2.3. はじめてのSpring MVCアプリケーション¶
Spring MVCの、詳細な使い方の解説に入る前に、実際にSpring MVCに触れることで、 Spring MVCを用いたWebアプリケーションの開発に対するイメージをつかむ。
2.3.1. 検証環境¶
本節の説明では、次の環境で動作検証している。(他の環境で実施する際は、本書をベースに適宜読み替えて設定していくこと。)
| Product | Version |
|---|---|
| JDK | 1.7.0_55 |
| Spring Tool Suite (STS) | 3.5.0.RELEASE |
| VMware vFabric tc Server Developer Edition | 2.9 |
| Fire Fox | ESR 24 |
Note
インターネット接続するために、プロキシサーバーを介する必要がある場合、 以下の作業を行うため、STSのProxy設定と、 MavenのProxy設定が必要である。
2.3.2. 新規プロジェクト作成¶
インターネットから mvn archetype:generate を利用して、プロジェクトを作成する。
mvn org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-archetype-plugin:2.4:generate -B^
-DarchetypeCatalog=http://repo.terasoluna.org/nexus/content/repositories/terasoluna-gfw-releases^
-DarchetypeGroupId=org.terasoluna.gfw.blank^
-DarchetypeArtifactId=terasoluna-gfw-web-blank-archetype^
-DarchetypeVersion=1.0.6.RELEASE^
-DgroupId=com.example.helloworld^
-DartifactId=helloworld^
-Dversion=1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
ここではwindows上にプロジェクトの元を作成する。
C:\work>mvn org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-archetype-plugin:2.4:generate -B^
More? -DarchetypeCatalog=http://repo.terasoluna.org/nexus/content/repositories/terasoluna-gfw-releases^
More? -DarchetypeGroupId=org.terasoluna.gfw.blank^
More? -DarchetypeArtifactId=terasoluna-gfw-web-blank-archetype^
More? -DarchetypeVersion=1.0.6.RELEASE^
More? -DgroupId=com.example.helloworld^
More? -DartifactId=helloworld^
More? -Dversion=1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
[INFO] Scanning for projects...
[INFO]
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Building Maven Stub Project (No POM) 1
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO]
[INFO] >>> maven-archetype-plugin:2.4:generate (default-cli) > generate-sources @ standalone-pom >>>
[INFO]
[INFO] <<< maven-archetype-plugin:2.4:generate (default-cli) < generate-sources @ standalone-pom <<<
[INFO]
[INFO] --- maven-archetype-plugin:2.4:generate (default-cli) @ standalone-pom ---
[INFO] Generating project in Batch mode
[INFO] Archetype repository not defined. Using the one from [org.terasoluna.gfw.blank:terasoluna-gfw-web-blank-archetype:1.0.0.RELEASE -> http://repo.terasoluna.org/nexus/content/repositories/terasoluna-gfw-releases] found in catalog http://repo.terasoluna.org/nexus/content/repositories/terasoluna-gfw-releases
[INFO] ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Using following parameters for creating project from Archetype: terasoluna-gfw-web-blank-archetype:1.0.6.RELEASE
[INFO] ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Parameter: groupId, Value: com.example.helloworld
[INFO] Parameter: artifactId, Value: helloworld
[INFO] Parameter: version, Value: 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
[INFO] Parameter: package, Value: com.example.helloworld
[INFO] Parameter: packageInPathFormat, Value: com/example/helloworld
[INFO] Parameter: package, Value: com.example.helloworld
[INFO] Parameter: version, Value: 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
[INFO] Parameter: groupId, Value: com.example.helloworld
[INFO] Parameter: artifactId, Value: helloworld
[INFO] project created from Archetype in dir: C:\work\helloworld
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESS
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 3.682 s
[INFO] Finished at: 2017-02-24T10:23:06+09:00
[INFO] Final Memory: 11M/193M
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
C:\work>
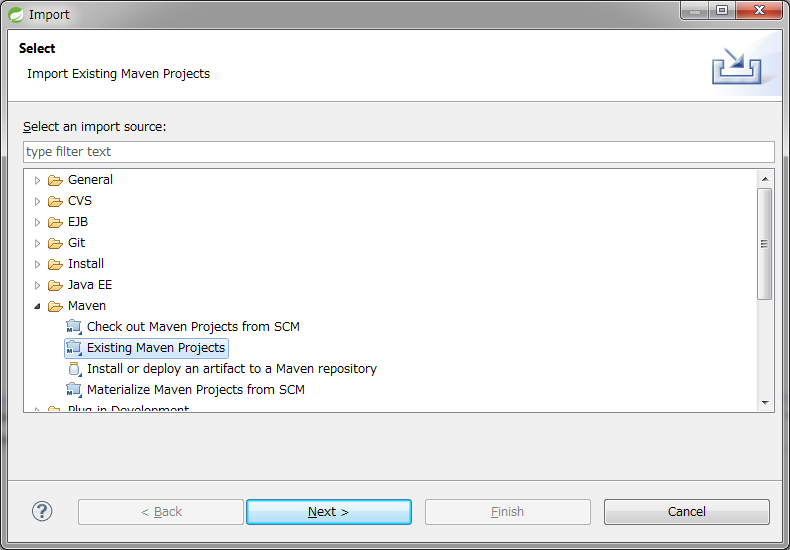
STSのメニューから、[File] -> [Import] -> [Maven] -> [Existing Maven Projects] -> [Next]を選択し、archetypeで作成したプロジェクトを選択する。
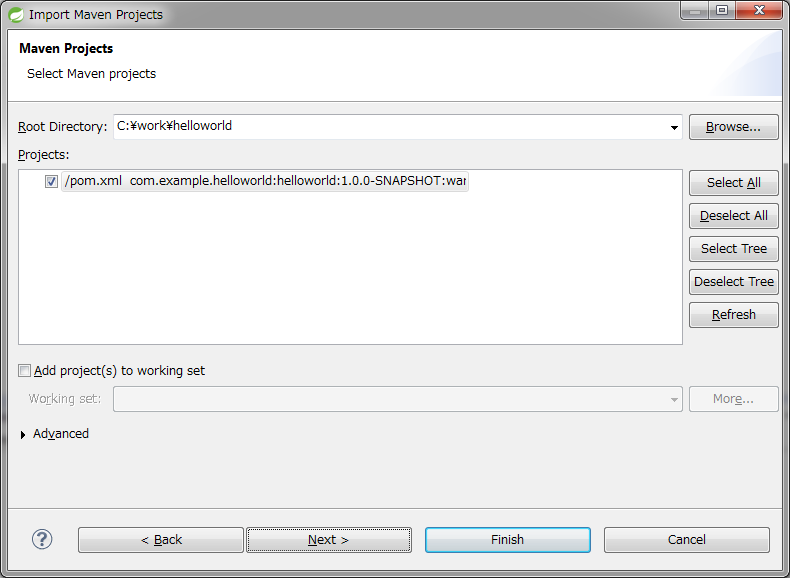
Root Directoryに C:\work\helloworldを設定し、Projectsにhelloworldのpom.xmlが選択された状態で、 [Finish] を押下する。
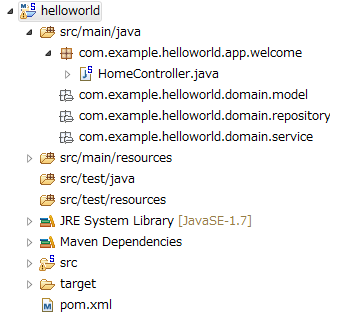
Package Explorerに、次のようなプロジェクトが生成される。
Spring MVCの設定方法を理解するために、生成されたSpring MVCの設定ファイル(src/main/resources/META-INF/spring/spring-mvc.xml)について、簡単に説明する。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder
location="classpath*:/META-INF/spring/*.properties" />
<!-- (1) Enables the Spring MVC @Controller programming model -->
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:argument-resolvers>
<bean
class="org.springframework.data.web.PageableHandlerMethodArgumentResolver" />
</mvc:argument-resolvers>
<!-- workarround to CVE-2016-5007. -->
<mvc:path-matching path-matcher="pathMatcher" />
</mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:default-servlet-handler />
<!-- (2) -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example.helloworld.app" />
<mvc:resources mapping="/resources/**"
location="/resources/,classpath:META-INF/resources/"
cache-period="#{60 * 60}" />
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**" />
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/resources/**" />
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/**/*.html" />
<bean
class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.logging.TraceLoggingInterceptor" />
</mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**" />
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/resources/**" />
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/**/*.html" />
<bean
class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.token.transaction.TransactionTokenInterceptor" />
</mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**" />
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/resources/**" />
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/**/*.html" />
<bean class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.codelist.CodeListInterceptor">
<property name="codeListIdPattern" value="CL_.+" />
</bean>
</mvc:interceptor>
<!-- REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**" />
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/resources/**" />
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/**/*.html" />
<bean
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.support.OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor" />
</mvc:interceptor>
REMOVE THIS LINE IF YOU USE JPA -->
</mvc:interceptors>
<!-- (3) Resolves views selected for rendering by @Controllers to .jsp resources in the /WEB-INF/views directory -->
<!-- Settings View Resolver. -->
<bean id="viewResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
<bean id="requestDataValueProcessor"
class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.mvc.support.CompositeRequestDataValueProcessor">
<constructor-arg>
<util:list>
<bean
class="org.springframework.security.web.servlet.support.csrf.CsrfRequestDataValueProcessor" factory-method="create" />
<bean
class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.token.transaction.TransactionTokenRequestDataValueProcessor" />
</util:list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- Setting Exception Handling. -->
<!-- Exception Resolver. -->
<bean class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.SystemExceptionResolver">
<property name="exceptionCodeResolver" ref="exceptionCodeResolver" />
<!-- Setting and Customization by project. -->
<property name="order" value="3" />
<property name="exceptionMappings">
<map>
<entry key="ResourceNotFoundException" value="common/error/resourceNotFoundError" />
<entry key="BusinessException" value="common/error/businessError" />
<entry key="InvalidTransactionTokenException" value="common/error/transactionTokenError" />
<entry key=".DataAccessException" value="common/error/dataAccessError" />
</map>
</property>
<property name="statusCodes">
<map>
<entry key="common/error/resourceNotFoundError" value="404" />
<entry key="common/error/businessError" value="409" />
<entry key="common/error/transactionTokenError" value="409" />
<entry key="common/error/dataAccessError" value="500" />
</map>
</property>
<property name="defaultErrorView" value="common/error/systemError" />
<property name="defaultStatusCode" value="500" />
</bean>
<!-- Setting AOP. -->
<bean id="handlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor"
class="org.terasoluna.gfw.web.exception.HandlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor">
<property name="exceptionLogger" ref="exceptionLogger" />
</bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="handlerExceptionResolverLoggingInterceptor"
pointcut="execution(* org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver.resolveException(..))" />
</aop:config>
<!-- Setting PathMatcher. -->
<bean id="pathMatcher" class="org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher">
<property name="trimTokens" value="false" />
</bean>
</beans>
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
<mvc:annotation-driven>要素を定義することにより、Spring MVCのデフォルト設定が行われる。デフォルトの設定については、 Springの公式ページである Enabling the MVC Java Config or the MVC XML Namespace を参照されたい。 |
(2)
|
Spring MVCで使用するコンポーネントを探すパッケージを定義する。 |
(3)
|
ViewのResolverを指定し、Viewの配置場所を定義する。 |
次に、Welcomeページを表示するためのController (com.example.helloworld.app.welcome.HelloController) を以下に示す。
package com.example.helloworld.app.welcome;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Locale;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
/**
* Handles requests for the application home page.
*/
@Controller // (4)
public class HelloController {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(HelloController.class);
/**
* Simply selects the home view to render by returning its name.
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST}) // (5)
public String home(Locale locale, Model model) {
logger.info("Welcome home! The client locale is {}.", locale);
Date date = new Date();
DateFormat dateFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.LONG,
DateFormat.LONG, locale);
String formattedDate = dateFormat.format(date);
model.addAttribute("serverTime", formattedDate); // (6)
return "welcome/home"; // (7)
}
}
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(4)
|
@Controller アノテーションを付けることで、DIコンテナにより、コントローラクラスが自動で読み込まれる。前述「Spring MVCの設定ファイルの説明(2)」の設定により、component-scanの対象となっている。 |
(5)
|
HTTPメソッドがGETで、Resource(もしくはRequest URL)が”/”で、アクセスする際に実行される。 |
(6)
|
Viewに渡したいオブジェクトをModelに設定する。 |
(7)
|
View名を返却する。前述「Spring MVCの設定ファイルの説明(3)」の設定により、”WEB-INF/views/home.jsp”がレンダリングされる。 |
最後に、Welcomeページを表示するためのJSP (src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/views/welcome/home.jsp) を以下に示す。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Home</title>
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/resources/app/css/styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="wrapper">
<h1>Hello world!</h1>
<p>The time on the server is ${serverTime}.</p> <%-- (8) --%>
</div>
</body>
</html>
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(8)
|
前述の「Controllerの説明(6)」でModelに設定したオブジェクト(serverTime)は、HttpServletRequestに格納される。
そのため、JSPで ただし、${XXX}の記述は、XSS対象になる可能性があるので、文字列を出力する場合はHTMLエスケープする必要がある。 |
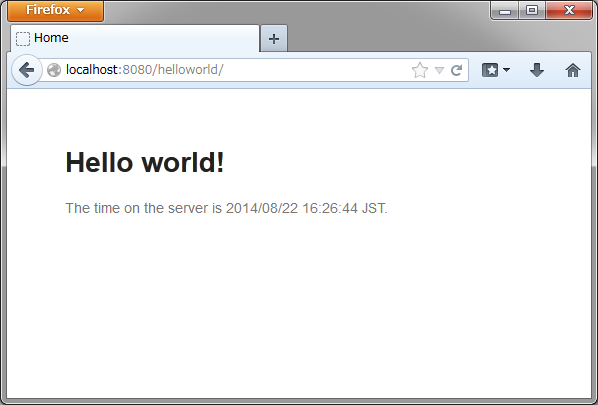
2.3.3. サーバーを起動する¶
2.3.4. エコーアプリケーションの作成¶
続いて、簡単なアプリケーションを作成する。作成するのは、次の図のようなテキストフィールドに、名前を入力すると メッセージを表示する、いわゆるエコーアプリケーションである。
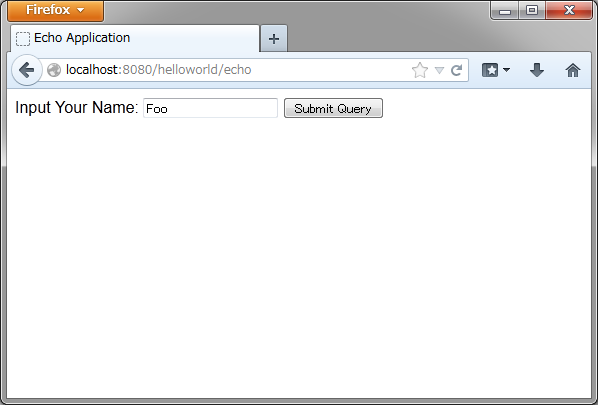
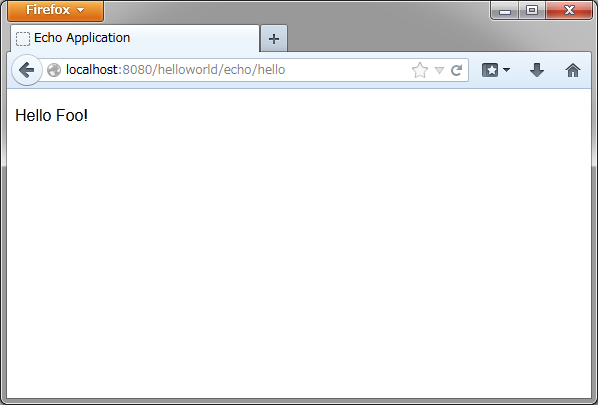
2.3.4.1. フォームオブジェクトの作成¶
com.example.helloworld.app.echoパッケージにEchoFormクラスを作成する。プロパティを1つだけ持つ、単純なJavaBeanである。package com.example.helloworld.app.echo;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class EchoForm implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2557725707095364445L;
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
2.3.4.2. Controllerの作成¶
com.example.helloworld.app.echo パッケージに、EchoController クラスを作成する。package com.example.helloworld.app.echo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("echo")
public class EchoController {
@ModelAttribute // (1)
public EchoForm setUpEchoForm() {
EchoForm form = new EchoForm();
return form;
}
@RequestMapping // (2)
public String index(Model model) {
return "echo/index"; // (3)
}
@RequestMapping(value = "hello", method = RequestMethod.POST) // (4)
public String hello(EchoForm form, Model model) {// (5)
model.addAttribute("name", form.getName()); // (6)
return "echo/hello";
}
}
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
@ModelAttribute というアノテーションを、メソッドに付加する。このアノテーションがついたメソッドの返り値は、自動でModelに追加される。Modelの属性名を、
@ModelAttribute で指定することもできるが、デフォルトでは、クラス名の先頭を小文字にした値が、属性名になる。この場合は、”echoForm”である。フォームの属性名は、次に説明する form:form タグ の modelAttribute 属性の値に一致している必要がある。 |
(2)
|
メソッドに付加した
@RequestMapping アノテーションの value 属性に、何も指定しない場合、クラスに付加した @RequestMapping のルートに、マッピングされる。この場合、”<contextPath>/echo”にアクセスすると、 index メソッドが呼ばれる。method 属性に何もしない場合は、任意のHTTPメソッドでマッピングされる。 |
(3)
|
View名で”echo/index”を返すので、ViewResolverにより、 “WEB-INF/views/echo/index.jsp”がレンダリングされる。
|
(4)
|
メソッドに付加した
@RequestMapping アノテーションのvalue属性に”hello”を、method属性にRequestMethod.POSTを指定しているので、この場合、”<contextPath>/echo/hello”にPOSTメソッドを使用してアクセスすると hello メソッドが呼ばれる。 |
(5)
|
引数に、EchoFormには(1)によりModelに追加されたEchoFormオブジェクトが渡される。
|
(6)
|
フォームで入力された
name を、Viewにそのまま渡す。 |
Note
@RequestMappingアノテーションのmethod属性に指定する値は、
クライアントから送信されたデータの扱い方によって変えるのが一般的である。
- データをサーバに保存する場合(更新系の処理の場合)は、POSTメソッド。
- データをサーバに保存しない場合(参照系の処理の場合)は、GETメソッド又は未指定(任意のメソッド)。
エコーアプリケーションでは、
indexメソッドはデータをサーバに保存しない処理なので未指定(任意のメソッド)helloメソッドはデータをModelオブジェクトに保存する処理なのでPOSTメソッド
を指定している。
2.3.4.3. JSPの作成¶
最後に、入力画面と、出力画面のJSPを作成する。それぞれのファイルパスは、View名に合わせて、次のようになる。
入力画面 (src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/views/echo/index.jsp) を作成する。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Echo Application</title>
</head>
<body>
<%-- (1) --%>
<form:form modelAttribute="echoForm" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/echo/hello">
<form:label path="name">Input Your Name:</form:label>
<form:input path="name" />
<input type="submit" />
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
タグライブラリを利用し、HTMLフォームを構築している。
modelAttribute 属性に、Controllerで用意したフォームオブジェクトの名前を指定する。タグライブラリは こちらを参照されたい。
|
Note
<form:form>タグのmethod属性を省略した場合は、POSTメソッドが使用される。
出力されるHTMLは、
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Echo Application</title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="echoForm" action="/helloworld/echo/hello" method="post">
<label for="name">Input Your Name:</label>
<input id="name" name="name" type="text" value=""/>
<input type="submit" />
<input type="hidden" name="_csrf" value="43595f38-3edd-4c08-843b-3c31a00d2b15" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
となる。
出力画面 (src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/views/echo/hello.jsp) を作成する。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Echo Application</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>
Hello <c:out value="${name}" /> <%-- (2) --%>
</p>
</body>
</html>
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(2)
|
Controllerから渡された”name”を出力する。
c:out タグにより、XSS対策を行っている。 |
Note
ここではXSS対策を標準タグの c:out で実現したが、より容易に使用できる f:h() 関数を共通ライブラリで用意している。
詳細は、 XSS対策 を参照されたい。
2.3.4.4. 入力チェックの実装¶
ここまでのアプリケーションでは、入力チェックを行っていない。 Spring MVCでは、 Bean Validation)をサポートしており、アノテーションベースな入力チェックを、簡単に 実装することができる。例として、エコーアプリケーションで名前の入力チェックを行う。
EchoFormのnameフォールドに、入力チェックルールを指定するアノーテションを付与する。
package com.example.helloworld.app.echo;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
public class EchoForm implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2557725707095364445L;
@NotNull // (1)
@Size(min = 1, max = 5) // (2)
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
@NotNull アノテーションをつけることで、HTTPリクエスト中に name パラメータがあることを確認する。 |
(2)
|
@Size(min = 1, max = 5) をつけることで、name のサイズが、1以上5以下であることを確認する。 |
入力チェックが実行されるように修正し、入力チェックでエラーが発生した場合の処理を実装する。
package com.example.helloworld.app.echo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("echo")
public class EchoController {
@ModelAttribute
public EchoForm setUpEchoForm() {
EchoForm form = new EchoForm();
return form;
}
@RequestMapping
public String index(Model model) {
return "echo/index";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "hello", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String hello(@Validated EchoForm form, BindingResult result, Model model) { // (1)
if (result.hasErrors()) { // (2)
return "echo/index";
}
model.addAttribute("name", form.getName());
return "echo/hello";
}
}
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
コントローラー側には、Validation対象の引数に
@Validated アノテーションを付加し、 BindingResult オブジェクトを引数に追加する。Bean Validationによる入力チェックは、自動で行われる。結果は、
BindingResult オブジェクトに渡される。 |
(2)
|
hasErrors メソッドを実行して、エラーがあるかどうかを確認する。入力エラーがある場合は、入力画面を表示するためのView名を返却する。 |
入力画面 (src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/views/echo/index.jsp) に、入力エラーのメッセージを表示するための実装を追加する。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Echo Application</title>
</head>
<body>
<form:form modelAttribute="echoForm" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/echo/hello">
<form:label path="name">Input Your Name:</form:label>
<form:input path="name" />
<form:errors path="name" cssStyle="color:red" /><%-- (1) --%>
<input type="submit" />
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
| 項番 | 説明 |
|---|---|
(1)
|
入力画面には、エラーがあった場合に、エラーメッセージを表示するため、
form:errors タグを追加する。 |
- 名前を空にして送信した場合
- 5文字より大きいサイズで送信した場合
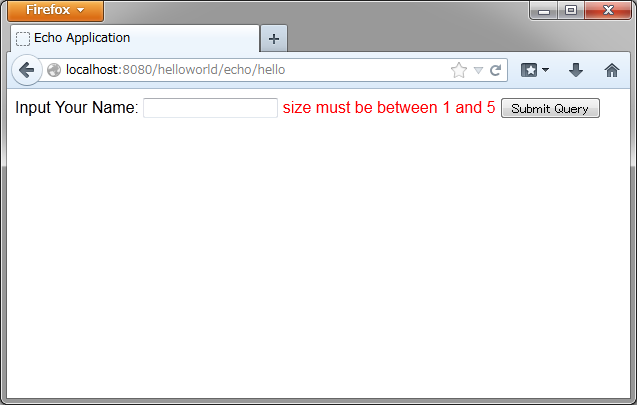
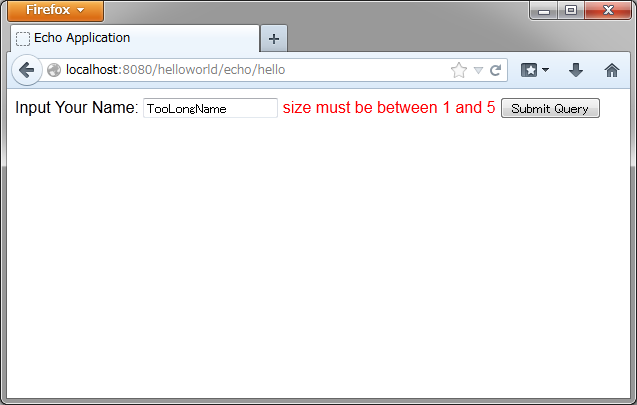
出力されるHTMLは、
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Echo Application</title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="echoForm" action="/helloworld/echo/hello" method="post">
<label for="name">Input Your Name:</label>
<input id="name" name="name" type="text" value=""/>
<span id="name.errors" style="color:red">size must be between 1 and 5</span>
<input type="submit" />
<input type="hidden" name="_csrf" value="6e94a78d-4a2c-4a41-a514-0a60f0dbedaf" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
となる。
2.3.4.5. まとめ¶
この章では、
mvn archetype:generateを利用したブランクプロジェクトの作成方法- SpringMVCの基本的な設定方法
- 最も簡易な、画面遷移方法
- 画面間での値の引き渡し方法
- シンプルな入力チェック方法
を学んだ。
上記の内容が理解できていない場合は、もう一度、本節を読み、環境構築から始めて、進めていくことで理解が深まる。