.
@Controller public class XxxController { (1) protected (2) yyyService; // omitted }
@Service @Transactional public class YyyServiceImpl implements YyyService { (1) protected (4) zzzRepository; // omitted }
Note
@Service,@Controllerareorg.springframework.stereotypepackage annotations and@Transactionalis the annotation oforg.springframework.transaction.annotation.Explain when to use
@Controller,@Service, and@Repositoryrespectively.Note
Each of them is
org.springframework.stereotypepackage annotation.Explain the difference between
@Resourceand@Inject.Note
@Resourceisjavax.annotationpackage annotation, and@Injectisjavax.injectpackage annotation.Explain the difference between singleton scope and prototype scope.
Fill (1)-(3) in the following Scope related description. However, either of “singleton” or “prototype” can be entered in (1) and (2), but same value cannot be entered for both. Skip the import statement.
@Component (3) public class XxxComponent { // omitted }
Note
@Componentisorg.springframework.stereotype.Component.Scope of bean with
@Componentis (1) by default. When changing scope to (2), it is better to add (3) (refer to above source code).In case of following Bean definition, what type of Bean is registered in DI container?
<bean id="foo" class="xxx.yyy.zzz.Foo" factory-method="create"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="aaa" /> <constructor-arg index="1" value="bbb" /> </bean>
Fill (1)-(3) of the following Bean definition such that contents in
com.example.domainpackage becomes target of component scan.<context:(1) (2)="(3)" />
Note
Bean definition file should include the definition of
xmlns:context=”http://www.springframework.org/schema/context”
Fill (1)-(2) in the following Properties file related description. Skip import statement.
It is possible to read the Bean definition file in
${key}format by removing the settings in properties file, if properties file path is set in thelocationsattribute of<context:property-placeholder>element. Specify as shown in (1) to read any properties file under META-INF/spring directory under the class path. Moreover, @(2) annotation should be added as shown in the following codes where the read properties value can also be injected in Bean.<context:property-placeholder locations="(1)" />
emails.min.count=1 emails.max.count=4
@Service @Transactional public class XxxServiceImpl implements XxxService { @(2)("${emails.min.count}") protected int emailsMinCount; @(2)("${emails.max.count}") protected int emailsMaxCount; // omitted }Note
Bean definition file should include the definitions of
xmlns:context=”http://www.springframework.org/schema/context”
Fill (1)-(5) in the following description for AOP Advice of Spring. The contents of (1)-(5) are all different.
Note
Advice (1) should be used when interrupting a process before calling a specific method, Advice (2) should be used when interrupting a process after calling a specific method. Advice (3) should be used when interrupting a process before and after calling a specific method. Advice (4) should be used only when the process is ended normally and Advice (5) should be used when there is an exception.
Insert (*) of following Bean definition for performing transaction management using
@Transactionalannotation.<tx:(*) />
Note
Bean definition file should include the definitions of
xmlns:tx=”http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx”